Top videos
Transurethral resection of the prostate (also known as TURP, plural TURPs and as a transurethral prostatic resection TUPR) is a urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, it is performed by visualising the prostate through the urethra and removing tissue by electrocautery or sharp dissection. This is considered the most effective treatment for BPH. This procedure is done with spinal or general anesthetic. A large triple lumen catheter is inserted through the urethra to irrigate and drain the bladder after the surgical procedure is complete. Outcome is considered excellent for 80-90% of BPH patients. Because of bleeding risks associated with the surgery, TURP is not considered safe for many patients with cardiac problems. As with all invasive procedures, the patient should first discuss medications they are taking with their doctor, most especially blood thinners or anticoagulants, such as warfarin (Coumadin), or aspirin. These may need to be discontinued prior to surgery. Postop complications include bleeding (most common), clotting and hyponatremia (due to bladder irrigation).
Additionally, transurethral resection of the prostate is associated with low but important morbidity and mortality.

Full Tummy Tuck 3D Video - http://drlandsman.com
Look great... feel great
•Smart Liposuction + Liposculpture
•Abdominplasty (Tummy Tuck)
+ Full Mini Modified
•Brazilian Lift with Fat Transfer
•Vaginal Aesthetics & Rejuvenation
•Laser Hair Removal
•Full Body Lift
•Thigh lift
•Brachioplasty (Arm Lift) + Short Scar
Expertise in Body Contouring
Board Certified Plastic Surgeon
Expertise in body contouring combines skin excision techniques and advanced fat contouring technology
Weight control personalized training and smoking cessation results in a healthier lifestyle improved shape and longer lasting results
With over 2 decades of experience Dr Lloyd Landsman provides state of the art cosmetic and plastic surgery
Dr Landsman integrates the finest and safest products with the newest procedures
A customized treatment plan is created for each patient utilizing classic surgical and minimally invasive techniques for optimal results
Call for your complimentary consultation to learn how Dr Landsman can help you look your very best
Visit http://drlandsman.com Call 631 864 4111
Main Office 994 W Jericho Tpke Smithtown NY 11787
Affiliates East Islip • Westbury • Jackson Heights • Manhattan

Am I missing something?
Subscribe to my fun weekly newsletter (for free!): http://eepurl.com/iaYycn
To check out a previous newsletter, click here: https://mailchi.mp/a9909f90cac....a/why-are-you-having
For more Doc Schmidt content, check out my website: https://www.docschmidt.org/
Check out my children's book here: https://www.amazon.com/Night-Before-Med-School-Medical/dp/B0B193KWXT/ref=sr_1_1?keywords=doc+schmidt&qid=1653339841&sprefix=doc+sc%2Caps%2C202&sr=8-1
Logo and graphics designed by iamlindaayoade.com and loigraphics.com (LOI Graphics Inc.)
Want me to make you a personalized video for you or your friend? Check me out on Cameo!
https://v.cameo.com/DFKBSe2HSib
Want to connect with me and watch more content?
Find me on TikTok!
https://vm.tiktok.com/ZMRFmqKts/
And Instagram!
https://instagram.com/docschmidtig?r=nametag
All content is intended as medical education or entertainment and is NOT intended to be medical advice. If you have any symptoms concerning you, please schedule an appointment with your doctor.
Join my channel to get access to perks! Click link below:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCLbidg2ZT49dWrxDk

Join Dr. Parsia Vagefi, Chief of Surgical Transplantation and Dr. Steven Hanish, Surgical Director of Liver Transplantation, as they grant unprecedented access to the OR while performing a #Liver #Transplant #Surgery.
To find out more about UT Southwestern's transplant programs visit:
https://www.utswmed.org/transplant
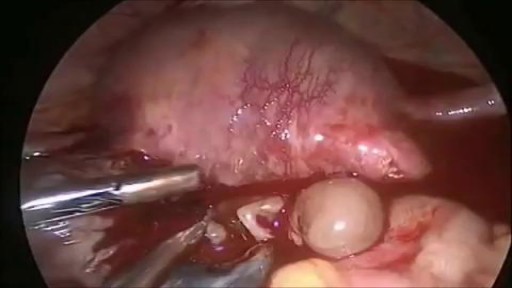
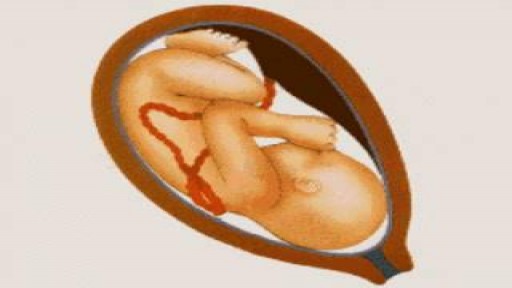
An ectopic pregnancy (EP) is a condition in which a fertilized egg settles and grows in any location other than the inner lining of the uterus. The vast majority of ectopic pregnancies are so-called tubal pregnancies and occur in the Fallopian tube.
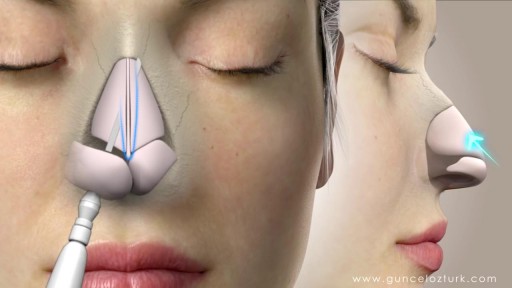
Rhinoplasty, sometimes referred to as a "nose job" or "nose reshaping" by patients, enhances facial harmony and the proportions of your nose. It can also correct impaired breathing caused by structural defects in the nose. What surgical rhinoplasty can treat Nose size in relation to facial balance Nose width at the bridge or in the size and position of the nostrils Nose profile with visible humps or depressions on the bridge Nasal tip that is enlarged or bulbous, drooping, upturned or hooked Nostrils that are large, wide or upturned Nasal asymmetry If you desire a more symmetrical nose, keep in mind that everyone's face is asymmetric to some degree. Results may not be completely symmetric, although the goal is to create facial balance and correct proportion. Rhinoplasty to correct a deviated septum Nose surgery that's done to improve an obstructed airway requires careful evaluation of the nasal structure as it relates to airflow and breathing. Correction of a deviated septum, one of the most common causes of breathing impairment, is achieved by adjusting the nasal structure to produce better alignment.

