Top videos
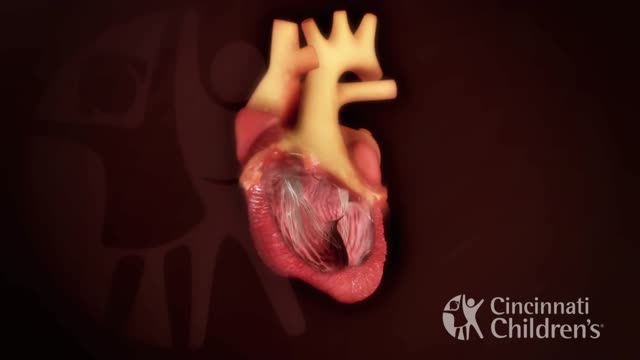
Truncus arteriosus is a rare type of heart disease that in which a single blood vessel (truncus arteriosus) comes out of the right and left ventricles, instead of the normal 2 vessels (pulmonary artery and aorta). It is present at birth (congenital heart disease)

Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of disorders that occur when blood vessels or nerves in the space between your collarbone and your first rib (thoracic outlet) are compressed. This can cause pain in your shoulders and neck and numbness in your fingers. Common causes of thoracic outlet syndrome include physical trauma from a car accident, repetitive injuries from job- or sports-related activities, certain anatomical defects (such as having an extra rib), and pregnancy. Sometimes doctors can't determine the cause of thoracic outlet syndrome. Treatment for thoracic outlet syndrome usually involves physical therapy and pain relief measures. Most people improve with these approaches. In some cases, however, your doctor may recommend surgery.
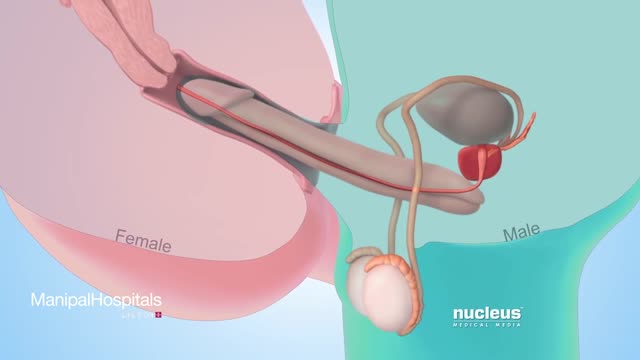
In some cases, the doctor will recommend that the couple seek assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as IVF (in vitro fertilisation). ART do not cure or treat the cause of infertility but they can help couples achieve a pregnancy, even if the man's sperm count is very low.

Ear Examination ENT is often a challenging examination, crossing over with the cranial nerve examination of the vestibular cochlear exam as well at other neurological assessments of balance
Here we will review the ear examination, looking both at the use of the otoscope, but also the Dix-Hallpike Manoeuvre, along with HINTS assessment. the Webers and Rinne's test is also included to determine types of hearing loss.
Often these ear examination techniques are performed separately, depending on the patients presenting complaint
#EARExamination #DrGill #ClinicalSkills

Comment Maigrir, Perdre Des Cuisses, Perdre Du Ventre Rapidement, Perdre 3 Kilos, Mincir Vite --- http://perte-poids-rapide.info-pro.co --- Comment maigrir uniquement du ventre ? Avoir un ventre gonflé et des bourrelets est le cauchemar des hommes comme des femmes. On n’est pas à l’aise dans son corps, on a du mal à s’habiller et dès que l’on fait un repas copieux, il faut déboutonner son pantalon. Alors quelles sont les solutions pour maigrir du ventre ? Changez vos habitudes alimentaires Maigrir uniquement du ventre est compliqué comme pour toutes les autres parties du corps. On ne peut pas maigrir qu’au niveau du ventre ou qu’au niveau des cuisses ou des fesses d’ailleurs. Si vous pensez qu’il est suffisant de faire des heures d’abdos pour retrouver un ventre plat, c’est une erreur. Il faut d’abord perdre la graisse avant d’attaquer le sport. Et pour cela, il va falloir passer par la case régime. Inutile de vous ruer sur le dernier régime à la mode qui vous promet de perdre 5 kilos dès que vous mangerez normalement. Pour perdre du poids au niveau de la ceinture abdominale sur du long terme, choisissez plutôt une méthode où vous apprendrez les bonnes habitudes alimentaires avec une alimentation saine et équilibrée. Pour cela, il va falloir : Stopper les grignotages Ne pas sauter de repas Mâcher lentement les aliments Supprimer l’alcool et les jus de fruit achetés en magasin Faire une croix sur les fast-foods et les plats industriels Tirer un trait sur les gâteaux, les viennoiseries, les fritures et les sauces Consommer des fruits et des légumes Mangez de la viande blanche, des œufs et du poisson Préférer le pain complet à la baguette traditionnelle Inclure des féculents à chaque repas Boire 1,5 litre d’eau par jour Découvrez Comment Mincir Durablement Sans Peser Les Aliments Ni Compter Les Calories... Cliquez ici: http://perte-poids-rapide.info-pro.co
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a condition in which extra bone grows along one or both of the bones that form the hip joint — giving the bones an irregular shape. Because they do not fit together perfectly, the bones rub against each other during movement. Over time this friction can damage the joint, causing pain and limiting activity.

