Top videos
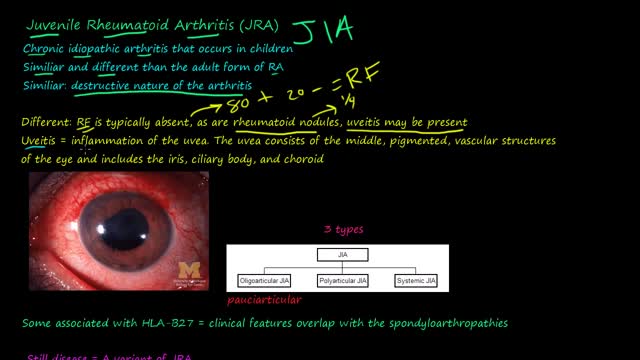
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, also known as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, is the most common type of arthritis in children under the age of 17. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis causes persistent joint pain, swelling and stiffness. Some children may experience symptoms for only a few months, while others have symptoms for the rest of their lives. Some types of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis can cause serious complications, such as growth problems and eye inflammation. Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis focuses on controlling pain, improving function and preventing joint damage.
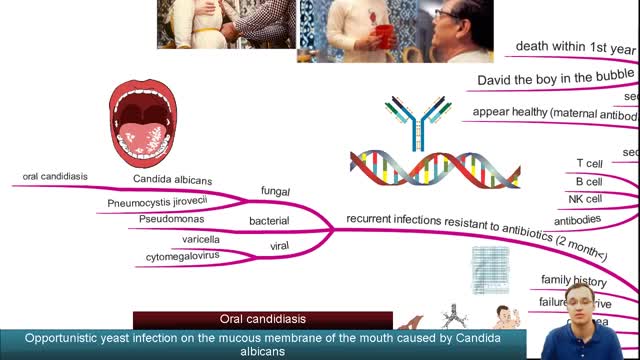
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a life-threatening syndrome of recurrent infections, diarrhea, dermatitis, and failure to thrive. It is the prototype of the primary immunodeficiency diseases and is caused by numerous molecular defects that lead to severe compromise in the number and function of T cells, B cells, and occasionally natural killer (NK) cells. Clinically, most patients present before age 3 months. Without intervention, SCID usually results in severe infection and death in children by age 2 years. A committee of experts, initially sponsored by the World Health Organization (WHO), meets every 2 years with the goal to classify the group of primary immunodeficiency diseases according to current understanding of the pathways that become defective in the immune system.[1] Eight classification groups have been determined, with SCID being one of the best studied. Over the past few decades, the diverse molecular genetic causes of SCID have been identified with progress from studies of the immune system.[2] SCID is considered a pediatric emergency because survival depends on expeditious stem cell reconstitution, usually by bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Appropriate diagnosis is essential because instituting proper treatment is lifesaving. Despite the heterogeneity in the pathogenesis of immune defects, common cutaneous manifestations and typical infections can provide clinical clues in diagnosing this pediatric emergency.[3] Skin manifestations were prevalent in primary immunodeficiency disorders studied in 128 pediatric patients in Kuwait; skin infections were the most prevalent findings, seen in 39 patients (30%), followed by dermatitis in 24 (19%).[4] Skin infections were significantly more prevalent in those with congenital defects in phagocyte number, function, or both, as well as in those with well-defined immunodeficiencies. Dermatitis was evident in all patients with hyper–immunoglobulin (Ig) E syndrome and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.[4] Erythroderma of infancy with diffuse alopecia was seen exclusively in patients with SCID disorders, and telangiectasia in patients with ataxia telangiectasia; and partial albinism with silvery gray hair was associated with Chediak-Higashi syndrome. With the advances in BMT and gene therapy, patients now have a better likelihood of developing a functional immune system in a previously lethal genetic disease. However, once an infant develops serious infections, intervention is rarely successful.

Arthritis occurs when the cartilage breaks down explains Dr. Derek Papp, Sports Medicine Physician with Miami Orthopedics & Sports Medicine Institute. This it’s a very common knee injury such as the damage of the cartilage and meniscus tear.
ACL tears is another common injury especially in sports like soccer or Australian football, the specialist explains.
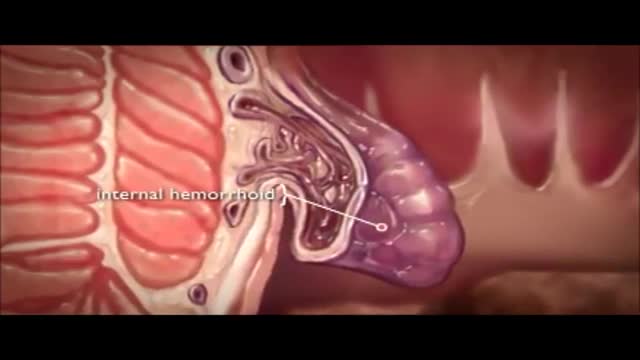
The veins around your anus tend to stretch under pressure and may bulge or swell. Swollen veins (hemorrhoids) can develop from an increase in pressure in the lower rectum. Factors that might cause increased pressure include: Straining during bowel movements.

