Top videos

Radiosurgery: Radiosurgery devices, such as the CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System, offer patients a new option for the treatment of lung cancer. The CyberKnife® System is used to treat lung cancer patients who cannot tolerate surgery, have an inoperable tumor, or are seeking an alternative to surgery.

To relieve mild menstrual cramps: Take aspirin or another pain reliever, such as Tylenol (acetaminophen), Motrin (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen). (Note: For best relief, you must take these medications as soon as bleeding or cramping starts.) Place a heating pad or hot water bottle on your lower back or abdomen

Your stomach must be empty, so you should not eat or drink anything for approximately 8 hours before the examination. Your physician will be more specific about the time to begin fasting depending on the time of day that your test is scheduled. Your current medications may need to be adjusted or avoided. Most medications can be continued as usual. Medication use such as aspirin, Vitamin E, non-steroidal anti-inflammatories, blood thinners and insulin should be discussed with your physician prior to the examination as well as any other medication you might be taking. It is therefore best to inform your physician of any allergies to medications, iodine, or shellfish. It is essential that you alert your physician if you require antibiotics prior to undergoing dental procedures, since you may also require antibiotics prior to ERCP. Also, if you have any major diseases, such as heart or lung disease that may require special attention during the procedure, discuss this with your physician. To make the examination comfortable, you will be sedated during the procedure, and, therefore, you will need someone to drive you home afterward. Sedatives will affect your judgment and reflexes for the rest of the day, so you should not drive or operate machinery until the next day.

Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of disorders that occur when blood vessels or nerves in the space between your collarbone and your first rib (thoracic outlet) are compressed. This can cause pain in your shoulders and neck and numbness in your fingers. Common causes of thoracic outlet syndrome include physical trauma from a car accident, repetitive injuries from job- or sports-related activities, certain anatomical defects (such as having an extra rib), and pregnancy. Sometimes doctors can't determine the cause of thoracic outlet syndrome. Treatment for thoracic outlet syndrome usually involves physical therapy and pain relief measures. Most people improve with these approaches. In some cases, however, your doctor may recommend surgery.

