Top videos

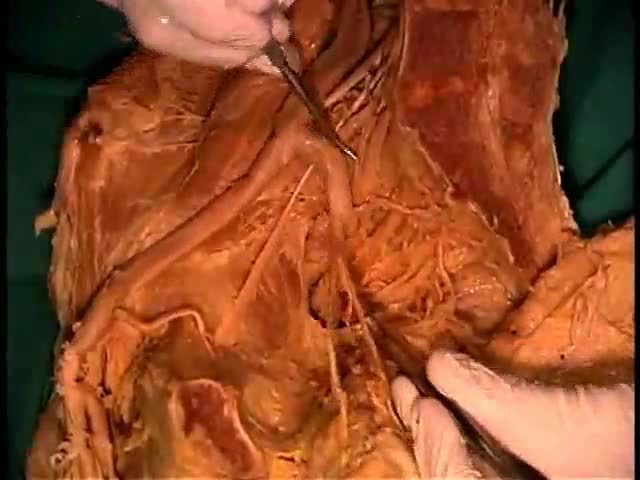
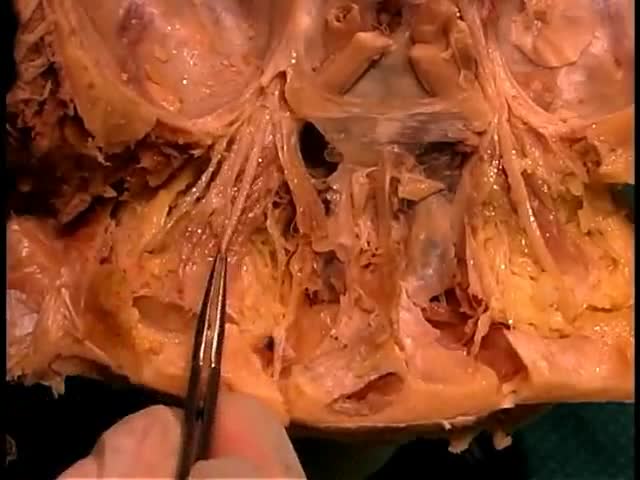
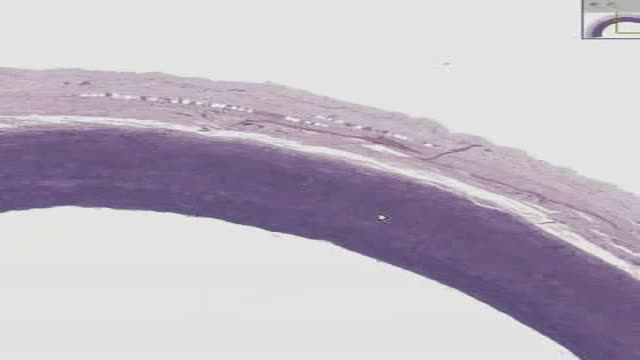
Most intact aortic aneurysms do not produce symptoms. As they enlarge, symptoms such as abdominal pain and back pain may develop. Compression of nerve roots may cause leg pain or numbness. Untreated, aneurysms tend to become progressively larger, although the rate of enlargement is unpredictable for any individual. Rarely, clotted blood which lines most aortic aneurysms can break off and result in an embolus. They may be found on physical examination. Medical imaging is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Symptoms may include: anxiety or feeling of stress; nausea and vomiting; clammy skin; rapid heart rate. In patients presenting with aneurysm of the arch of the aorta, a common symptom is a hoarse voice as the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (a branch of the vagus nerve) is stretched. This is due to the recurrent laryngeal nerve winding around the arch of the aorta. If an aneurysm occurs in this location, the arch of the aorta will swell, hence stretching the left recurrent laryngeal nerve. The patient therefore has a hoarse voice as the recurrent laryngeal nerve allows function and sensation in the voicebox. Abdominal aortic aneurysms, hereafter referred to as AAAs, are the most common type of aortic aneurysm. One reason for this is that elastin, the principal load-bearing protein present in the wall of the aorta, is reduced in the abdominal aorta as compared to the thoracic aorta (nearer the heart). Another is that the abdominal aorta does not possess vasa vasorum, hindering repair. Most are true aneurysms that involve all three layers (tunica intima, tunica media and tunica adventitia), and are generally asymptomatic before rupture. The most common sign for the aortic aneuysm is the Erythema nodosum also known as leg lesions typically found near the ankle area. The prevalence of AAAs increases with age, with an average age of 65–70 at the time of diagnosis. AAAs have been attributed to atherosclerosis, though other factors are involved in their formation. An AAA may remain asymptomatic indefinitely. There is a large risk of rupture once the size has reached 5 cm, though some AAAs may swell to over 15 cm in diameter before rupturing. Before rupture, an AAA may present as a large, pulsatile mass above the umbilicus. A bruit may be heard from the turbulent flow in a severe atherosclerotic aneurysm or if thrombosis occurs. Unfortunately, however, rupture is usually the first hint of AAA. Once an aneurysm has ruptured, it presents with a classic pain-hypotension-mass triad. The pain is classically reported in the abdomen, back or flank. It is usually acute, severe and constant, and may radiate through the abdomen to the back. The diagnosis of an abdominal aortic aneurysm can be confirmed at the bedside by the use of ultrasound. Rupture could be indicated by the presence of free fluid in potential abdominal spaces, such as Morison's pouch, the splenorenal space (between the spleen and left kidney), subdiaphragmatic spaces (underneath the diaphragm) and peri-vesical spaces. A contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan is needed for confirmation. Only 10–25% of patients survive rupture due to large pre- and post-operative mortality. Annual mortality from ruptured abdominal aneurysms in the United States alone is about 15,000. Another important complication of AAA is formation of a thrombus in the aneurysm.
Sclerotherapy is a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and veins. Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together and the blood to clot.

