Top videos
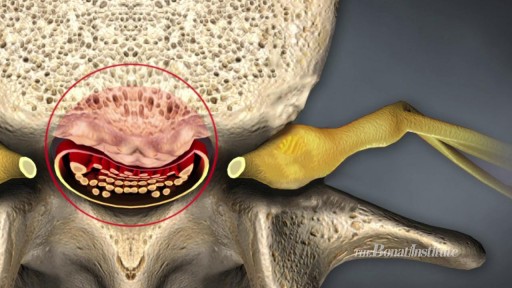
Watch Spinal Stenosis Videos Spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal cord in the neck (cervical spine) or the spinal nerve roots in the lower back (lumbar spine) are compressed. Symptoms of lumbar stenosis often include leg pain (sciatica) and leg tingling, weakness, or numbness. Arm pain is a typical symptom of cervical spinal stenosis. For cervical spinal stenosis with myelopathy, difficulty with coordination often occurs. Stenosis treatment may include non-surgical options (exercise, anti-inflammatory medication, epidural injections, and activity modification) or back surgery.
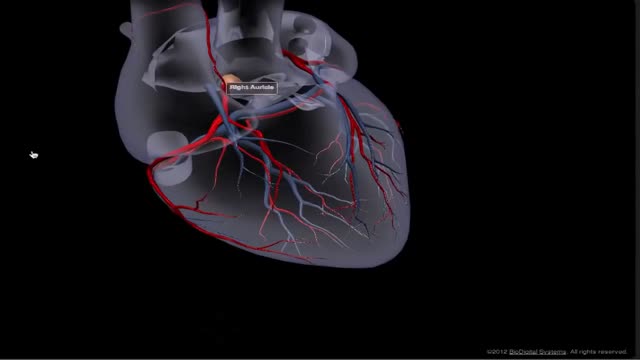
The heart receives its own supply of blood from the coronary arteries. Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet. These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
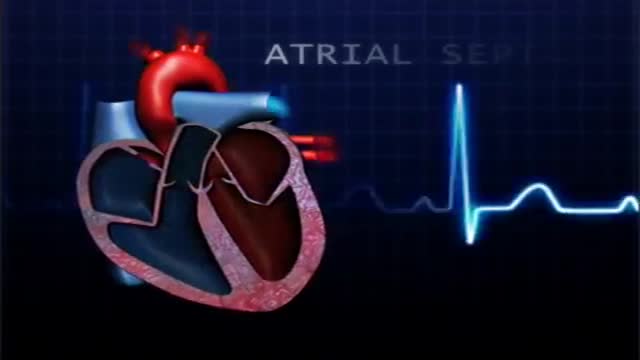
atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications
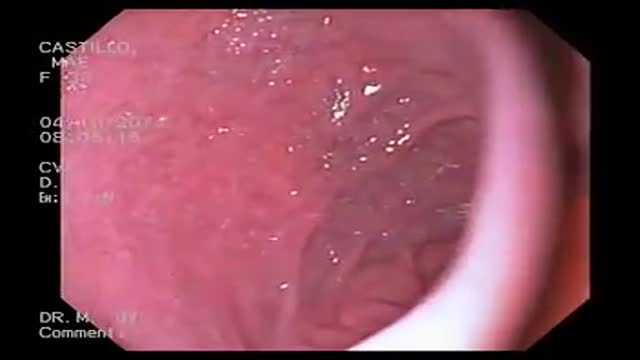
A gastroscopy is a procedure where a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope is used to look inside the oesophagus (gullet), stomach and first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It's also sometimes referred to as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. The endoscope has a light and a camera at one end.
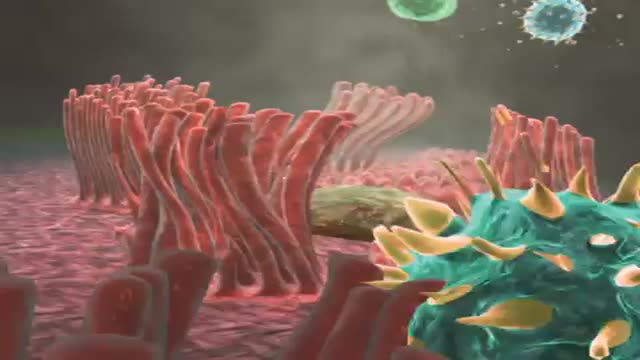
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you're allergic to, such as a peanut or the venom from a bee sting. The flood of chemicals released by your immune system during anaphylaxis can cause you to go into shock; your blood pressure drops suddenly and your airways narrow, blocking normal breathing. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include a rapid, weak pulse, a skin rash, and nausea and vomiting. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include certain foods, some medications, insect venom and latex. Anaphylaxis requires an immediate trip to the emergency department and an injection of epinephrine. If anaphylaxis isn't treated right away, it can lead to unconsciousness or even death.

