Top videos
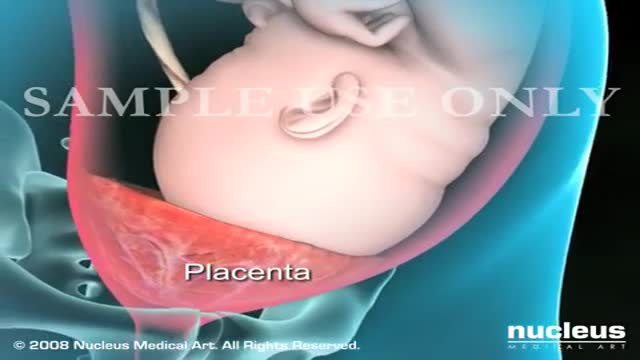
A Cesarean section (C-section) is surgery to deliver a baby. The baby is taken out through the mother's abdomen. In the United States, almost one in three women has their babies this way. Some C-sections are planned, but many are done when unexpected problems happen during delivery. Reasons for a C-section may include
A bulla is a fluid-filled sac or lesion that appears when fluid is trapped under a thin layer of your skin. It’s a type of blister. Bullae (pronounced as “bully”) is the plural word for bulla. To be classified as a bulla, the blister must be larger than 0.5 centimeters (5 millimeters) in diameter. Smaller blisters are called vesicles.

Fibromialgia Remedios Naturales, Como Curar La Fibromialgia, Medicamento Para Fibromialgia. http://fibromialgia-cura.info-pro.co/ -- Medicina Natural Para La Fibromialgia. Se estima que 5 millones de estadounidenses sufren de fibromialgia. Los dolores profundos y crónicos pueden tener un enorme impacto en la salud física y emocional. Desafortunadamente, los tratamientos son pocos y distantes entre sí, y los que existen a menudo vienen con la posibilidad de efectos secundarios desagradables. La medicina natural para la fibromialgia puede ser una bendición para los enfermos que la padecen. Estas terapias complementarias, suelen ser efectivas y pueden mejorar la calidad de vida y rejuvenecer un cuerpo atormentado por el dolor crónico. El masaje es a menudo uno de los métodos más eficaces para reducir los síntomas de fibromialgia. Alivia la rigidez, mejora el rango de movimiento, reduce el dolor y ayuda a controlar el estrés. Una técnica llamada liberación miofascial es especialmente adecuado para la fibromialgia el dolor calmante. La fascia es un tejido conectivo delgada que cubre y se extiende a lo largo del músculo. Los pacientes con fibromialgia sufren comúnmente de apriete de la fascia que contribuye al dolor y la fatiga muscular. La liberación miofascial es una técnica suave que relaja la fascia y reduce el dolor asociado. Las terapias naturales pueden ayudar desde dentro también. La investigación ha encontrado que muchos enfermos de fibromialgia tienen niveles bajos de vitamina D y magnesio. 100% natural aliviar el dolor y mejorar tu calidad de vida solo haciendo click aqui. http://fibromialgia-cura.info-pro.co

Tobacco use is the most common preventable cause of death. About half of the people who don't quit smoking will die of smoking-related problems. Quitting smoking is important for your health. Soon after you quit, your circulation begins to improve, and your blood pressure starts to return to normal. Your sense of smell and taste return, and it's easier for you to breathe. In the long term, giving up tobacco can help you live longer. Your risk of getting cancer decreases with each year you stay smoke-free. Quitting is not easy. You may have short-term affects such as weight gain, irritability, and anxiety. Some people try several times before they succeed. There are many ways to quit smoking. Some people stop "cold turkey." Others benefit from step-by-step manuals, counseling, or medicines or products that help reduce nicotine addiction. Some people think that switching to e-cigarettes can help you quit smoking, but that has not been proven. Your health care provider can help you find the best way for you to quit.

Description: Use warm water and sea salt. Soak the wart for 10 to 15 minutes in warm salt water to moisten the skin. Scrape the dead skin layers off the wart using a nail file, pumice stone or mild sandpaper. You could also use your fingers, but wash them thoroughly before and after, as warts can easily spread.

Take your left leg and place your ankle against the knee. Hold the position for a moment before changing legs. This helps stretch the tiny piriformis muscle, which sometimes becomes inflamed and presses against the sciatic nerve causing pain. Repeat by switching sides and doing the same exercise with the other leg.
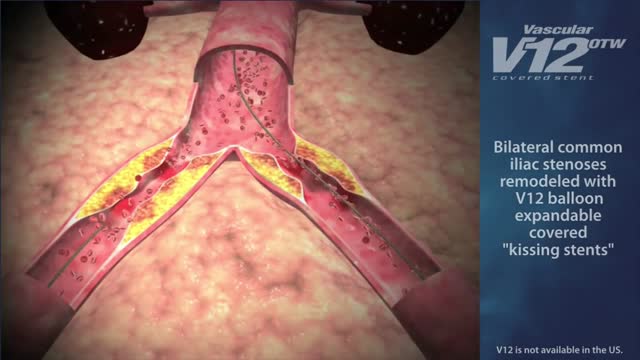
Indications for endovascular repair of the iliac artery are: Stenosis or (short-segment) occlusion of iliac artery (TASC type A and B, TASC C lesions are controversial) with ipsilateral lower extremity ischemia (lifestyle-limiting, progressive claudication, rest pain, gangrene). Patients with asymptomatic aneurysm greater than 4 cm in diameter. An iliac aneurysm which has also increased in size by 0.5 cm in last six months. Symptomatic iliac artery aneurysms mandate endovascular (or open) repair regardless of size. Patients with long occluded lesions/poor run-off/acute limb ischemia are poor endovascular candidates.

This video: The veins around your anus tend to stretch under pressure and may bulge or swell. Swollen veins (hemorrhoids) can develop from an increase in pressure in the lower rectum. Factors that might cause increased pressure include: Straining during bowel movements.