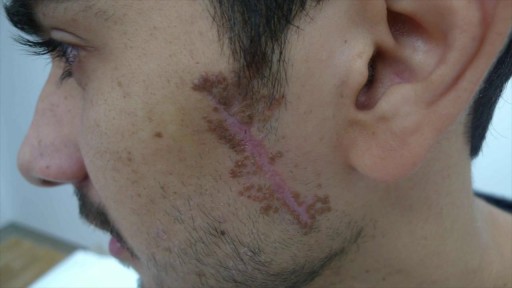
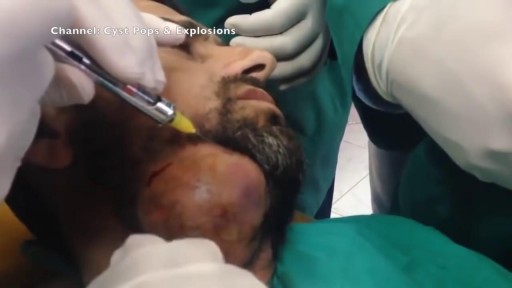
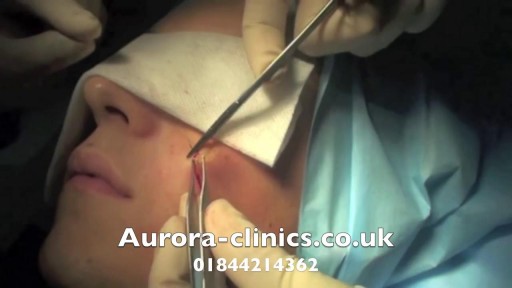
En iyi videolar
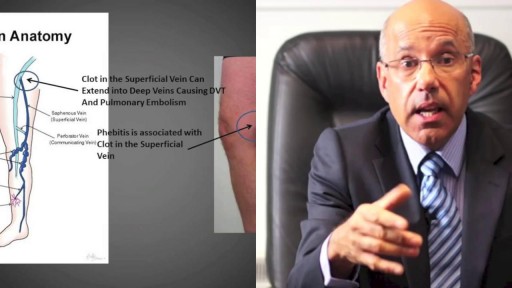
Phlebitis may occur with or without a blood clot. It can affect surface or deep veins. When caused by a blood clot, it's called thrombophlebitis. Trauma to the vein, for instance from an IV catheter, is a possible cause. Symptoms include redness, warmth, and pain in the affected area. Treatments may include a warm compress, anti-inflammatory medication, compression stockings, and blood thinners.
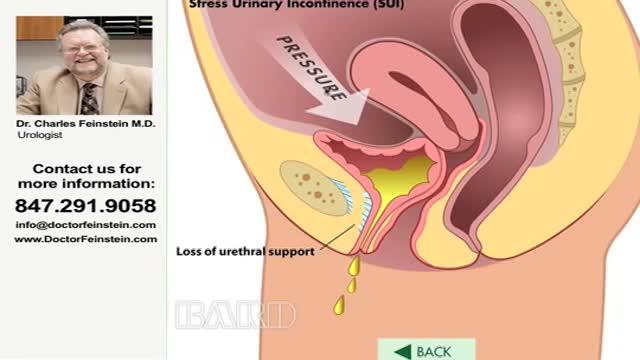
Urinary incontinence — the loss of bladder control — is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having an urge to urinate that's so sudden and strong you don't get to a toilet in time. If urinary incontinence affects your daily activities, don't hesitate to see your doctor. For most people, simple lifestyle changes or medical treatment can ease discomfort or stop urinary incontinence
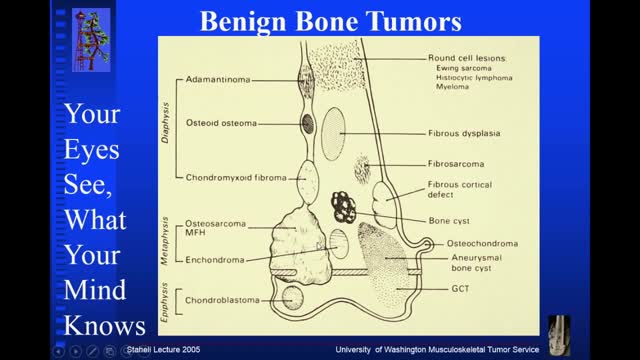
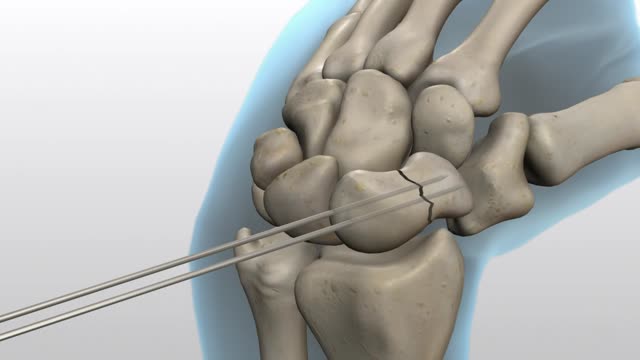
Osteochondroma. Osteochondromas (osteocartilaginous exostoses), the most common benign bone tumors, may arise from any bone but tend to occur near the ends of long bones. ... Enchondroma. ... Chondroblastoma. ... Chondromyxofibroma. ... Osteoid osteoma. ... Nonossifying fibroma (fibrous cortical defect) ... Benign giant cell tumor of bone.
Very small currents can be imperceptible. Larger current passing through the body may make it impossible for a shock victim to let go of an energized object. Still larger currents can cause fibrillation of the heart and damage to tissues. Death caused by an electric shock is called electrocution.
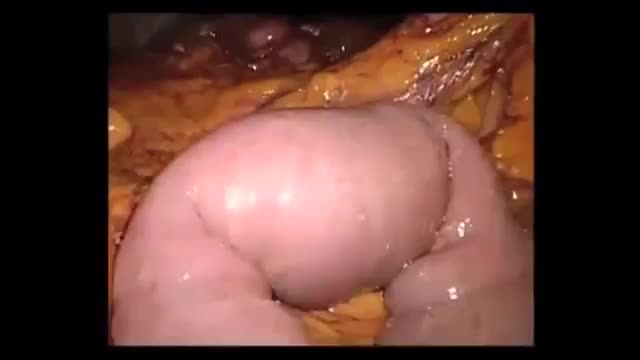
Gallstone ileus is an important, though infrequent, cause of mechanical bowel obstruction, affecting older adult patients who often have other significant medical conditions. It is caused by impaction of a gallstone in the ileum after being passed through a biliary-enteric fistula. The diagnosis is often delayed since symptoms may be intermittent and investigations fail to identify the cause of the obstruction. The mainstay of treatment is removal of the obstructing stone after resuscitating the patient. Gallstone ileus continues to be associated with relatively high rates of morbidity and mortality.