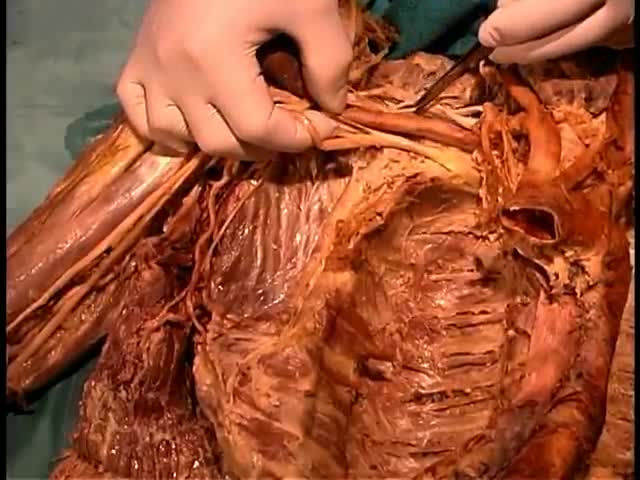
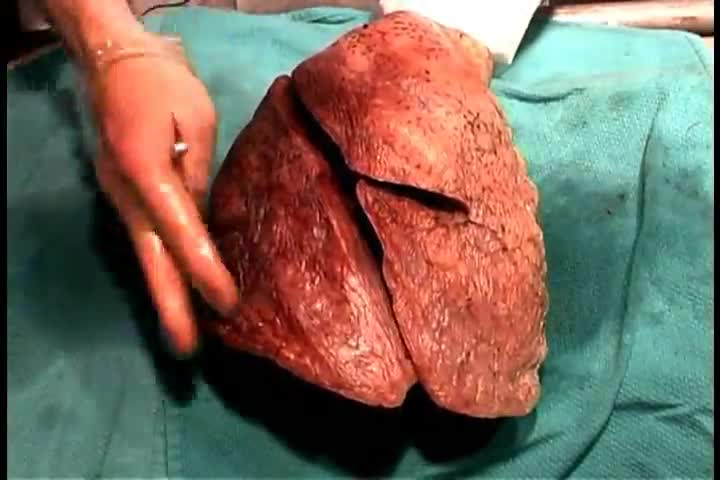
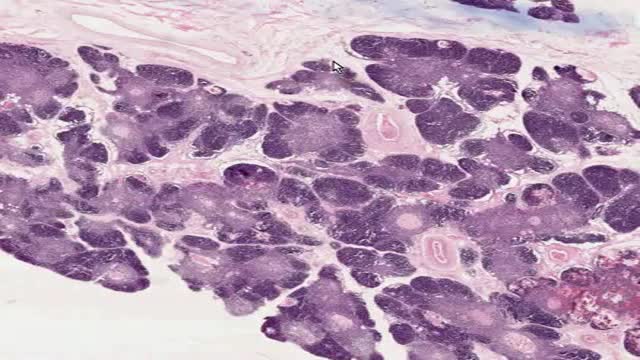
Top videos
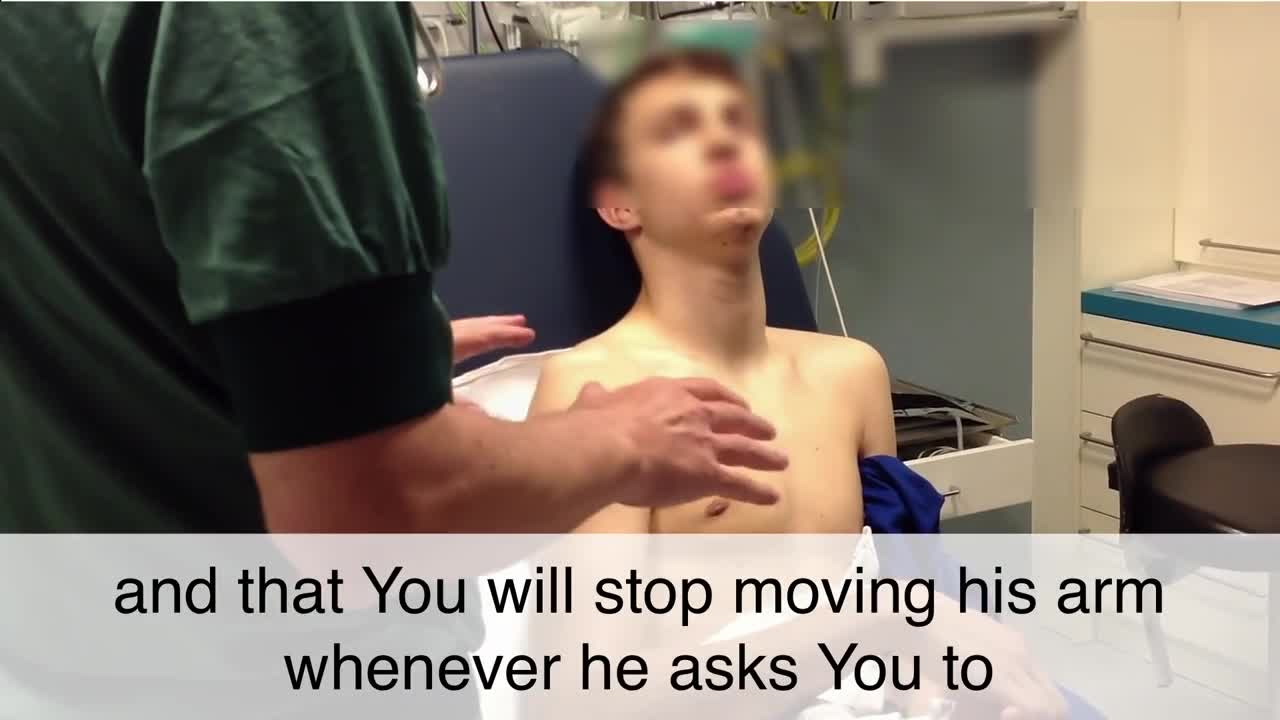
Reduction techniques can vary in terms of required force, time, equipment, and staff. [7] No single reduction method is successful in every instance; therefore, the clinician should be familiar with several reduction techniques. Techniques commonly used to reduce anterior shoulder dislocations include the following [35, 36, 37, 38, 39] : Stimson maneuver Scapular manipulation External rotation Milch technique Spaso technique Traction-countertraction