Children are not little adults, which is why even the simplest of procedures requires a hospital that is 100 percent dedicated to caring for children. Children’s Mercy is one of only 10 centers in the country to be as recognized as a Level 1 Children’s Surgery Center, the highest possible rating. The result? An organization with pediatrics specialists in every subspecialty that sets the standard of care instead of just practicing it.

Find our full video library only on Osmosis Prime: http://osms.it/more.
Join over 3 million current & future clinicians who learn by Osmosis, and over 130 universities around the world who partner with us to make medical and health education more engaging and efficient. We have unparalleled tools and materials to prepare you to succeed in school, on board exams, and as a future clinician. Sign up for a free trial at http://osms.it/more. If you're interested in exploring an institutional partnership, visit osmosis.org/educators to request a personalized demo.
Follow us on social:
Facebook: http://osms.it/facebook
Twitter: http://osms.it/twitter
Instagram for med: http://osms.it/instagram
Instagram for nursing: https://osms.it/ignursing
Linkedin: https://osms.it/linkedin
Our Vision: Everyone who cares for someone will learn by Osmosis.
Our Mission: To empower the world’s clinicians and caregivers with the best learning experience possible. Learn more here: http://osms.it/mission
Medical disclaimer: Knowledge Diffusion Inc (DBA Osmosis) does not provide medical advice. Osmosis and the content available on Osmosis's properties (Osmosis.org, YouTube, and other channels) do not provide a diagnosis or other recommendation for treatment and are not a substitute for the professional judgment of a healthcare professional in diagnosis and treatment of any person or animal. The determination of the need for medical services and the types of healthcare to be provided to a patient are decisions that should be made only by a physician or other licensed health care provider. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you have regarding a medical condition. © 2023 Elsevier. All rights reserved.
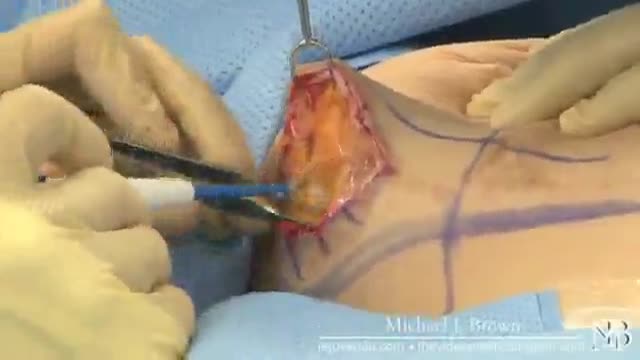
METHODS:
Previously existing methods are characterized by unpleasant scars that, despite surgeons promises, remain for life.
Incisions are:
- around the areola (Round block) leading to a flat areola, often unpleasant hypertophic skars, skin rippling.
- inverted T (around the areola, vertically down and in the fold under the breast).
- Vertical (around the areola and vertically down). Due to the extess skin, incisions often turn into inverted L or T. Rearrangement of glandular tissue and skin changes the shape of the breasts and may be different from expectations. Scars worry patients and sometimes cause disturbances in the relationship with their partner.
- No scars. The "Serdev Suture" lifting technique for breast lifting without scars (only points - needle perforations in the skin) is created by the Bulgarian cosmetic surgeon Prof. Dr. Nikolay Serdev. It is a novelty that had changed the cosmetic surgery world in the last 10-14 years for young patients. The technique is especially important in Asia and Latin America, for Asians, African-Americans, Indians, and others who form keloids and lumpy scars after operations.
The Serdev suture method can achieve lift upto and over 14 centimeters and is most suitable for the following types of breasts:
- not very heavy full breasts.
- in the presence of subpectoral implants with subsequent drooping of the breasts after childbirth and lactation.
- empty and loose breasts after childbirth and breastfeeding. In such cases this technique is combined with subpectoral implants. In sagging breasts implants should not be placed in the skin over the pectoral muscles, because thus will lead to even more drooping. Therefore, breast lift requires breast fixation to the level of the pectoral muscle (the normal position in young women), and then placement of appropriate implants under the muscle, to hold them in the appropriated position.
- in drooping breasts after subglandular augmentation (over the muscle). In such cases, patients should not wait until the skin elongation becomes visible. The implants should be removed, the capsule removed - a difficult but a necessary operation, preventing postop seromas and infection. Implants should be placed under the pectoralis muscle to wear them. Patients should orient the cosmetic surgeon at what level they want the nipples - in the middle of the implant, higher or lower.
Implants should be generally replaced - below the muscle implants should be smooth, move naturally without hurting the muscle.
Because of modern anesthetics and new methods without trauma, pain and swelling after surgery are not significant. In 3-4 days, patients can return to social life, even the next day, but it is preferable to rest for 2-3 days.
Exercises with the arms and weight lifting is prohibited for a month and a half.
Due to lack of scars, the breast lift using the Serdev sutures can be repeated to maintain the aesthetic appearence of the breasts even in advanced age.
Gigantomastia i.e. very large, very heavy and drooping breasts can not be operated in this manner, because of gravity and overskin.
Early mastopexy using Serdev sutures is recommended before too much changes in the tissues. If late, more and more complex interventions are required.
"A lot of people are opting for various breast procedures and one of the most common among them is “mastopexy”. This is the surgery that involved uplifting of sagging breasts and, in certain cases, repositioning of the nipple and areola in order to restore normality and beauty. The excess skin is removed and firmness is provided to the breasts. Though mastopexy can be done as a stand alone surgery, many people combine it with breast augmentation which involves inserting implants inside the b

