Top videos

-Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for mothers colonized with group B Streptococcus can prevent early-onset neonatal disease. Adequate prophylaxis consists of ampicillin, penicillin, or cefazolin for ;::4 hours before delivery. Regardless of intrapartum treatment, all high-risk infants must be observed for ;::49 hours. A complete blood count with differential and blood culture are indicated if the infant is preterm <37 weeks or was exposed to prolonged rupture of membranes.>18 hrs.
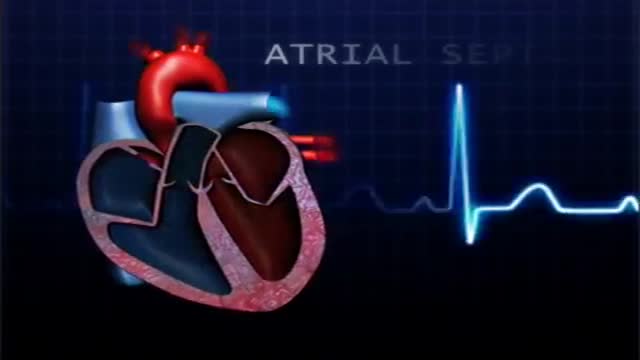
atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications
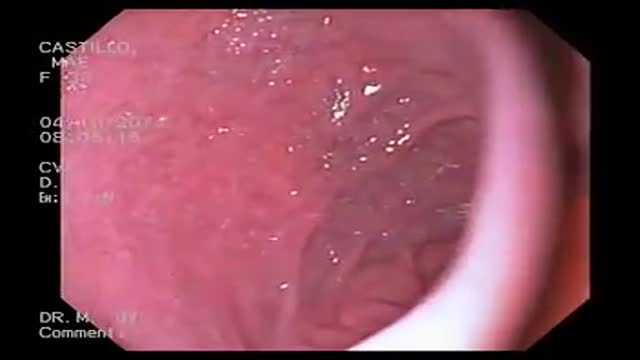
A gastroscopy is a procedure where a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope is used to look inside the oesophagus (gullet), stomach and first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It's also sometimes referred to as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. The endoscope has a light and a camera at one end.
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you're allergic to, such as a peanut or the venom from a bee sting. The flood of chemicals released by your immune system during anaphylaxis can cause you to go into shock; your blood pressure drops suddenly and your airways narrow, blocking normal breathing. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include a rapid, weak pulse, a skin rash, and nausea and vomiting. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include certain foods, some medications, insect venom and latex. Anaphylaxis requires an immediate trip to the emergency department and an injection of epinephrine. If anaphylaxis isn't treated right away, it can lead to unconsciousness or even death.

Controlled studies on treatment of catscratch disease (CSD) are lacking. Thus, treatment recommendations are based on case reports, reviews, a single controlled trial, and anecdotal data. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections, including CSD, have been established.Oct 19, 2016

Obesity is one of the most pervasive, chronic diseases in need of new strategies for medical treatment and prevention. As a leading cause of United States mortality, morbidity, disability, healthcare utilization and healthcare costs, the high prevalence of obesity continues to strain the United States healthcare system. Obesity is defined as excess adipose tissue. There are several different methods for determining excess adipose (fat) tissue; the most common being the Body Mass Index (BMI) (see below). A fat cell is an endocrine cell and adipose tissue is an endocrine organ. As such, adipose tissue secretes a number of products, including metabolites, cytokines, lipids, and coagulation factors among others. Significantly, excess adiposity or obesity causes increased levels of circulating fatty acids and inflammation. This can lead to insulin resistance, which in turn can lead to type 2 diabetes.
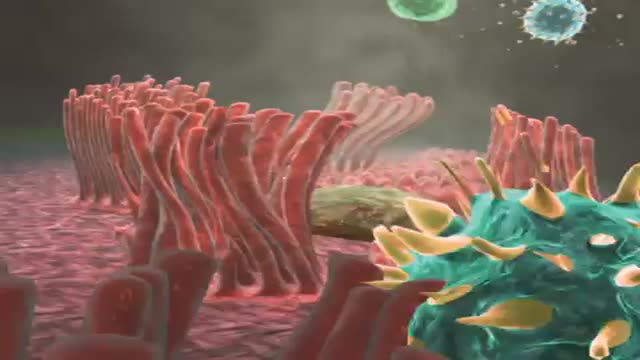
Cells may have slender extensions of the cell membrane to form cilia or the smaller extensions called microvilli. The microscopic microvilli effectively increase the surface area of the cell and are useful for absorption and secretion functions. A dramatic example is the human small intestine. The tissue has small fingerlike extensions called villi which are collections of cells, and those cells have many microvilli to even further increase the available surface area for the digestion process. According to Audesirk & Audesirk, this can give an effective surface area of about 250 square meters for absorption.

