Top videos

Common causes of the knee pain
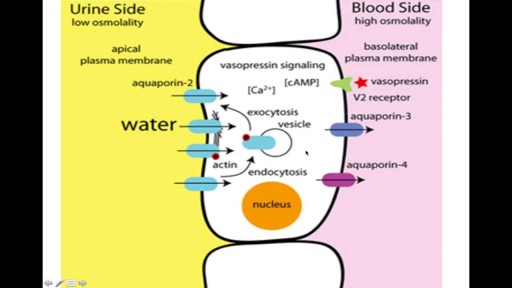
Knee pain is very common and in this video we will present the most common problems that can cause pain in the knee. (Patella) itself, which is in front of the knee, or from the tendons that are attached to the kneecap (patellar tendon and quadricep tendon). One of the most common problems is patellar chondromalacia which is chronic pain due to the softening of the cartilage beneath the kneecap. The cartilage of the kneecap will have some erosions, defects, or holes from mild to complete inside the joint (exactly in the back of the kneecap).
• Pain in the front of the knee
• Occurs more in young people
• Becomes worse from climbing up stairs and going downstairs
Treatment is usually nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, and surgery is very rare. Also in front of the kneecap, the patient may get pain due to prepatellar bursitis.
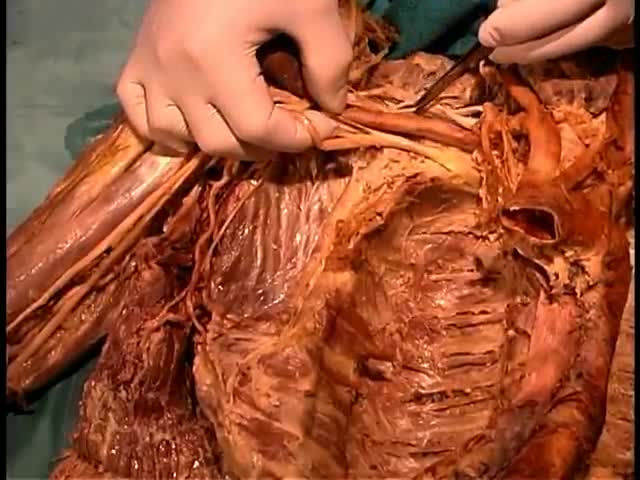
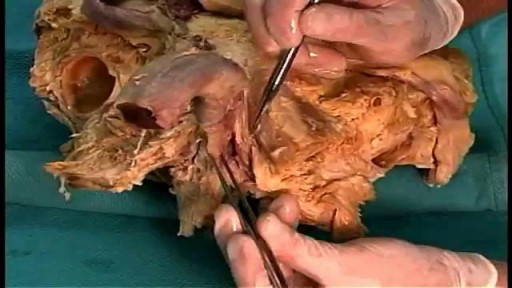
When there is prepatellar bursitis, the patient will see that the swelling, the inflammation, and the pain is located over the front of the kneecap. The bursa becomes inflamed and fills with fluid at the top of the knee, causing pain, swelling, tenderness and a lump in that area on top of the kneecap. If the pain is in front of the knee but below or above the patella, this may indicate that the patient has tendonitis. Patellar tendonitis is an overuse condition that often occurs in athletes who perform repetitive jumping activities. Patellar tendonitis is a knee pain that is associated with focal patellar tendon tenderness and it is usually activity related. It is located below the kneecap and is called "jumper's knee". Patellar tendonitis affects approximately 20% of jumping athletes. There will be tenderness to palpation at the distal pole of the patella in extension and not in flexion. Quadriceps inflexibility, atrophy and hamstring tightness are predisposing factors for this condition. Treatment is rest, anti-inflammatory medication, stretching and strengthening of the hamstrings and quadriceps. Use an eccentric exercise program. The early stages of patellar tendonitis will respond well to nonoperative treatment. Another important cause of knee pain is a meniscal tear. The meniscus is the cushion that protects the cartilage in the knee. Injury will cause pain on the medial or the lateral side of the knee exactly at the level of the joint. The patient will complain of a history of locking, instability and swelling of the knee. McMurray test will be positive. A painful pop or click is obtained as the knee is brought from flexion to extension with either internal or external rotation of the knee. Arthritis of the knee Knee arthritis is very common. The cartilage cells die with age and its repair response decreases in the joint collapses with increased breakdown of the framework of the cartilage. The patient will have progressive blurring away of the cartilage of the joint with decreased joint space as seen on x-rays. Another source of pain is the Baker's cyst. The cyst is in the back of the knee between the semimembranosus yes and the medial gastrocnemius muscles. Another important source of knee pain is a ligament injury. Here is a normal knee without a ligament injury. Here you can see from the front, you can see the lateral and medial collateral ligament. You can see the ACL and PCL from the side view. These ligaments are usually injured as a result of a sports activity. Here is an example of a sports knee injury. Here is an example of the medial collateral ligament injury. This is the most commonly injury knee ligament injury to this ligament is on the inner part of the knee. Here is an example of an injury of the anterior cruciate ligament. It involves a valgus stress to the knee. Lachman test is usually positive, and MRI is diagnostic. Another important cause of knee pain is iliotibial band syndrome of the knee. Inflammation of the thickening of the iliotibial band results from excessive friction as the iliotibial band slides over the lateral femoral condyle. The iliotibial band is a thick band of fascia that extends along the lateral thigh from the iliac crest to the knee. And as the knee moves, the IT band was repeatedly shifted forwards and backwards across the lateral femoral condyle. The patient will complain of swelling, tenderness, and crepitus over the lateral femoral condyle. The condition occurs in the ITB S occurs in runners, cyclist and athletes that require repeated knee flexion and extension. The pain may be reproduced by doing a single-leg squat. The Ober's test is used to at assess tightness of the iliotibial band. MRI may show edema in the area of the ITB. Treatment is usually nonoperative with rest and ice, physical therapy, with stretching, proprioception, and improvement in neuromuscular coordination. Training modification and injections may be helpful. Surgery is a last resort. Surgical excision of the scarred inflamed part of the iliotibial band.

Like any syndrome, fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a group of signs and symptoms that appear together and indicate a certain condition. In the case of FAS, the signs and symptoms are birth defects that result from a woman's use of alcohol during her pregnancy.
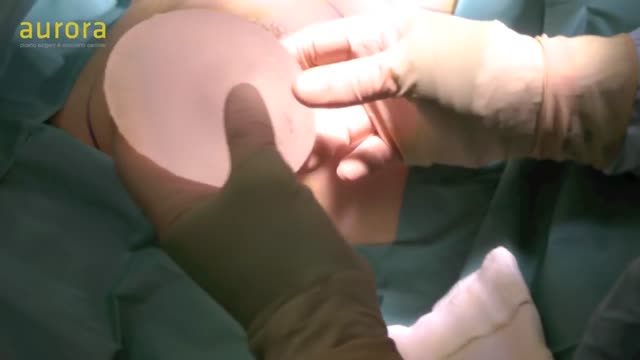
PIP breast implants exchanged with Nagor 4th generation silicone implants by plastic surgeon Adrian Richards at Aurora clinics in Milton Keynes. During PIP removal procedure, the implants appear in good shape, but as with majority of PIP implants, evidence of silicone gel bleed is found inside the patient's breast pocket, as well as free silicone which caused pain and discomfort to this patient.
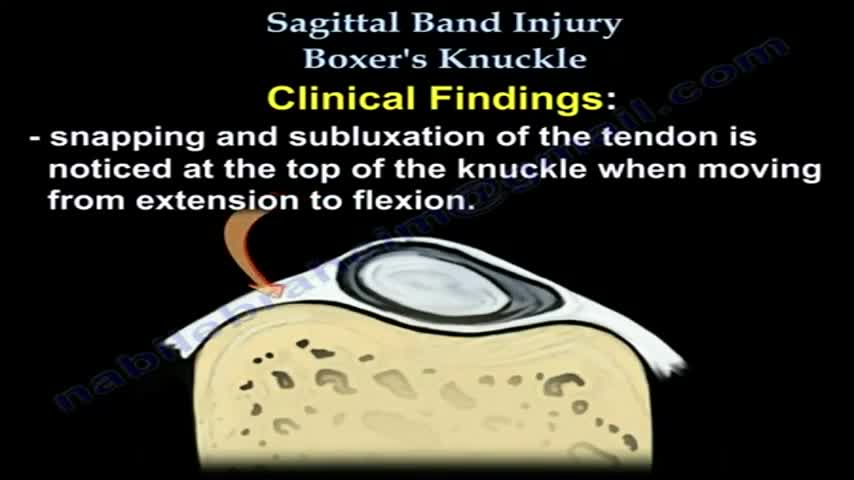
Boxer’s Knuckle is an injury to the structures around the first knuckle of a finger, also known as the metacarpophalangeal joint (MPJ). The skin, extensor tendon, ligaments, joint cartilage, and the bone of the metacarpal head may all be involved. Repeated impacts to the extensor tendon over the knuckle causes Hypertrophic Interstitial Tendonosis, or HIT Syndrome. This is a thickening, weakening, inflammation, and scarring of the extensor tendon.

