Top video's

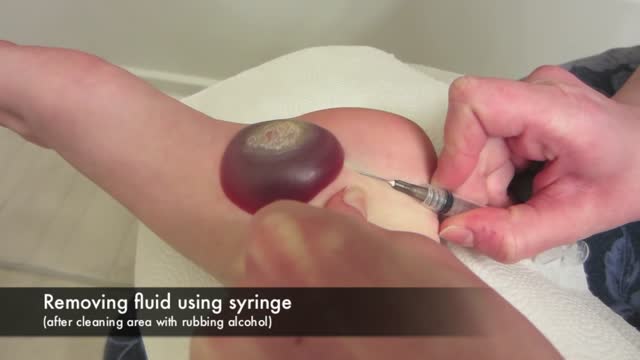
Sebaceous cysts are common noncancerous cysts of the skin. Cysts are abnormalities in the body that may contain liquid or semiliquid material. Sebaceous cysts are mostly found on the face, neck, or torso. They grow slowly and are not life-threatening, but they may become uncomfortable if they go unchecked. Doctors usually diagnose a cyst with only a physical examination and medical history. In some cases, a cyst will be examined more thoroughly for signs of cancer
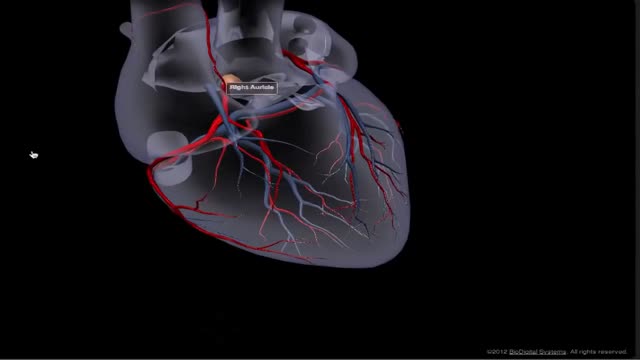
The heart receives its own supply of blood from the coronary arteries. Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet. These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.

A C-reactive protein (CRP) test is a blood test that measures the amount of a protein called C-reactive protein in your blood. C-reactive protein measures general levels of inflammation in your body. High levels of CRP are caused by infections and many long-term diseases.

Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can affect almost any part of your body, most often your joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood, or brain. Your two kidneys are part of your renal system, which also includes two ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. As the primary organs of the renal system, your kidneys are responsible for: Maintaining the correct amount and type of body fluids Removing waste products and toxic substances Regulating the hormones (chemical messengers) that help control blood pressure and blood volume
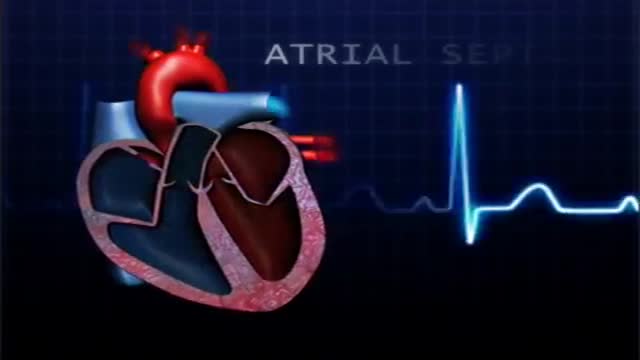
atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you're allergic to, such as a peanut or the venom from a bee sting. The flood of chemicals released by your immune system during anaphylaxis can cause you to go into shock; your blood pressure drops suddenly and your airways narrow, blocking normal breathing. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include a rapid, weak pulse, a skin rash, and nausea and vomiting. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include certain foods, some medications, insect venom and latex. Anaphylaxis requires an immediate trip to the emergency department and an injection of epinephrine. If anaphylaxis isn't treated right away, it can lead to unconsciousness or even death.

This is an introduction to ventilator settings like FIO2, PEEP, Flow rate,trigger,TV, and RR. I also discuss how these settings relate to CO2 and O2 control and to complications like oxygen toxicity and barotrauma with an emphasis on physiology.
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the uterus. The uterus is the hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ in women where fetal development occurs. Endometrial cancer begins in the layer of cells that form the lining (endometrium) of the uterus. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called uterine cancer. Other types of cancer can form in the uterus, including uterine sarcoma, but they are much less common than endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is often detected at an early stage because it frequently produces abnormal vaginal bleeding, which prompts women to see their doctors. If endometrial cancer is discovered early, removing the uterus surgically often cures endometrial cancer.

Radiosurgery: Radiosurgery devices, such as the CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System, offer patients a new option for the treatment of lung cancer. The CyberKnife® System is used to treat lung cancer patients who cannot tolerate surgery, have an inoperable tumor, or are seeking an alternative to surgery.
Cells may have slender extensions of the cell membrane to form cilia or the smaller extensions called microvilli. The microscopic microvilli effectively increase the surface area of the cell and are useful for absorption and secretion functions. A dramatic example is the human small intestine. The tissue has small fingerlike extensions called villi which are collections of cells, and those cells have many microvilli to even further increase the available surface area for the digestion process. According to Audesirk & Audesirk, this can give an effective surface area of about 250 square meters for absorption.
Frostbite is an injury caused by freezing of the skin and underlying tissues. First your skin becomes very cold and red, then numb, hard and pale. Frostbite is most common on the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin. Exposed skin in cold, windy weather is most vulnerable to frostbite. But frostbite can occur on skin covered by gloves or other clothing.
A modified radical mastectomy is a procedure in which the entire breast is removed, including the skin, areola, nipple, and most axillary lymph nodes; the pectoralis major muscle is spared. Historically, a modified radical mastectomy was the primary method of treatment of breast cancer. [1, 2] As the treatment of breast cancer evolved, breast conservation has become more widely used. [3, 4] However, mastectomy still remains a viable option for women with breast cancer. [5, 6]