Priapism is a prolonged erection of the penis. The persistent erection continues hours beyond or isn't caused by sexual stimulation. Priapism is usually painful. Although priapism is an uncommon condition overall, it occurs commonly in certain groups, such as people who have sickle cell anemia. Prompt treatment for priapism is usually needed to prevent tissue damage that could result in the inability to get or maintain an erection (erectile dysfunction). Priapism is most common in men in their 30s.
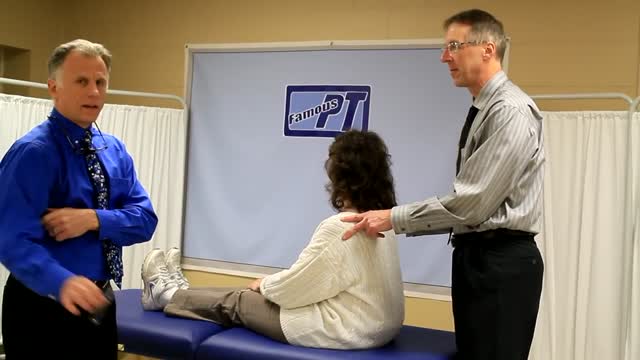
Epley maneuver: Step 1 You will sit on the doctor's exam table with your legs extended in front of you. The doctor will turn your head so that it is halfway between looking straight ahead and looking directly to the side that causes the worst vertigo. Without changing your head position, the doctor will guide you back quickly so that your shoulders are on the table but your head is hanging over the edge of the table. In this position, the side of your head that is causing the worst vertigo is facing the floor. The doctor will hold you in this position for 30 seconds or until your vertigo stops. Epley maneuver: Step 2 Then, without lifting up your head, the doctor will turn your head to look at the same angle to the opposite side, so that the other side of your head is now facing the floor. The doctor will hold you in this position for 30 seconds or until your vertigo stops. Epley maneuver: Step 3 The doctor will help you roll in the same direction you are facing so that you are now lying on your side. (For example, if you are looking to your right, you will roll onto your right side.) The side that causes the worst vertigo should be facing up. The doctor will hold you in this position for another 30 seconds or until your vertigo stops. Epley maneuver: Step 4 The doctor will then help you to sit back up with your legs hanging off the table on the same side that you were facing. This maneuver is done with the assistance of a doctor or physical therapist. A single 10- to 15-minute session usually is all that is needed. When your head is firmly moved into different positions, the crystal debris (canaliths) causing vertigo will move freely and no longer cause symptoms.