Acromegaly is usually caused by a noncancerous tumor. Middle-aged adults are most commonly affected. Symptoms include enlargement of the face, hands, and feet. Prompt treatment is needed to avoid serious illness. Drugs can reduce the effects of growth hormone. If needed, surgery and radiation may be used to remove tumor cells.
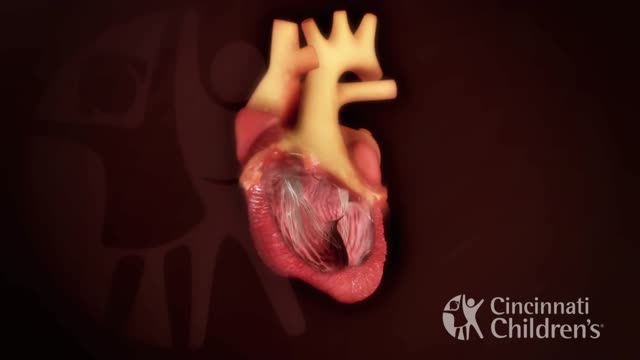
Truncus arteriosus is a rare type of heart disease that in which a single blood vessel (truncus arteriosus) comes out of the right and left ventricles, instead of the normal 2 vessels (pulmonary artery and aorta). It is present at birth (congenital heart disease)

Comment Maigrir, Perdre Des Cuisses, Perdre Du Ventre Rapidement, Perdre 3 Kilos, Mincir Vite --- http://perte-poids-rapide.info-pro.co --- Comment maigrir uniquement du ventre ? Avoir un ventre gonflé et des bourrelets est le cauchemar des hommes comme des femmes. On n’est pas à l’aise dans son corps, on a du mal à s’habiller et dès que l’on fait un repas copieux, il faut déboutonner son pantalon. Alors quelles sont les solutions pour maigrir du ventre ? Changez vos habitudes alimentaires Maigrir uniquement du ventre est compliqué comme pour toutes les autres parties du corps. On ne peut pas maigrir qu’au niveau du ventre ou qu’au niveau des cuisses ou des fesses d’ailleurs. Si vous pensez qu’il est suffisant de faire des heures d’abdos pour retrouver un ventre plat, c’est une erreur. Il faut d’abord perdre la graisse avant d’attaquer le sport. Et pour cela, il va falloir passer par la case régime. Inutile de vous ruer sur le dernier régime à la mode qui vous promet de perdre 5 kilos dès que vous mangerez normalement. Pour perdre du poids au niveau de la ceinture abdominale sur du long terme, choisissez plutôt une méthode où vous apprendrez les bonnes habitudes alimentaires avec une alimentation saine et équilibrée. Pour cela, il va falloir : Stopper les grignotages Ne pas sauter de repas Mâcher lentement les aliments Supprimer l’alcool et les jus de fruit achetés en magasin Faire une croix sur les fast-foods et les plats industriels Tirer un trait sur les gâteaux, les viennoiseries, les fritures et les sauces Consommer des fruits et des légumes Mangez de la viande blanche, des œufs et du poisson Préférer le pain complet à la baguette traditionnelle Inclure des féculents à chaque repas Boire 1,5 litre d’eau par jour Découvrez Comment Mincir Durablement Sans Peser Les Aliments Ni Compter Les Calories... Cliquez ici: http://perte-poids-rapide.info-pro.co