The Ortolani method is an examination method that identifies a dislocated hip that can be reduced into the socket (acetabulum). Ortolani described the feeling of reduction as a “Hip Click” but the translation from Italian was interpreted a sound instead of a sensation of the hip moving over the edge of the socket when it re-located. After the age of six weeks, this sensation is rarely detectable and should not be confused with snapping that is common and can occur in stable hips when ligaments in and around the hip create clicking noises. When the Ortolani test is positive because the hip is dislocated, treatment is recommended to keep the hip in the socket until stability has been established
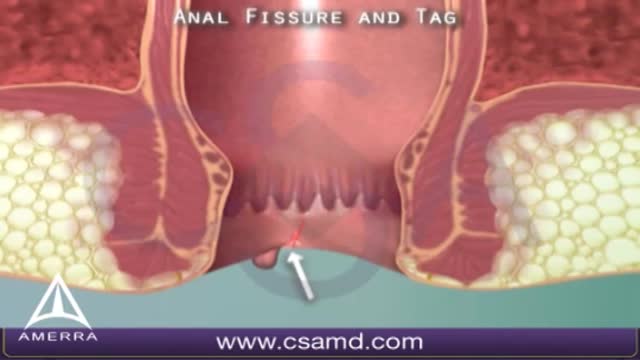
An anal fissure is a small tear in the thin, moist tissue (mucosa) that lines the anus. An anal fissure may occur when you pass hard or large stools during a bowel movement. Anal fissures typically cause pain and bleeding with bowel movements. You also may experience spasms in the ring of muscle at the end of your anus (anal sphincter). Anal fissures are very common in young infants but can affect people of any age. Most anal fissures get better with simple treatments, such as increased fiber intake or sitz baths. Some people with anal fissures may need medication or, occasionally, surgery.
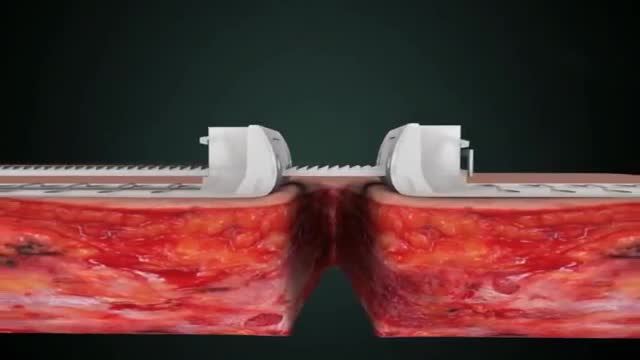
Wound closure techniques have evolved from the earliest development of suturing materials to comprise resources that include synthetic sutures, absorbables, staples, tapes, and adhesive compounds. The engineering of sutures in synthetic material along with standardization of traditional materials (eg, catgut, silk) has made for superior aesthetic results. Similarly, the creation of topical skin adhesives (the monomer 2-octyl cyanoacrylate), surgical staples, and tapes to substitute for sutures has supplemented the armamentarium of wound closure techniques. Aesthetic closure of a wound, whether traumatic or surgically induced, is based on knowledge of healing mechanisms and skin anatomy (see the image below), as well as an appreciation of suture material and closure technique. Choosing the proper materials and wound closure technique ensures optimal healing.[1]

Cholangitis Email this page to a friend Email this page to a friend Facebook Twitter Google+ Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile is a liquid made by the liver that helps digest food. Causes Cholangitis is most often caused by bacteria. This can occur when the duct is blocked by something, such as a gallstone or tumor. The infection causing this condition may also spread to the liver. Risk factors include a previous history of gallstones, sclerosing cholangitis, HIV, narrowing of the common bile duct, and rarely, travel to countries where you might catch a worm or parasite infection. Symptoms The following symptoms may occur: Pain on the upper right side or upper middle part of the abdomen. It may also be felt in the back or below the right shoulder blade. The pain may come and go and feel sharp, cramp-like, or dull. Fever and chills. Dark urine and clay-colored stools. Nausea and vomiting. Yellowing of the skin (jaundice), which may come and go.
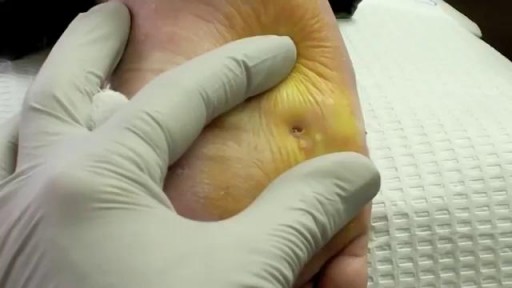
Curettage, electrosurgery, and laser surgery are more likely than cryotherapy to leave scars, so they are usually reserved for hard-to-remove or recurring warts. If you have a large area of warts, curettage may not be an effective treatment. Some surgical treatments may be too painful for some children.

Most people start smoking when they are in their teens and are addicted by the time they reach adulthood. Some have tried to quit but have returned to cigarettes because smoking is such a strong addiction. It is a habit that is very difficult to break. There are many different reasons why people smoke.

Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look inside your uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus.