Top videos

Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHSE covers Incentive Spirometry. The Critical Nursing Skills - Shorts series is intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN #clinicalskills #safety
Comments? Suggestions? Please share! Your feedback can help inform our future videos and study resources. 🙂
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our flashcards are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of 5-star reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
Our #Clinical Nursing Skills Flashcards are available at
➡️ https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills
👇SHOP ALL OUR FLASHCARDS👇
http://bit.ly/allstudycards
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://www.leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
Want perks? Join our channel!
➡️ https://www.youtube.com/leveluprn/join ⬅️
👩⚕️ LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.
👋 STAY CONNECTED 👋
TikTok: https://tiktok.com/@leveluprn
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/leveluprn/
Facebook: https://fb.me/LevelUpRN
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/leveluprn/
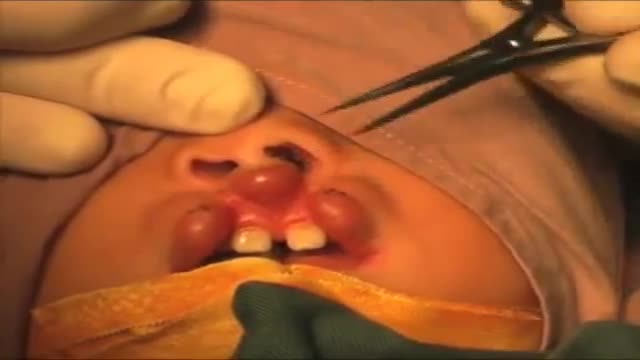
A bilateral complete cleft lip, which has been previously treated with nasoalvoelar molding, is repaired with the Millard-Mulliken technique, which employs reconstruction of the orbicularis oris muscle by advancing bilateral muscular segments. This tutorial for medical professionals was developed to supplement learning of a common surgical technique and is not intended to replace formal surgical training. This slideshow is primarily intended for use on tablets or larger screens. Some detail might be lost on mobile screens.
As the liver becomes more severely damaged, more obvious and serious symptoms can develop, such as: yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice) swelling in the legs, ankles and feet, due to a build-up of fluid (oedema) swelling in your abdomen, due to a build-up of fluid known as ascites.
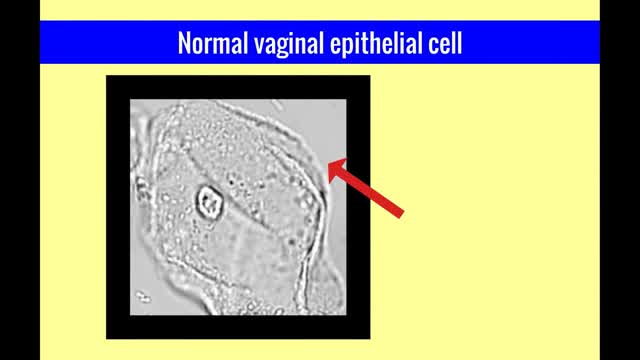
The vulvar vaginal diseases service sees referrals to help women with short--and long--term problems of the outer genital area (vulva), vagina and pelvic floor muscles including: Vulvar vaginal burning, itching, irritation and pain Vulvar Vestibulitis Pain with intercourse Discharge Yeast infections Bacterial vaginosis Pelvic floor muscle dysfunction A patient must be referred by her local health care provider. Services include: Skin care education Examinations-Your healthcare provider will examine you and talk with you about recommendations for treatment and/or management of your symptoms. Some vulvar diseases require a biopsy to diagnose the condition. Referrals-Your healthcare team may refer you to other specialists, including physical therapists or health psychologists. Separate insurance authorization is necessary for these services. The clinic staff provides general education and support to help women cope with these very personal health problems. Following a clinic visit, a letter is promptly sent to your local health care provider. The letter provides the results of your exam and the plan of care.

Septoplasty (SEP-toe-plas-tee) is a surgical procedure to correct a deviated septum — a displacement of the bone and cartilage that divides your two nostrils. During septoplasty, your nasal septum is straightened and repositioned in the middle of your nose.
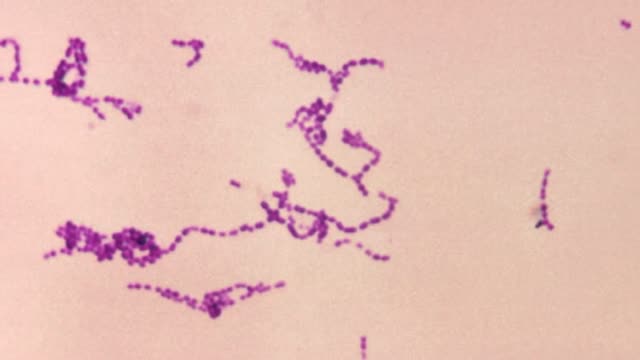
- Group A streptococcal pharyngitis Classic physical examination findings include tonsillar exudates, tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy, and palatal petechiae. Diagnosis should be confirmed with throat culture (preferred) or rapid antigen testing prior to initiation of antibiotics.

Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer. Fibroids range in size from seedlings, undetectable by the human eye, to bulky masses that can distort and enlarge the uterus. You can have a single fibroid or multiple ones. In extreme cases, multiple fibroids can expand the uterus so much that it reaches the rib cage. Many women have uterine fibroids sometime during their lives. But most women don't know they have uterine fibroids because they often cause no symptoms. Your doctor may discover fibroids incidentally during a pelvic exam or prenatal ultrasound.
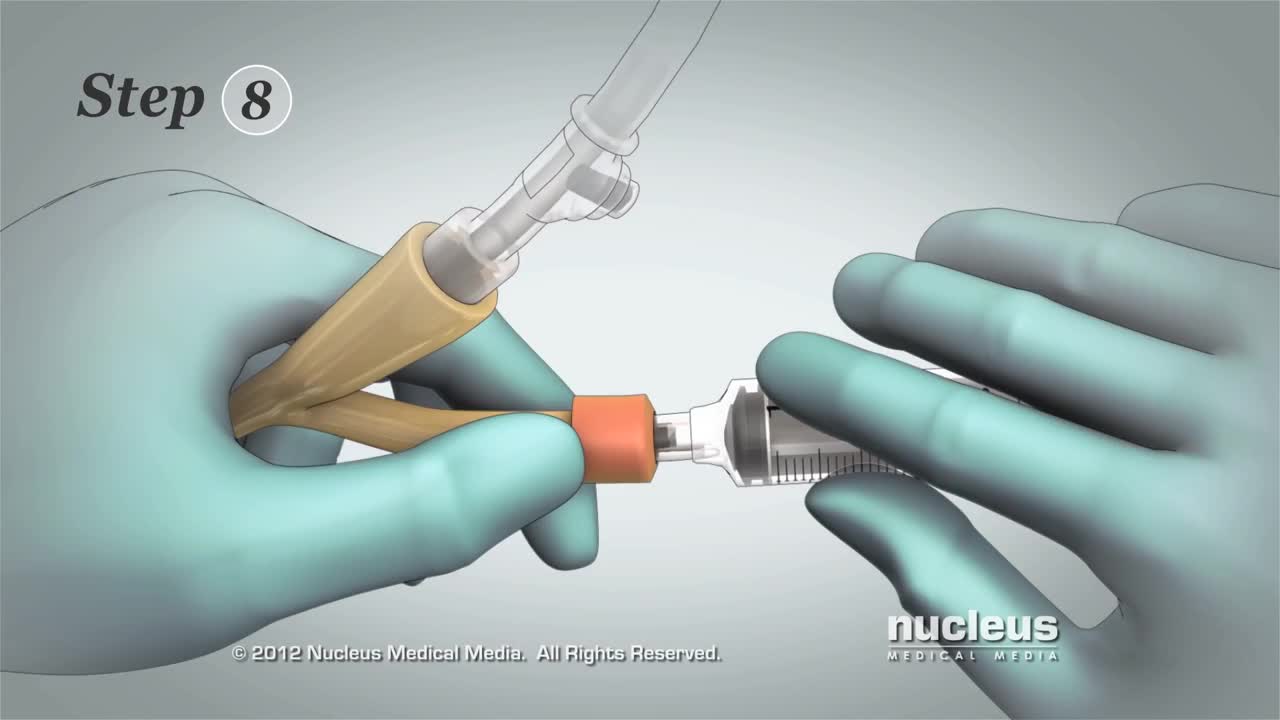
This 3D medical animation contains the discharge instructions for removal of a Foley catheter from a man. The step-by-step procedures for emptying the Foley bag and removing the Foley catheter are shown. Symptoms requiring a follow-up call to the surgeon are listed.

Menorrhagia is the medical term for menstrual periods with abnormally heavy or prolonged bleeding. Although heavy menstrual bleeding is a common concern among premenopausal women, most women don't experience blood loss severe enough to be defined as menorrhagia. With menorrhagia, every period you have causes enough blood loss and cramping that you can't maintain your usual activities. If you have menstrual bleeding so heavy that you dread your period, talk with your doctor. There are many effective treatments for menorrhagia.

procedure is usually done in the hospital or outpatient surgical center under general anesthesia (while you are asleep and pain-free). The procedure is performed in the following way: The surgeon makes a small cut (incision) below the belly button (navel). A needle or tube is inserted into the incision. Carbon dioxide gas is passed into the abdomen through the needle or tube. The gas helps expand the area, giving the surgeon more room to work, and helping the surgeon see the organs more clearly. A tube is placed through the cut in your abdomen. A tiny video camera (laparoscope) goes through this tube and is used to see the inside of your pelvis and abdomen. More small cuts may be made if other instruments are needed to get a better view of certain organs. If you are having gynecologic laparoscopy, dye may be injected into your cervix area so the surgeon can view your fallopian tubes. After the exam, the gas, laparoscope, and instruments are removed, and the cuts are closed. You will have bandages over those areas.

Instead, try these natural solutions and lifestyle changes, which may help you stop snoring. Change Your Sleep Position. ... Lose Weight. ... Avoid Alcohol. ... Practice Good Sleep Hygiene. ... Open Nasal Passages. ... Change Your Pillows. ... Stay Well Hydrated.
Sclerotherapy is a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and veins. Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together and the blood to clot.

The easy experimental answer to this question is 264 hours (about 11 days). In 1965, Randy Gardner, a 17-year-old high school student, set this apparent world-record for a science fair. Several other normal research subjects have remained awake for eight to 10 days in carefully monitored experiments. None of these individuals experienced serious medical, neurological, physiological or psychiatric problems. On the other hand, all of them showed progressive and significant deficits in concentration, motivation, perception and other higher mental processes as the duration of sleep deprivation increased. Nevertheless, all experimental subjects recovered to relative normality within one or two nights of recovery sleep. Other anecdotal reports describe soldiers staying awake for four days in battle, or unmedicated patients with mania going without sleep for three to four days.

Tummy Tuck Surgery | Immediate Before and After Results | Abdominoplasty
Here are the stunning before and after results of a tummy tuck surgery performed at Divine Cosmetic Surgery.
#tummytuck #tummytuckdelhi #fatreduction #fatreductionlipo #liposuctiondelhi #liposuctionIndia #bodyreshaping
Know more
https://www.divinecosmeticsurg....ery.com/tummy-tuck.p
Tummy Tuck Before & After,
Tummy Tuck Surgery in Delhi,
Abdominoplasty surgeon,
tummy tuck results before and after,
Dr. Amit Gupta,
tummy tuck immediate result,
Tummy fat reduction,
tummy loose skin removal,
𝗗𝗿. 𝗔𝗺𝗶𝘁 𝗚𝘂𝗽𝘁𝗮 (𝗙𝗼𝘂𝗻𝗱𝗲𝗿 & 𝗗𝗶𝗿𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿) of Divine Cosmetic Surgery
Skin removal Step 2 of Tummy Tuck - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cc9xsk9T_AU
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A to Z of Tummy Tuck - https://youtu.be/5i6zD0xBkwA
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Differences between Liposuction & Tummy tuck - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jzgeiz4mvc8
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tummy tuck surgery with Vaser (A to Z Steps) - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6abeUkb1ZcA&t=15s
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more details about Tummy tuck Visit - https://www.divinecosmeticsurgery.com/
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dr. Amit Gupta
MBBS, M.S., DNB (Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery)
Divine Cosmetic Surgery | Call us at +91 9811994417
info@divinecosmeticsurgery.com | 01141828787
Delhi | Mumbai | Gurgaon
𝗦𝗼𝗰𝗶𝗮𝗹 𝗠𝗲𝗱𝗶𝗮 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗬𝗼𝘂𝘁𝘂𝗯𝗲 𝘃𝗶𝗱𝗲𝗼 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗹 : -
🎦 http://www.youtube.com/c/DrAmi....tGuptaBestPlasticCos
👍🏻 https://www.facebook.com/dramitguptaplasticsurgeon
📷 https://www.instagram.com/divineaesthetics_delhi/
🐥 https://twitter.com/dramitguptajee
🖇️ https://www.linkedin.com/compa....ny/divinecosmeticsur
📌 https://pinterest.com/divinesurgery
#tummytuck #TummyTuckResult #TummyTuckResultBeforeandAfter #dramitgupta #divinecosmeticsurgery #fatreduction #tummytuckdelhi #shorts
Disclaimer: The information on our videos & social media is provided for informational purposes only and is not meant for the advice provided by your surgeon.
We are not responsible for any harm if anyone misguides you from our name. Our all-social media official handles are linked up on our website. All images & content used on our videos & social media are for illustrative concerns only, original results and processes may vary.