In this video, the viewer will learn the key aspects of the newborn physical exam, and how to distinguish between normal and abnormal findings.
Direct Links to chapters:
0:00-Intro
1:30-Head
3:49-Face
8:05-Neck
8:30-Chest
10:13-Abdomen
11:01-Groin
13:17-Extremities
14:05-Back
14:47-Neurologic
Please visit: www.openpediatrics.org
OPENPediatrics™ is an interactive digital learning platform for healthcare clinicians sponsored by Boston Children's Hospital and in collaboration with the World Federation of Pediatric Intensive and Critical Care Societies. It is designed to promote the exchange of knowledge between healthcare providers around the world caring for critically ill children in all resource settings. The content includes internationally recognized experts teaching the full range of topics on the care of critically ill children. All content is peer-reviewed and open access-and thus at no expense to the user.
For further information on how to enroll, please email: openpediatrics@childrens.harvard.edu
Please note: OPENPediatrics does not support nor control any related videos in the sidebar, these are placed by Youtube. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.

Neck Examination - Cervical Spine Assessment - Clinical Skills - Dr Gill
Compose a new pain within athletes is cervical spine discomfort, thankfully in the vast majority of cases when the neck is examined the cause of the neck pain is found to be muscular.
However, pain can also refer from the neck to the arm, in which case it is important to be able to assess for cervical radiculopathy prior to gaining more information which may indicate an MRI is needed
We assess for radiculopathy by doing Spurling's test, an often overlooked part of the neck examination, but it should be included for completeness and reassurance of the patient - not forgetting the athlete or not, neck pain can be a considerable source of distress, so it's vital to be able to get information from the neck examination which allows you to safely reassure a patient when appropriate, or comment that neck exam found evidence that needs further investigation
#DRGill #neck #asmr
A modified radical mastectomy is a procedure in which the entire breast is removed, including the skin, areola, nipple, and most axillary lymph nodes; the pectoralis major muscle is spared. Historically, a modified radical mastectomy was the primary method of treatment of breast cancer. [1, 2] As the treatment of breast cancer evolved, breast conservation has become more widely used. [3, 4] However, mastectomy still remains a viable option for women with breast cancer. [5, 6]

AB_A_1016
This 3D animation depicts (1) the patient prepped for surgery, (2) removal of abdominal skin, (3) repair of diastasis of the rectus muscles, (4) suction-assisted lipectomy, and (5) closure of the incision.
To view more animations and exhibits, visit our medical library: https://www.trialexhibitsinc.c....om/library/multimedi
Contact us on your next case for consulting, trial graphics, animations, medical illustrations or presentation services. 800-591-1123 [a]www.trialex.com[/a]
This video is for reference only. The video may not be otherwise used, reproduced nor modified. For more information to purchase a copy or permission to use this animation on your next case, project, website or TV, contact us at [a]www.trialex.com[/a] or 800-591-1123.
Copyright @ Trial Exhibits, Inc.

Diabetes is a growing global health concern, as is obesity. Diabetes and obesity are intrinsically linked: obesity increases the risk of diabetes and also contributes to disease progression and cardiovascular disease. Although the benefits of weight loss in the prevention of diabetes and as a critical component of managing the condition are well established, weight reduction remains challenging for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to a host of metabolic and psychological factors. For many patients, lifestyle intervention is not enough to achieve weight loss, and alternative options, such as pharmacotherapy, need to be considered. However, many traditional glucose-lowering medications may lead to weight gain. This article focuses on the potential of currently available pharmacological strategies and on emerging approaches in development to support the glycemic and weight-loss goals of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Two pharmacotherapy types are considered: those developed primarily for blood glucose control that have a favorable effect on body weight and those developed primarily to induce weight loss that have a favorable effect on blood glucose control. Finally, the potential of combination therapies for the management of obese patients with type 2 diabetes is discussed.

Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed: Donepezil (Aricept) is approved to treat all stages of Alzheimer's. Rivastigmine (Exelon) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Galantamine (Razadyne) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer's. But drug and non-drug treatments may help with both cognitive and behavioral symptoms. Researchers are looking for new treatments to alter the course of the disease and improve the quality of life for people with dementia. ... Medications for Memory Loss.
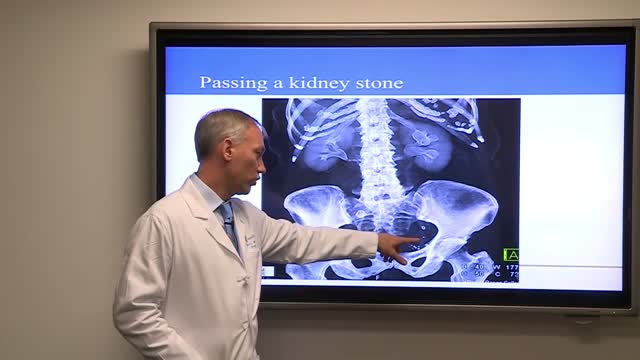
Treatment for kidney stones varies, depending on the type of stone and the cause. Small stones with minimal symptoms Most kidney stones won't require invasive treatment. You may be able to pass a small stone by: Drinking water. Drinking as much as 2 to 3 quarts (1.9 to 2.8 liters) a day may help flush out your urinary system. Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, drink enough fluid — mostly water — to produce clear or nearly clear urine. Pain relievers. Passing a small stone can cause some discomfort. To relieve mild pain, your doctor may recommend pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve). Medical therapy. Your doctor may give you a medication to help pass your kidney stone. This type of medication, known as an alpha blocker, relaxes the muscles in your ureter, helping you pass the kidney stone more quickly and with less pain. Large stones and those that cause symptoms Kidney stones that can't be treated with conservative measures — either because they're too large to pass on their own or because they cause bleeding, kidney damage or ongoing urinary tract infections — may require more extensive treatment. Procedures may include: Using sound waves to break up stones. For certain kidney stones — depending on size and location — your doctor may recommend a procedure called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). ESWL uses sound waves to create strong vibrations (shock waves) that break the stones into tiny pieces that can be passed in your urine. The procedure lasts about 45 to 60 minutes and can cause moderate pain, so you may be under sedation or light anesthesia to make you comfortable. ESWL can cause blood in the urine, bruising on the back or abdomen, bleeding around the kidney and other adjacent organs, and discomfort as the stone fragments pass through the urinary tract. Surgery to remove very large stones in the kidney. A procedure called percutaneous nephrolithotomy (nef-row-lih-THOT-uh-me) involves surgically removing a kidney stone using small telescopes and instruments inserted through a small incision in your back. You will receive general anesthesia during the surgery and be in the hospital for one to two days while you recover. Your doctor may recommend this surgery if ESWL was unsuccessful. Using a scope to remove stones. To remove a smaller stone in your ureter or kidney, your doctor may pass a thin lighted tube (ureteroscope) equipped with a camera through your urethra and bladder to your ureter. Once the stone is located, special tools can snare the stone or break it into pieces that will pass in your urine. Your doctor may then place a small tube (stent) in the ureter to relieve swelling and promote healing. You may need general or local anesthesia during this procedure. Parathyroid gland surgery. Some calcium phosphate stones are caused by overactive parathyroid glands, which are located on the four corners of your thyroid gland, just below your Adam's apple. When these glands produce too much parathyroid hormone (hyperparathyroidism), your calcium levels can become too high and kidney stones may form as a result. Hyperparathyroidism sometimes occurs when a small, benign tumor forms in one of your parathyroid glands or you develop another condition that leads these glands to produce more parathyroid hormone. Removing the growth from the gland stops the formation of kidney stones. Or your doctor may recommend treatment of the condition that's causing your parathyroid gland to overproduce the hormone.

Sebaceous cysts are common noncancerous cysts of the skin. Cysts are abnormalities in the body that may contain liquid or semiliquid material. Sebaceous cysts are mostly found on the face, neck, or torso. They grow slowly and are not life-threatening, but they may become uncomfortable if they go unchecked. Doctors usually diagnose a cyst with only a physical examination and medical history. In some cases, a cyst will be examined more thoroughly for signs of cancer