Controlled studies on treatment of catscratch disease (CSD) are lacking. Thus, treatment recommendations are based on case reports, reviews, a single controlled trial, and anecdotal data. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections, including CSD, have been established.Oct 19, 2016
Cells may have slender extensions of the cell membrane to form cilia or the smaller extensions called microvilli. The microscopic microvilli effectively increase the surface area of the cell and are useful for absorption and secretion functions. A dramatic example is the human small intestine. The tissue has small fingerlike extensions called villi which are collections of cells, and those cells have many microvilli to even further increase the available surface area for the digestion process. According to Audesirk & Audesirk, this can give an effective surface area of about 250 square meters for absorption.
A modified radical mastectomy is a procedure in which the entire breast is removed, including the skin, areola, nipple, and most axillary lymph nodes; the pectoralis major muscle is spared. Historically, a modified radical mastectomy was the primary method of treatment of breast cancer. [1, 2] As the treatment of breast cancer evolved, breast conservation has become more widely used. [3, 4] However, mastectomy still remains a viable option for women with breast cancer. [5, 6]

Hair Transplant Results Before and After Photos who undergone Hair Transplant. View our patient's successful results with the FUE, Bio - FUE and B.E.S.T FUE hair transplant technique. Comparable before & after photos! For More Visit Here:- https://www.hairtransplantchennai.org/hair-transplant-results-chennai.php or call us:- +91-8939636222

Diabetes is a growing global health concern, as is obesity. Diabetes and obesity are intrinsically linked: obesity increases the risk of diabetes and also contributes to disease progression and cardiovascular disease. Although the benefits of weight loss in the prevention of diabetes and as a critical component of managing the condition are well established, weight reduction remains challenging for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to a host of metabolic and psychological factors. For many patients, lifestyle intervention is not enough to achieve weight loss, and alternative options, such as pharmacotherapy, need to be considered. However, many traditional glucose-lowering medications may lead to weight gain. This article focuses on the potential of currently available pharmacological strategies and on emerging approaches in development to support the glycemic and weight-loss goals of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Two pharmacotherapy types are considered: those developed primarily for blood glucose control that have a favorable effect on body weight and those developed primarily to induce weight loss that have a favorable effect on blood glucose control. Finally, the potential of combination therapies for the management of obese patients with type 2 diabetes is discussed.

Ellis demonstrates how to set up an intravenous piggyback medication (i.e., secondary).
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #ClinicalSkills #IVPush #IVpiggyback #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN
00:00 What to expect from IV Piggyback
00:32 Ejecting air, saline flush for IV Piggyback
1:11 Saline lock
2:28 Clamping tubing
2:38 Spiking bag
2:50 Hanging bag
3:07 Priming the tubing
3:50 Attaching to pump port
4:04 Unclamping tubing
4:45 Lowering the primary
5:08 Setting the pump
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed: Donepezil (Aricept) is approved to treat all stages of Alzheimer's. Rivastigmine (Exelon) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Galantamine (Razadyne) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer's. But drug and non-drug treatments may help with both cognitive and behavioral symptoms. Researchers are looking for new treatments to alter the course of the disease and improve the quality of life for people with dementia. ... Medications for Memory Loss.