This medication is used to treat certain types of serious (possibly fatal) irregular heartbeat (such as persistent ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia). It is used to restore normal heart rhythm and maintain a regular, steady heartbeat. Amiodarone is known as an anti-arrhythmic drug. It works by blocking certain electrical signals in the heart that can cause an irregular heartbeat.
Anorectal malformations are defects that occur during the fifth to seventh weeks of fetal development. With these defects, the anus (opening at the end of the large intestine through which stool passes) and the rectum (area of the large intestine just above the anus) do not develop properly
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the uterus. The uterus is the hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ in women where fetal development occurs. Endometrial cancer begins in the layer of cells that form the lining (endometrium) of the uterus. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called uterine cancer. Other types of cancer can form in the uterus, including uterine sarcoma, but they are much less common than endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is often detected at an early stage because it frequently produces abnormal vaginal bleeding, which prompts women to see their doctors. If endometrial cancer is discovered early, removing the uterus surgically often cures endometrial cancer.

Tobacco use is the most common preventable cause of death. About half of the people who don't quit smoking will die of smoking-related problems. Quitting smoking is important for your health. Soon after you quit, your circulation begins to improve, and your blood pressure starts to return to normal. Your sense of smell and taste return, and it's easier for you to breathe. In the long term, giving up tobacco can help you live longer. Your risk of getting cancer decreases with each year you stay smoke-free. Quitting is not easy. You may have short-term affects such as weight gain, irritability, and anxiety. Some people try several times before they succeed. There are many ways to quit smoking. Some people stop "cold turkey." Others benefit from step-by-step manuals, counseling, or medicines or products that help reduce nicotine addiction. Some people think that switching to e-cigarettes can help you quit smoking, but that has not been proven. Your health care provider can help you find the best way for you to quit.
A bulla is a fluid-filled sac or lesion that appears when fluid is trapped under a thin layer of your skin. It’s a type of blister. Bullae (pronounced as “bully”) is the plural word for bulla. To be classified as a bulla, the blister must be larger than 0.5 centimeters (5 millimeters) in diameter. Smaller blisters are called vesicles.

The best way to prepare yourself for your small group exercises is to first watch the cardiac exam video from beginning to end, then proceed through all the explanations of cardiac anatomy and physiology that follow. To go through the material in the recommended sequence, just click the "Next" button in the upper right corner of the screen. But you may also jump to any section using the menu to the left.

Fibromialgia Remedios Naturales, Como Curar La Fibromialgia, Medicamento Para Fibromialgia. http://fibromialgia-cura.info-pro.co/ -- Medicina Natural Para La Fibromialgia. Se estima que 5 millones de estadounidenses sufren de fibromialgia. Los dolores profundos y crónicos pueden tener un enorme impacto en la salud física y emocional. Desafortunadamente, los tratamientos son pocos y distantes entre sí, y los que existen a menudo vienen con la posibilidad de efectos secundarios desagradables. La medicina natural para la fibromialgia puede ser una bendición para los enfermos que la padecen. Estas terapias complementarias, suelen ser efectivas y pueden mejorar la calidad de vida y rejuvenecer un cuerpo atormentado por el dolor crónico. El masaje es a menudo uno de los métodos más eficaces para reducir los síntomas de fibromialgia. Alivia la rigidez, mejora el rango de movimiento, reduce el dolor y ayuda a controlar el estrés. Una técnica llamada liberación miofascial es especialmente adecuado para la fibromialgia el dolor calmante. La fascia es un tejido conectivo delgada que cubre y se extiende a lo largo del músculo. Los pacientes con fibromialgia sufren comúnmente de apriete de la fascia que contribuye al dolor y la fatiga muscular. La liberación miofascial es una técnica suave que relaja la fascia y reduce el dolor asociado. Las terapias naturales pueden ayudar desde dentro también. La investigación ha encontrado que muchos enfermos de fibromialgia tienen niveles bajos de vitamina D y magnesio. 100% natural aliviar el dolor y mejorar tu calidad de vida solo haciendo click aqui. http://fibromialgia-cura.info-pro.co

Take your left leg and place your ankle against the knee. Hold the position for a moment before changing legs. This helps stretch the tiny piriformis muscle, which sometimes becomes inflamed and presses against the sciatic nerve causing pain. Repeat by switching sides and doing the same exercise with the other leg.