Top videos
Know About Cardiothoracic Surgery in 60 Seconds About what cardiothoracic surgery is, why it is done and what is the result of such surgery. A Major Session on #cardiothoracic #surgery at #Congress #2018HCC 2018 Healthcare and Cardiology Conference #BANGKOK http://cosmicseries.org/cardiology-conferences/

An ectopic pregnancy results when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Unfortunately, there's no way to transplant an ectopic pregnancy into your uterus, so ending the pregnancy is the only option. About 2 percent of pregnancies are ectopic. Because ectopic pregnancy is potentially dangerous for you, it's important to recognize the early signs and get treatment as soon as possible.

Tobacco use is the most common preventable cause of death. About half of the people who don't quit smoking will die of smoking-related problems. Quitting smoking is important for your health. Soon after you quit, your circulation begins to improve, and your blood pressure starts to return to normal. Your sense of smell and taste return, and it's easier for you to breathe. In the long term, giving up tobacco can help you live longer. Your risk of getting cancer decreases with each year you stay smoke-free. Quitting is not easy. You may have short-term affects such as weight gain, irritability, and anxiety. Some people try several times before they succeed. There are many ways to quit smoking. Some people stop "cold turkey." Others benefit from step-by-step manuals, counseling, or medicines or products that help reduce nicotine addiction. Some people think that switching to e-cigarettes can help you quit smoking, but that has not been proven. Your health care provider can help you find the best way for you to quit.
Frostbite is an injury caused by freezing of the skin and underlying tissues. First your skin becomes very cold and red, then numb, hard and pale. Frostbite is most common on the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin. Exposed skin in cold, windy weather is most vulnerable to frostbite. But frostbite can occur on skin covered by gloves or other clothing. Frostnip, the first stage of frostbite, doesn't cause permanent skin damage. You can treat very mild frostbite with first-aid measures, including rewarming your skin. All other frostbite requires medical attention because it can damage skin, tissues, muscle and bones. Possible complications of severe frostbite include infection and nerve damage.

Description: Use warm water and sea salt. Soak the wart for 10 to 15 minutes in warm salt water to moisten the skin. Scrape the dead skin layers off the wart using a nail file, pumice stone or mild sandpaper. You could also use your fingers, but wash them thoroughly before and after, as warts can easily spread.

In breastfeeding, the latch is the moment everything comes together: Your baby takes a big mouthful of your nipple and areola (or "latches on"), begins to suck, and draws out your milk. When your baby has established a good latch, your nipple soreness is minimized and your little one gets the nourishment he needs. How do you pull all that off? First and most important, have faith in yourself and your baby. "Babies are designed to breastfeed," says Emily Pease, R.N., international board certified lactation consultant (IBCLC), of Swedish Hospital's Breastfeeding Center in Seattle. "They are born with instincts that help them find Mom's breast and latch on often with very little assistance. And if problems do come up, there are lots of ways to troubleshoot." Here are more steps to get a good latch right from the start.

Take your left leg and place your ankle against the knee. Hold the position for a moment before changing legs. This helps stretch the tiny piriformis muscle, which sometimes becomes inflamed and presses against the sciatic nerve causing pain. Repeat by switching sides and doing the same exercise with the other leg.
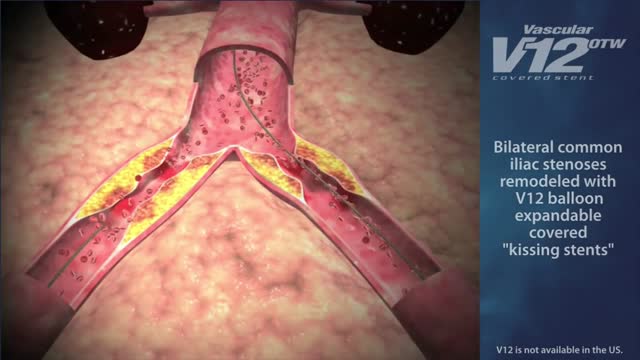
Indications for endovascular repair of the iliac artery are: Stenosis or (short-segment) occlusion of iliac artery (TASC type A and B, TASC C lesions are controversial) with ipsilateral lower extremity ischemia (lifestyle-limiting, progressive claudication, rest pain, gangrene). Patients with asymptomatic aneurysm greater than 4 cm in diameter. An iliac aneurysm which has also increased in size by 0.5 cm in last six months. Symptomatic iliac artery aneurysms mandate endovascular (or open) repair regardless of size. Patients with long occluded lesions/poor run-off/acute limb ischemia are poor endovascular candidates.
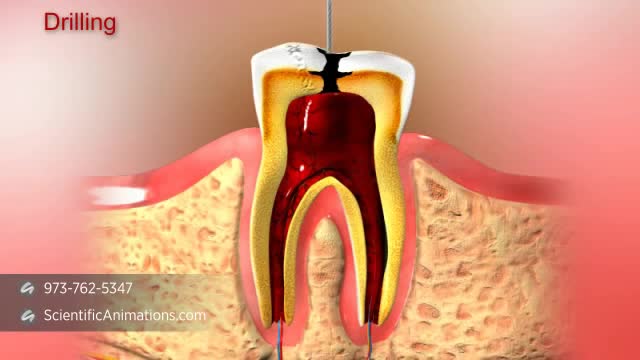
During root canal treatment, the inflamed or infected pulp is removed and the inside of the tooth is carefully cleaned and disinfected, then filled and sealed with a rubber-like material called gutta-percha. Afterwards, the tooth is restored with a crown or filling for protection.

Thank you so much for watching❤
If you enjoyed this video ▶Please leave a LIKE👍 ▶SHARE this video ▶【SUBSCRIBE】my channel for more new videos And click the BELL 🔔so you don't miss any of my videos HERE
https://www.youtube.com/c/nurs....eminder?sub_confirma
You can support my work by purchasing your NurseMinder Merch https://teespring.com/stores/nurseminder-nation (or click on merch pics under the video)
Or simply do your Amazon shopping after clicking on one of the links below
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Thank you so much! I appreciate you!♥♥
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nurses often prime IV lines with the hopes that there are no air bubbles. In this video, I will share a couple of tips to help reduce the risk or frequency of air bubbles during line priming. I will also talk about how to troubleshoot the air bubbles when they appear during an infusion
Providing patient care and influencing safe patient outcomes requires that registered nurses and licensed practice nurses maintain air free IV lines. Learn the strategies and tips to decrease the risk of air bubbles appearing in your primary or secondary medication line as well as troubleshooting tips to remove those alarming bubbles. Your patients will thank you!
Whether you are providing normal saline, a medication, or a combination, ensure that all fluids are compatible.
Supplies used in this video include the Alaris Primary Infusion line, alcohol swabs and a sterile 10 cc syringe ... and a nail in the wall :)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
❤️ ~ You may also be interested in watching ~ ❤️
PICC line assessment https://youtu.be/tnKClpU-J1g
How To Access a PICC line https://youtu.be/SCF6bmk8KWc
Putting on Sterile Gloves https://youtu.be/xNwkKLqDJn4
Organizational Plans for Nursing https://youtu.be/_NATxwPwHzc
Medication Conversions https://youtu.be/TCPBXg2TYCs
------------------------------------------------------------------------
💻COMMENT in the description box below and share your ideas
👍 LIKE the video
🗣 SHARE with your friends
📥 SUBSCRIBE ... hit the BELL 🔔
Subscribe to NurseMinder https://www.youtube.com/c/nurs....eminder?sub_confirma
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Amazon Affiliate Links
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Want to support me in another way? Enter Amazon through my links and continue to do your shopping. Simple and Easy Way to support the work I do.
The following list is the equipment I use (or if my version is no longer sold, a close replica).
📱 Phone 11 Cell Phone https://amzn.to/2WpOJfz
💻 MacBook Pro https://amzn.to/2YyxQC1
👉 Final Cut Video Editing software https://amzn.to/3fqlAd9
🎙️ Rode NT USB microphone (Audio Recording) for post-production voiceover https://amzn.to/2W2RJj1
👉 Neewer Professional Recording Stand – mount microphone and adjust positioning to keep it close but out of the camera’s view: https://amzn.to/3fjB4zs
👉 Manfrotto Tripod (hold cell phone) https://amzn.to/2YKGYUz
💡 Neewer Ring Light to reduce shadows and improve lighting. https://amzn.to/3dk5OP5
Disclaimer: I recommend only products that I know and trust to be of high quality. Links are provided for quick access. Some of the links contained in this checklist are affiliate links and I may receive a commission if make a purchase from the affiliate. This helps me to keep creating and offering free content.