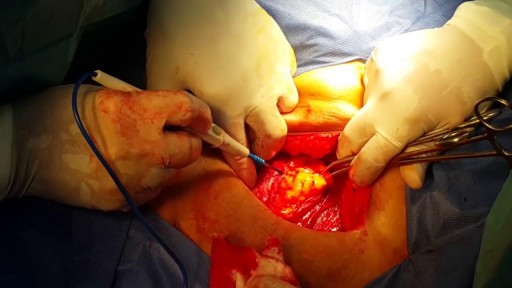
This minimally invasive technique allows surgeons to remove skull base tumors as large as softballs through the nose, with less trauma to the brain and critical nerves than with a traditional craniotomy.
To learn more, please visit https://www.upmc.com/
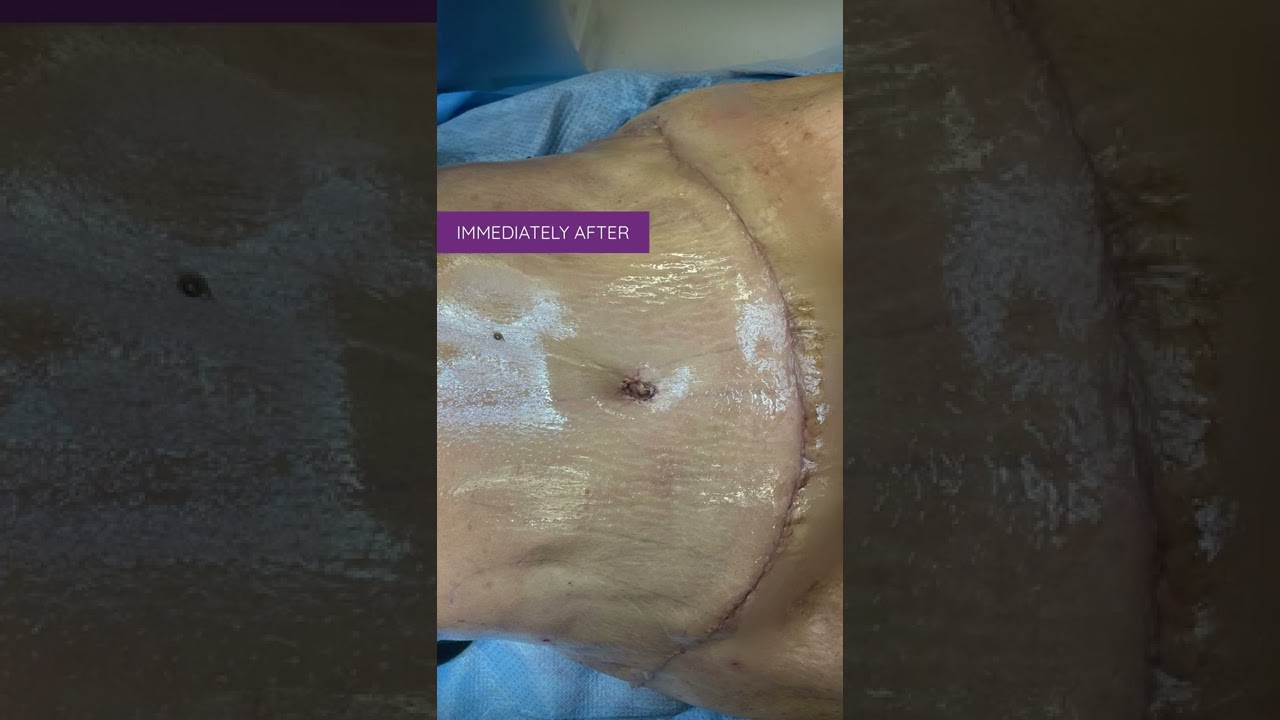
Liposuction in tummy tuck requires special planning and technique. I need to ensure that the blood circulation is well maintained for good healing. Yet proper liposuction is important to have a nice flat and contoured tummy.
#hdliposuction #tummytuck #lipoabdominoplasty #surgicalplanning #skinremovalsurgery #imeediatelyafter #plasticsurgeondubai #cocoonaclinic #drsanjayparashar #dubai
For more information visit www.drsanjayparashar.com
For more content, follow me on my social media
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/drsanjayparashar/
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/drsanjayparashar