Top videos
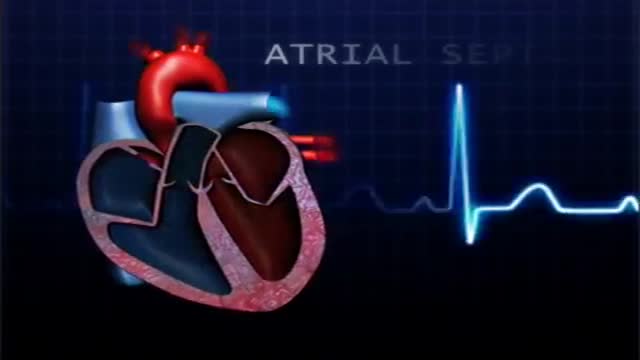
atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications
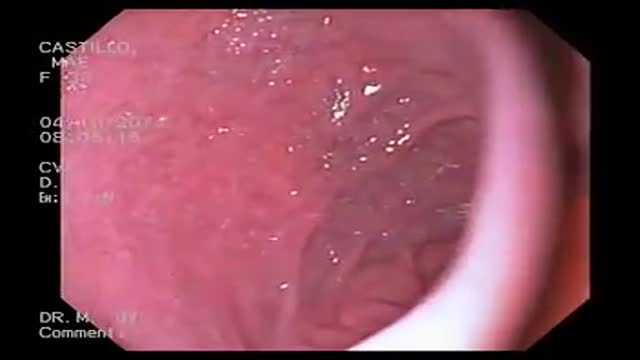
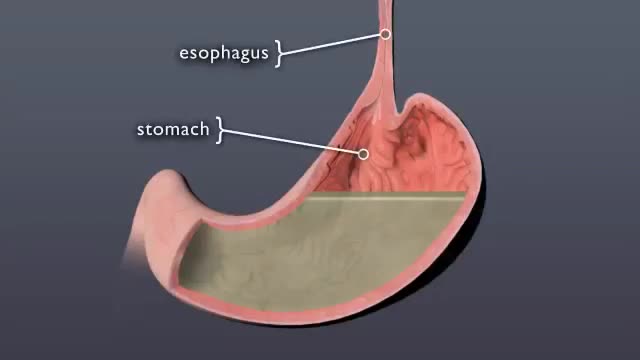
A gastroscopy is a procedure where a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope is used to look inside the oesophagus (gullet), stomach and first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It's also sometimes referred to as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. The endoscope has a light and a camera at one end.
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you're allergic to, such as a peanut or the venom from a bee sting. The flood of chemicals released by your immune system during anaphylaxis can cause you to go into shock; your blood pressure drops suddenly and your airways narrow, blocking normal breathing. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include a rapid, weak pulse, a skin rash, and nausea and vomiting. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include certain foods, some medications, insect venom and latex. Anaphylaxis requires an immediate trip to the emergency department and an injection of epinephrine. If anaphylaxis isn't treated right away, it can lead to unconsciousness or even death.
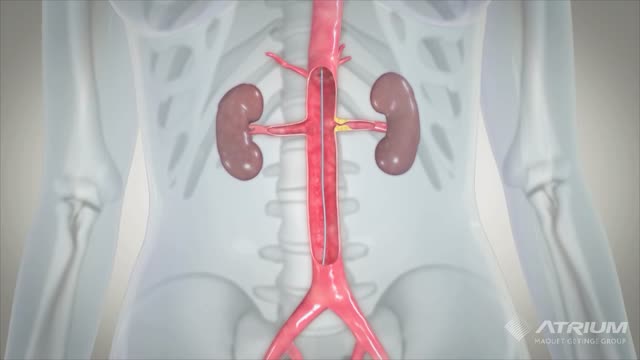
A ureteral stent, sometimes as well called ureteric stent, is a thin tube inserted into the ureter to prevent or treat obstruction of the urine flow from the kidney. The length of the stents used in adult patients varies between 24 to 30 cm.

Controlled studies on treatment of catscratch disease (CSD) are lacking. Thus, treatment recommendations are based on case reports, reviews, a single controlled trial, and anecdotal data. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections, including CSD, have been established.Oct 19, 2016

Duke Sports Medicine Specialists Jocelyn Wittstein, MD, Janna Fonseca, ATC, and Michael Messer ,PT, present on Soccer Injury Prevention including Concussion Management and the 11+ program that significantly reduces ACL tear rates in soccer.
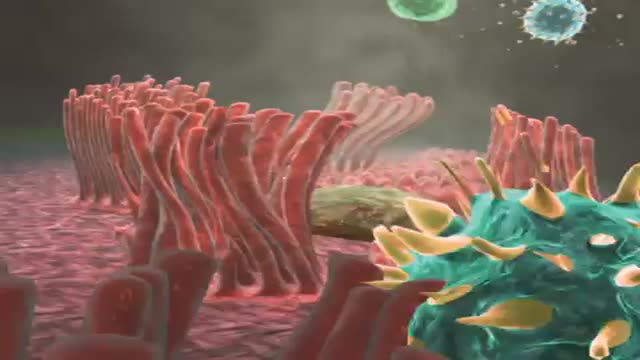
Cells may have slender extensions of the cell membrane to form cilia or the smaller extensions called microvilli. The microscopic microvilli effectively increase the surface area of the cell and are useful for absorption and secretion functions. A dramatic example is the human small intestine. The tissue has small fingerlike extensions called villi which are collections of cells, and those cells have many microvilli to even further increase the available surface area for the digestion process. According to Audesirk & Audesirk, this can give an effective surface area of about 250 square meters for absorption.

Hair Transplant Results Before and After Photos who undergone Hair Transplant. View our patient's successful results with the FUE, Bio - FUE and B.E.S.T FUE hair transplant technique. Comparable before & after photos! For More Visit Here:- https://www.hairtransplantchennai.org/hair-transplant-results-chennai.php or call us:- +91-8939636222
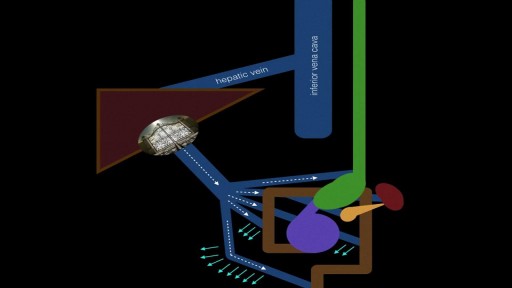
Portal hypertension is an increase in the blood pressure within a system of veins called the portal venous system. ... If the vessels in the liver are blocked due to liver damage, blood cannot flow properly through the liver. As a result, high pressure in the portal system develops
A modified radical mastectomy is a procedure in which the entire breast is removed, including the skin, areola, nipple, and most axillary lymph nodes; the pectoralis major muscle is spared. Historically, a modified radical mastectomy was the primary method of treatment of breast cancer. [1, 2] As the treatment of breast cancer evolved, breast conservation has become more widely used. [3, 4] However, mastectomy still remains a viable option for women with breast cancer. [5, 6]

Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed: Donepezil (Aricept) is approved to treat all stages of Alzheimer's. Rivastigmine (Exelon) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Galantamine (Razadyne) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer's. But drug and non-drug treatments may help with both cognitive and behavioral symptoms. Researchers are looking for new treatments to alter the course of the disease and improve the quality of life for people with dementia. ... Medications for Memory Loss.