Acromegaly is usually caused by a noncancerous tumor. Middle-aged adults are most commonly affected. Symptoms include enlargement of the face, hands, and feet. Prompt treatment is needed to avoid serious illness. Drugs can reduce the effects of growth hormone. If needed, surgery and radiation may be used to remove tumor cells.
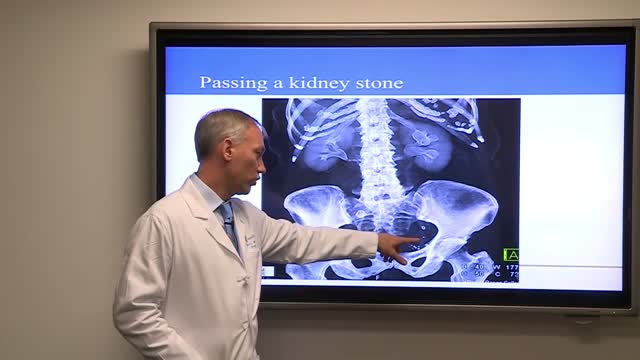
Treatment for kidney stones varies, depending on the type of stone and the cause. Small stones with minimal symptoms Most kidney stones won't require invasive treatment. You may be able to pass a small stone by: Drinking water. Drinking as much as 2 to 3 quarts (1.9 to 2.8 liters) a day may help flush out your urinary system. Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, drink enough fluid — mostly water — to produce clear or nearly clear urine. Pain relievers. Passing a small stone can cause some discomfort. To relieve mild pain, your doctor may recommend pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve). Medical therapy. Your doctor may give you a medication to help pass your kidney stone. This type of medication, known as an alpha blocker, relaxes the muscles in your ureter, helping you pass the kidney stone more quickly and with less pain. Large stones and those that cause symptoms Kidney stones that can't be treated with conservative measures — either because they're too large to pass on their own or because they cause bleeding, kidney damage or ongoing urinary tract infections — may require more extensive treatment. Procedures may include: Using sound waves to break up stones. For certain kidney stones — depending on size and location — your doctor may recommend a procedure called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). ESWL uses sound waves to create strong vibrations (shock waves) that break the stones into tiny pieces that can be passed in your urine. The procedure lasts about 45 to 60 minutes and can cause moderate pain, so you may be under sedation or light anesthesia to make you comfortable. ESWL can cause blood in the urine, bruising on the back or abdomen, bleeding around the kidney and other adjacent organs, and discomfort as the stone fragments pass through the urinary tract. Surgery to remove very large stones in the kidney. A procedure called percutaneous nephrolithotomy (nef-row-lih-THOT-uh-me) involves surgically removing a kidney stone using small telescopes and instruments inserted through a small incision in your back. You will receive general anesthesia during the surgery and be in the hospital for one to two days while you recover. Your doctor may recommend this surgery if ESWL was unsuccessful. Using a scope to remove stones. To remove a smaller stone in your ureter or kidney, your doctor may pass a thin lighted tube (ureteroscope) equipped with a camera through your urethra and bladder to your ureter. Once the stone is located, special tools can snare the stone or break it into pieces that will pass in your urine. Your doctor may then place a small tube (stent) in the ureter to relieve swelling and promote healing. You may need general or local anesthesia during this procedure. Parathyroid gland surgery. Some calcium phosphate stones are caused by overactive parathyroid glands, which are located on the four corners of your thyroid gland, just below your Adam's apple. When these glands produce too much parathyroid hormone (hyperparathyroidism), your calcium levels can become too high and kidney stones may form as a result. Hyperparathyroidism sometimes occurs when a small, benign tumor forms in one of your parathyroid glands or you develop another condition that leads these glands to produce more parathyroid hormone. Removing the growth from the gland stops the formation of kidney stones. Or your doctor may recommend treatment of the condition that's causing your parathyroid gland to overproduce the hormone.
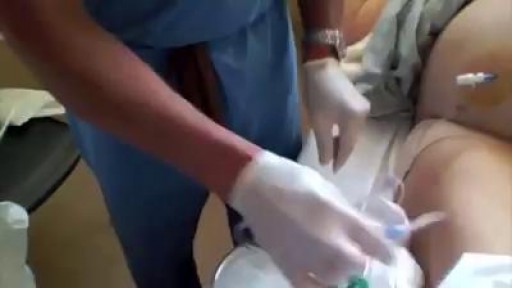
Paracentesis is a procedure to take out fluid that has collected in the belly (peritoneal fluid). This fluid buildup is called ascites camera.gif. Ascites may be caused by infection, inflammation, an injury, or other conditions, such as cirrhosis or cancer. The fluid is taken out using a long, thin needle put through the belly. The fluid is sent to a lab and studied to find the cause of the fluid buildup. Paracentesis also may be done to take the fluid out to relieve belly pressure or pain in people with cancer or cirrhosis.