Although individual surgeons and centers employ different methods to insert a left ventricular assist device (LVAD), the fundamental concepts remain true for all. That is, most devices use the apex of the left ventricle (LV) as the inflow site to the pump, which subsequently gives off an outflow graft to the aorta, thus bypassing the ailing LV. Currently available devices do not differ significantly with regard to general implantation technique. The sequence of implantation can vary also from patient to patient, depending on the particular situation. In some cases, concomitant procedures may be performed in conjunction with LVAD implantation without adversely affecting outcome.
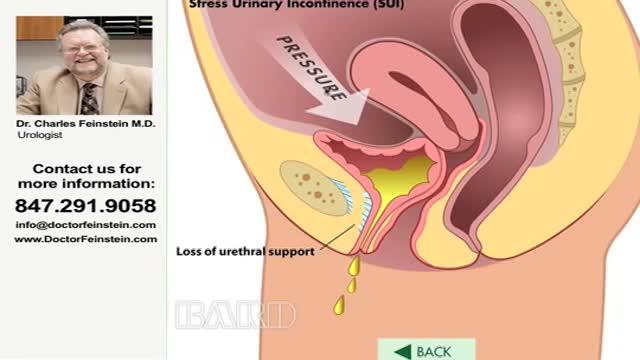
Urinary incontinence — the loss of bladder control — is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having an urge to urinate that's so sudden and strong you don't get to a toilet in time. If urinary incontinence affects your daily activities, don't hesitate to see your doctor. For most people, simple lifestyle changes or medical treatment can ease discomfort or stop urinary incontinence
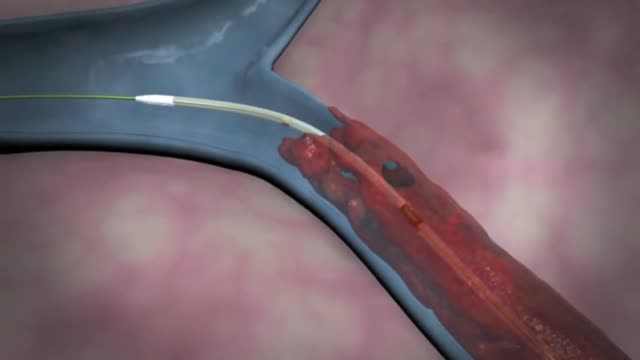
The removal of a clot is called an embolectomy. An embolectomy might be done during a surgery. Or it might be done with a minimally invasive procedure that uses a catheter (a thin tube that is guided through a blood vessel). This type of treatment for pulmonary embolism is used only in rare cases.
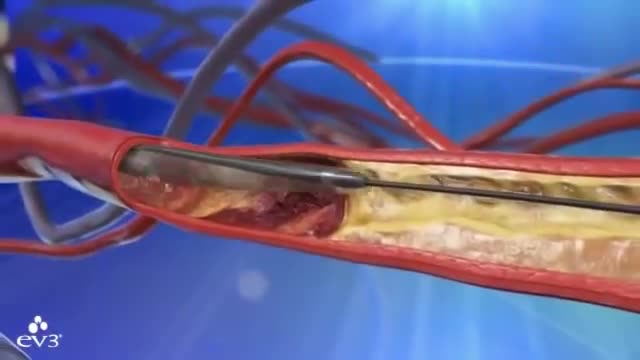
Preventing heart attacks and stroke can involve extensive surgery to remove plaque from your arteries, but as FOX17's Nick Paranjape shows us, there's a new procedure in Middle Tennessee that is less invasive and substantially cuts down on your recovery time. At 76, Jimmy Wilkie of Hendersonville exercises on his treadmill 3-4 times a week. Recently, he started having pain in his left leg. It was so bad, he couldn't even walk. Turned out, Mr. Wilkie had a blocked artery in his leg. In years past, this would've required major bypass surgery. Not anymore!"The Turbohawk Catheter has really opened a new door for us," says Dr. Dan Wunder.Dr. Wunder, an Interventional Radiologist at Premier Radiology in Madison, is talking about the Turbohawk. It's a device which is inserted into the blocked artery, and inside the Turbohawk are 4 tiny blades."It can cut the plaque and with that shape of the disc it cuts with it pushes it forward into the catheter," says Dr. Wunder.The one-hour procedure doesn't just push the plaque to the sides where it can re-grow, but instead grabs it and removes it!"We pull it back out and it fills up," says Dr. Wunder. "Empty it out, go back down and we can cut some more out."Before and after images really say it all."They used a roto rooter as he called it," says Wilkie.A roto rooter, Turbohawk, call it what you want, but Wilkie says all he knows is the procedure worked right away!"There wasn't any pain at all in my leg," says Wilkie.It's rare, but the outpatient procedure can have complications like plaque getting pushed down in the leg. Dr. Wunder says the main symptoms of a blockage in your legs is having severe pain or cramping when you're walking or exercising.

🔥 Multivitamins for Men: https://lynxshort.com/Multivitamins-for-Men
✨ Multivitamins for Women: https://lynxshort.com/Multivitamins-for-Women
⭐ Multivitamins for Kids: https://lynxshort.com/Multivitamins-for-Kids
📙 Book of the Day 📚 https://lynxshort.com/Book-of-the-Day
This is one of the most interesting medical topics to discuss. What are the responsibilities of a doctor? What are the basic skills a doctor needs to have? and what are the responsibilities of a doctor?
**** CONNECT ****
- " Medical Videos " Android application on Google Play store:
https://play.google.com/store/....apps/details?id=com.
https://healthusher.com
https://www.facebook.com/MedicalVideosAnimated
https://www.instagram.com/medical_videos1
👉 Support Us to Help Us Continue Making Videos.. Thanks in Advance :)
- Via PayPal: https://www.paypal.me/medicalvideos
- Via Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/medicalvideosanimated
- The creator:
Pharmacist. Alaa Nasr
#MedicalVideosAnimated
Affiliate Disclaimer: This video and description contains affiliate links, which means that if you click on one of the product links, I'll receive a small commission. This is at no extra cost to you and in many cases include exclusive discounts where applicable. This helps support the channel and allows me to continue to make free videos like this. Thank you for the support!

Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of disorders that occur when blood vessels or nerves in the space between your collarbone and your first rib (thoracic outlet) are compressed. This can cause pain in your shoulders and neck and numbness in your fingers. Common causes of thoracic outlet syndrome include physical trauma from a car accident, repetitive injuries from job- or sports-related activities, certain anatomical defects (such as having an extra rib), and pregnancy. Sometimes doctors can't determine the cause of thoracic outlet syndrome. Treatment for thoracic outlet syndrome usually involves physical therapy and pain relief measures. Most people improve with these approaches. In some cases, however, your doctor may recommend surgery.