A visual prosthesis, often referred to as a bionic eye, is an experimental visual device intended to restore functional vision in those suffering from partial or total blindness. In 1983 Joao Lobo Antunes, a Portuguese doctor, implanted a bionic eye in a person born blind.
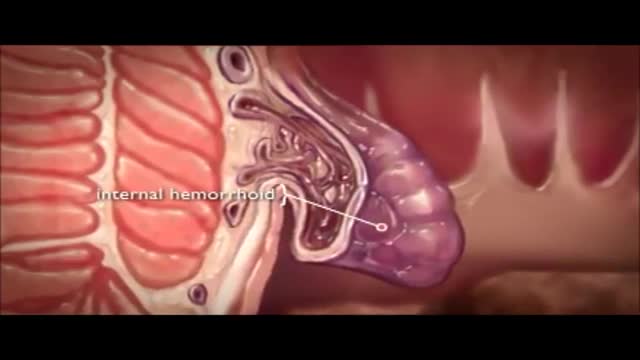
The veins around your anus tend to stretch under pressure and may bulge or swell. Swollen veins (hemorrhoids) can develop from an increase in pressure in the lower rectum. Factors that might cause increased pressure include: Straining during bowel movements.
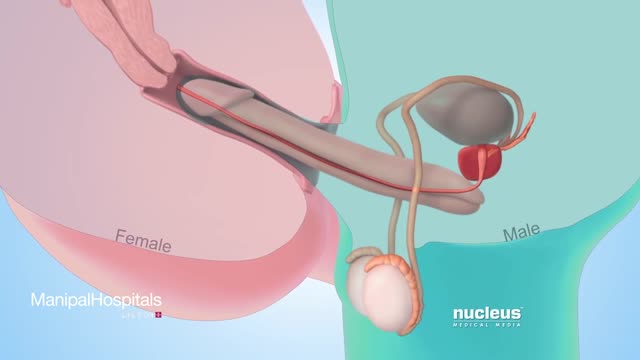
In some cases, the doctor will recommend that the couple seek assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as IVF (in vitro fertilisation). ART do not cure or treat the cause of infertility but they can help couples achieve a pregnancy, even if the man's sperm count is very low.
The future of Medicine - Il futuro della medicina - Die Zukunft der Medizin: High Tech, Robots, VR ⚡️Anatomia Biomeccanica Fisiologia by Ticinosthetics: tutto gira attorno alla palestra ©️2017 - www.ticinostheticsgs.com
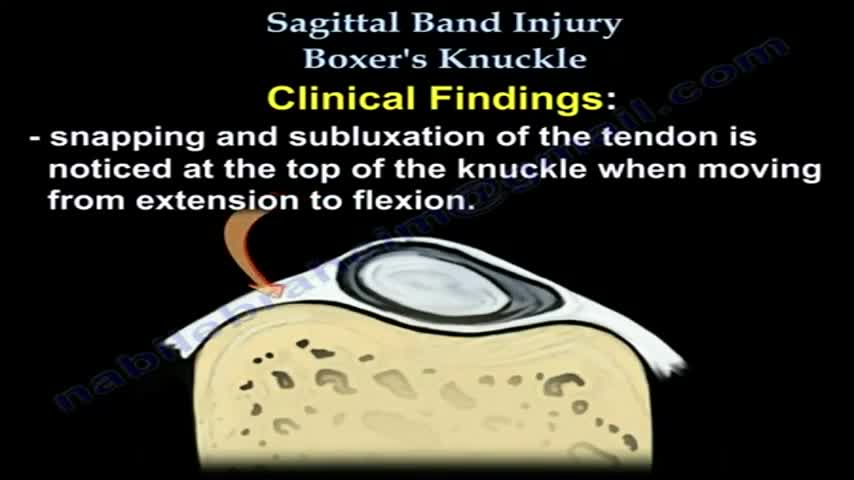
Boxer’s Knuckle is an injury to the structures around the first knuckle of a finger, also known as the metacarpophalangeal joint (MPJ). The skin, extensor tendon, ligaments, joint cartilage, and the bone of the metacarpal head may all be involved. Repeated impacts to the extensor tendon over the knuckle causes Hypertrophic Interstitial Tendonosis, or HIT Syndrome. This is a thickening, weakening, inflammation, and scarring of the extensor tendon.

From our beginnings in 1990 in primary healthcare, Healthway Medical has grown to become a respected medical group in Singapore. With over 100 clinics and medical centres, Healthway Medical has a wide network of medical centres and clinics in Singapore.
We offer comprehensive services including GP & family medicine clinics, health screening, adult specialists, baby & child specialists, dental services and allied healthcare services.