This video: The veins around your anus tend to stretch under pressure and may bulge or swell. Swollen veins (hemorrhoids) can develop from an increase in pressure in the lower rectum. Factors that might cause increased pressure include: Straining during bowel movements.
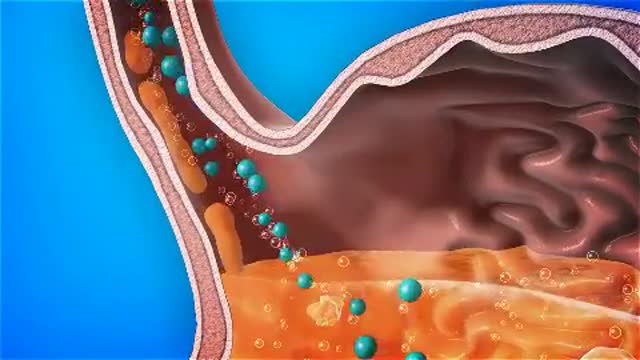
Stomach acid is natural, a valuable chemical contributor to orderly digestion. But in excess or in the wrong place, it's a menace, inflaming and irritating the esophagus, typically causing heartburn and sometimes contributing to the development of ulcers in the stomach and the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine.
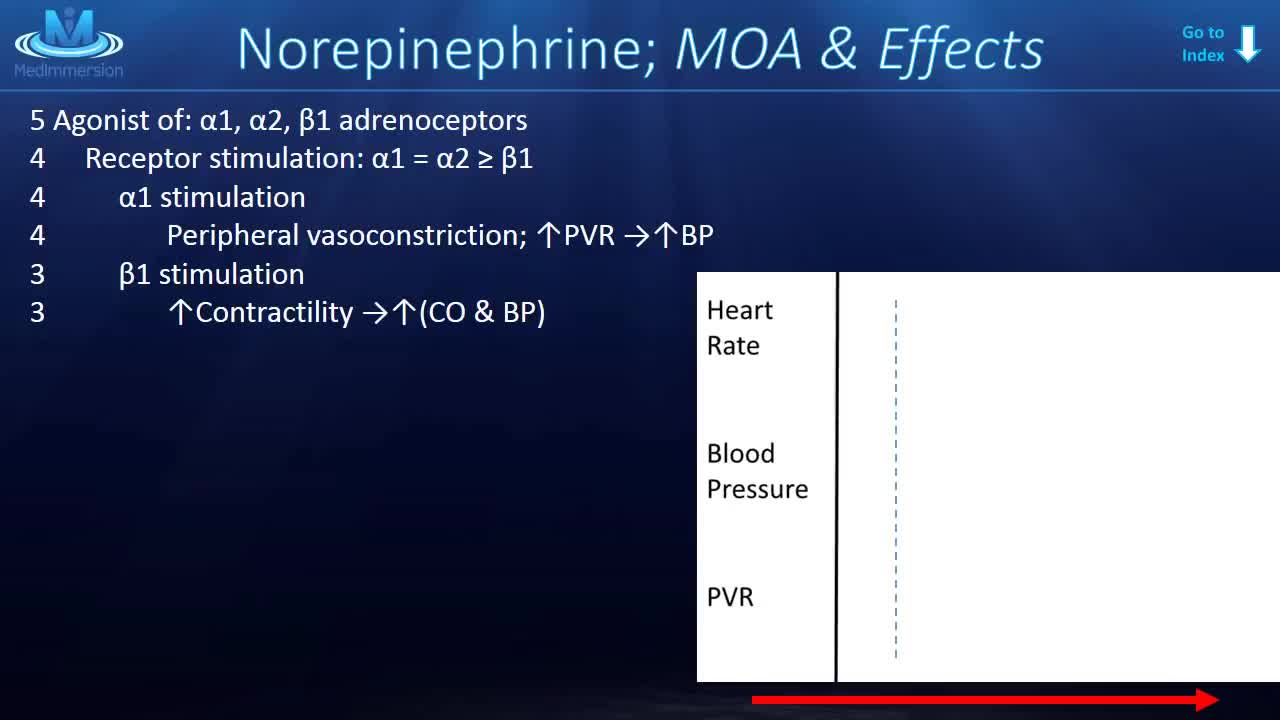
Norepinephrine is synthesized from dopamine by dopamine β-hydroxylase.[7] It is released from the adrenal medulla into the blood as a hormone, and is also a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and sympathetic nervous system where it is released from noradrenergic neurons.