Top videos

New York Plastic Surgeon, Carlin Vickery, MD (http://www.5thavesurgery.com) performs a CoolSculpting by Zeltiq procedure.
A NYC patient in this video explains her interest in the CoolSculpting procedure and discusses her experience on camera while receiving this Zeltiq treatment.

Tampa body sculpting is the specialty of Dr. Thomas Su of the Artistic Lipo Sculpting Center. Dr. Su’s dedication to body contouring has allowed him to finely hone his craft over the years, making him the most trusted Tampa lipo surgeon. To learn more about Tampa fat removal procedures, visit http://www.artlipo.com/liposuction/liposuction-body-areas/lipo-abdomen.html.

A man's age matters. As men get older, the chances of conceiving and having a healthy child decline. Male fertility starts to decline after 40 when sperm quality decreases. This means it takes longer for their partners to conceive and when they do, there's an increased risk of miscarriage.
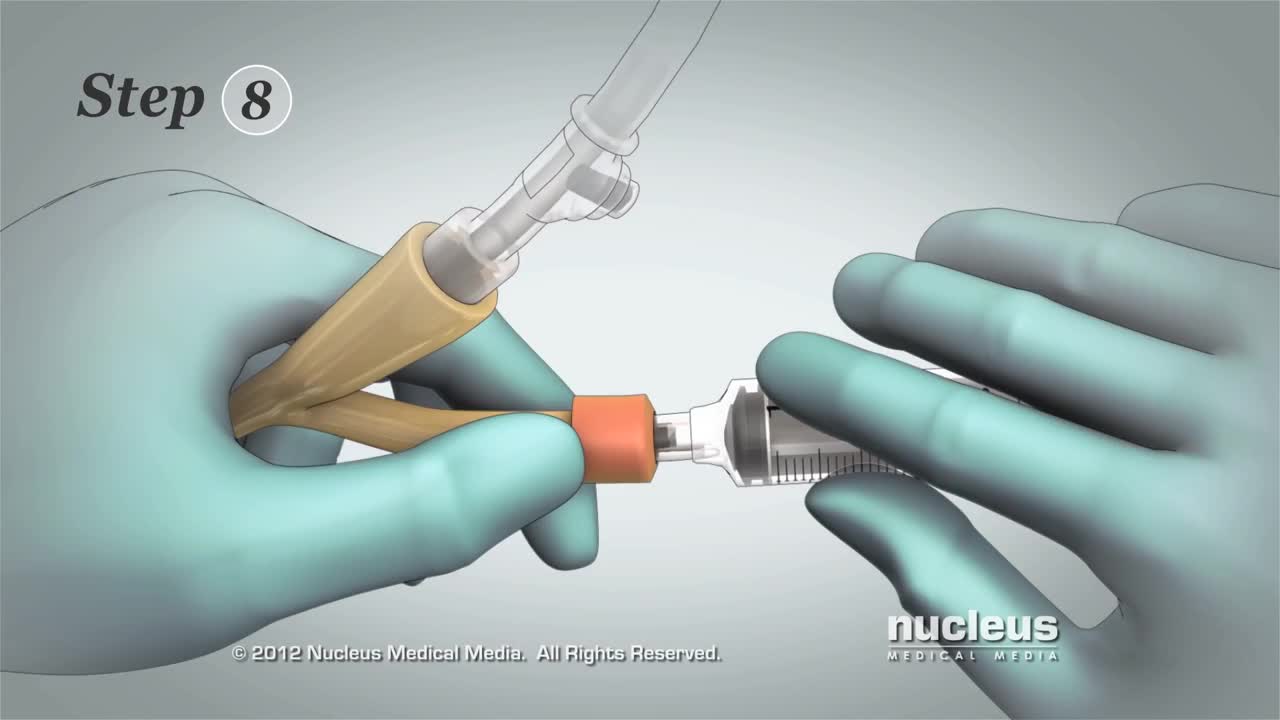
This 3D medical animation contains the discharge instructions for removal of a Foley catheter from a man. The step-by-step procedures for emptying the Foley bag and removing the Foley catheter are shown. Symptoms requiring a follow-up call to the surgeon are listed.
The vulvar vaginal diseases service sees referrals to help women with short--and long--term problems of the outer genital area (vulva), vagina and pelvic floor muscles including: Vulvar vaginal burning, itching, irritation and pain Vulvar Vestibulitis Pain with intercourse Discharge Yeast infections Bacterial vaginosis Pelvic floor muscle dysfunction A patient must be referred by her local health care provider. Services include: Skin care education Examinations-Your healthcare provider will examine you and talk with you about recommendations for treatment and/or management of your symptoms. Some vulvar diseases require a biopsy to diagnose the condition. Referrals-Your healthcare team may refer you to other specialists, including physical therapists or health psychologists. Separate insurance authorization is necessary for these services. The clinic staff provides general education and support to help women cope with these very personal health problems. Following a clinic visit, a letter is promptly sent to your local health care provider. The letter provides the results of your exam and the plan of care.
Swelling is a typical symptom of lymphedema and commonly affects legs and arms. Compression stockings work to encourage the movement of lymph out of an affected limb. Lymphedema is incurable. However, treatment can help reduce the swelling and pain
Sclerotherapy is a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and veins. Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together and the blood to clot.

Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of disorders that occur when blood vessels or nerves in the space between your collarbone and your first rib (thoracic outlet) are compressed. This can cause pain in your shoulders and neck and numbness in your fingers. Common causes of thoracic outlet syndrome include physical trauma from a car accident, repetitive injuries from job- or sports-related activities, certain anatomical defects (such as having an extra rib), and pregnancy. Sometimes doctors can't determine the cause of thoracic outlet syndrome. Treatment for thoracic outlet syndrome usually involves physical therapy and pain relief measures. Most people improve with these approaches. In some cases, however, your doctor may recommend surgery.
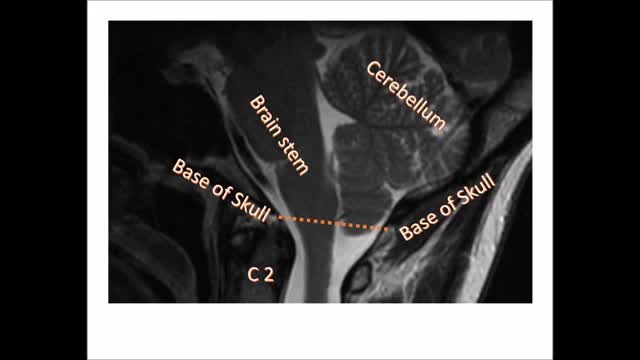
Chiari malformation (kee-AH-ree mal-for-MAY-shun) is a condition in which brain tissue extends into your spinal canal. It occurs when part of your skull is abnormally small or misshapen, pressing on your brain and forcing it downward.

Menorrhagia is the medical term for menstrual periods with abnormally heavy or prolonged bleeding. Although heavy menstrual bleeding is a common concern among premenopausal women, most women don't experience blood loss severe enough to be defined as menorrhagia. With menorrhagia, every period you have causes enough blood loss and cramping that you can't maintain your usual activities. If you have menstrual bleeding so heavy that you dread your period, talk with your doctor. There are many effective treatments for menorrhagia.
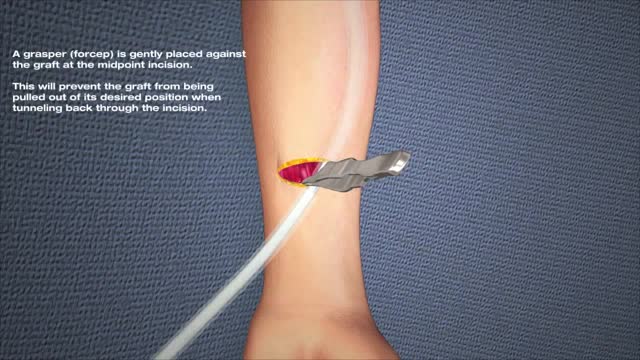
Hemodialysis, also called dialysis, is the most common treatment for kidney failure. A dialysis machine is an artificial kidney which cleanses the blood. During dialysis, blood is drawn from the patient into the dialysis machine, circulated through the machine, and then returned to the patient. Two needles are inserted into the patient's bloodstream to allow this process to occur. Hemodialysis is normally performed three times a week and the purpose of vascular access is to provide reliable sites where the bloodstream can be easily accessed each time. There are three major types of vascular access: arteriovenous fistula, arteriovenous graft, and venous catheter. The great majority of vascular accesses are created in the arm, but they can also be created in the leg.