New York Plastic Surgeon, Carlin Vickery, MD (http://www.5thavesurgery.com) performs a CoolSculpting by Zeltiq procedure.
A NYC patient in this video explains her interest in the CoolSculpting procedure and discusses her experience on camera while receiving this Zeltiq treatment.

Tampa body sculpting is the specialty of Dr. Thomas Su of the Artistic Lipo Sculpting Center. Dr. Su’s dedication to body contouring has allowed him to finely hone his craft over the years, making him the most trusted Tampa lipo surgeon. To learn more about Tampa fat removal procedures, visit http://www.artlipo.com/liposuction/liposuction-body-areas/lipo-abdomen.html.

Peritoneal dialysis (per-ih-toe-NEE-ul die-AL-uh-sis) is a way to remove waste products from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do the job adequately. A cleansing fluid flows through a tube (catheter) into part of your abdomen and filters waste products from your blood. After a prescribed period of time, the fluid with filtered waste products flows out of your abdomen and is discarded. Peritoneal dialysis differs from hemodialysis, a more commonly used blood-filtering procedure. With peritoneal dialysis, you can give yourself treatments at home, at work or while traveling. Peritoneal dialysis isn't an option for everyone wit

In most cases, your body's immune system defeats an HPV infection before it creates warts. When warts do appear, they vary in appearance depending on which variety of HPV is involved: Genital warts. These appear as flat lesions, small cauliflower-like bumps or tiny stem-like protrusions. In women, genital warts appear mostly on the vulva but can also occur near the anus, on the cervix or in the vagina. In men, genital warts appear on the penis and scrotum or around the anus. Genital warts rarely cause discomfort or pain, though they may itch. Common warts. Common warts appear as rough, raised bumps and usually occur on the hands, fingers or elbows. In most cases, common warts are simply unsightly, but they can also be painful or susceptible to injury or bleeding.