The Ortolani method is an examination method that identifies a dislocated hip that can be reduced into the socket (acetabulum). Ortolani described the feeling of reduction as a “Hip Click” but the translation from Italian was interpreted a sound instead of a sensation of the hip moving over the edge of the socket when it re-located. After the age of six weeks, this sensation is rarely detectable and should not be confused with snapping that is common and can occur in stable hips when ligaments in and around the hip create clicking noises. When the Ortolani test is positive because the hip is dislocated, treatment is recommended to keep the hip in the socket until stability has been established
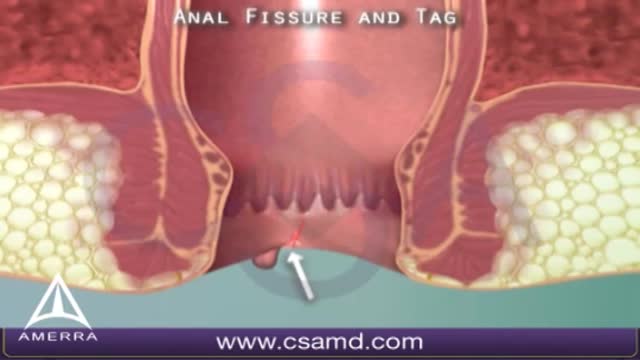
An anal fissure is a small tear in the thin, moist tissue (mucosa) that lines the anus. An anal fissure may occur when you pass hard or large stools during a bowel movement. Anal fissures typically cause pain and bleeding with bowel movements. You also may experience spasms in the ring of muscle at the end of your anus (anal sphincter). Anal fissures are very common in young infants but can affect people of any age. Most anal fissures get better with simple treatments, such as increased fiber intake or sitz baths. Some people with anal fissures may need medication or, occasionally, surgery.
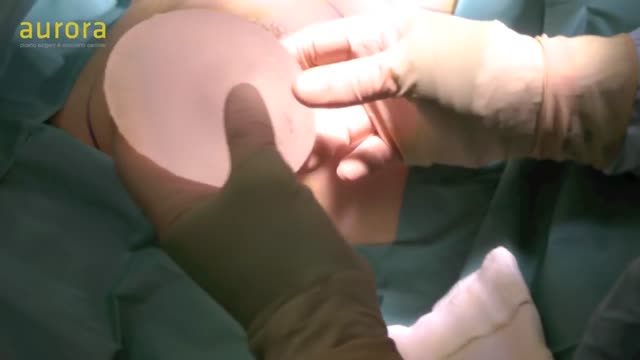
PIP breast implants exchanged with Nagor 4th generation silicone implants by plastic surgeon Adrian Richards at Aurora clinics in Milton Keynes. During PIP removal procedure, the implants appear in good shape, but as with majority of PIP implants, evidence of silicone gel bleed is found inside the patient's breast pocket, as well as free silicone which caused pain and discomfort to this patient.
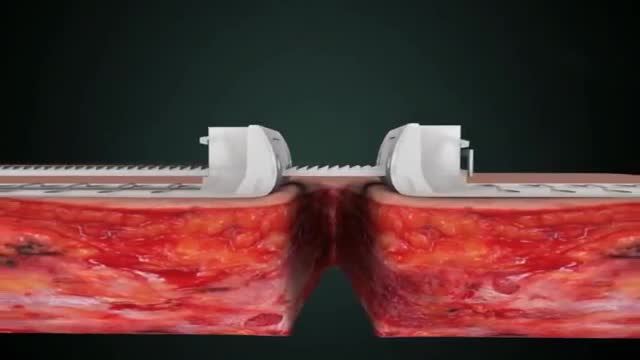
Wound closure techniques have evolved from the earliest development of suturing materials to comprise resources that include synthetic sutures, absorbables, staples, tapes, and adhesive compounds. The engineering of sutures in synthetic material along with standardization of traditional materials (eg, catgut, silk) has made for superior aesthetic results. Similarly, the creation of topical skin adhesives (the monomer 2-octyl cyanoacrylate), surgical staples, and tapes to substitute for sutures has supplemented the armamentarium of wound closure techniques. Aesthetic closure of a wound, whether traumatic or surgically induced, is based on knowledge of healing mechanisms and skin anatomy (see the image below), as well as an appreciation of suture material and closure technique. Choosing the proper materials and wound closure technique ensures optimal healing.[1]

Cholangitis Email this page to a friend Email this page to a friend Facebook Twitter Google+ Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile is a liquid made by the liver that helps digest food. Causes Cholangitis is most often caused by bacteria. This can occur when the duct is blocked by something, such as a gallstone or tumor. The infection causing this condition may also spread to the liver. Risk factors include a previous history of gallstones, sclerosing cholangitis, HIV, narrowing of the common bile duct, and rarely, travel to countries where you might catch a worm or parasite infection. Symptoms The following symptoms may occur: Pain on the upper right side or upper middle part of the abdomen. It may also be felt in the back or below the right shoulder blade. The pain may come and go and feel sharp, cramp-like, or dull. Fever and chills. Dark urine and clay-colored stools. Nausea and vomiting. Yellowing of the skin (jaundice), which may come and go.