Top videos
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In humans, this event occurs when the follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm

A VCUG (Voiding Cystourethrogram) is a test that looks at how well your child's kidneys, ureters and bladder are working. Your child's kidneys make urine. The urine flows from the kidneys through thin tubes (called ureters) into your child's bladder.

Microcalcifications in the breast can be the first sign of cancer. They are, as the name says, very small and clustered. A precise biopsy without pain under stereotactic guidance is the standard procedure. What makes this Spirotome different from the vacuum assisted biopsies is that only a few biopsies are needed and that the approach of the needle towards the microcalcifications is direct and frontal. There is no damage to the surrounding tissues making this procedure rather painfree and with minimal bleeding.
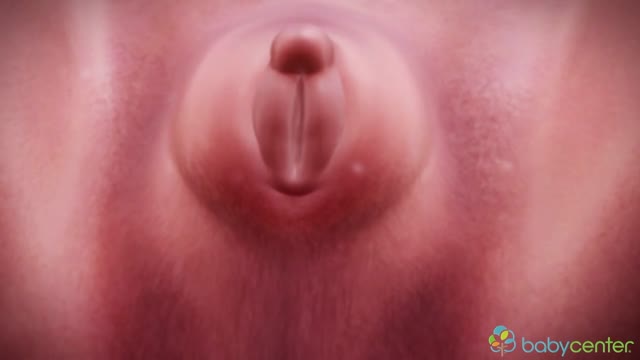
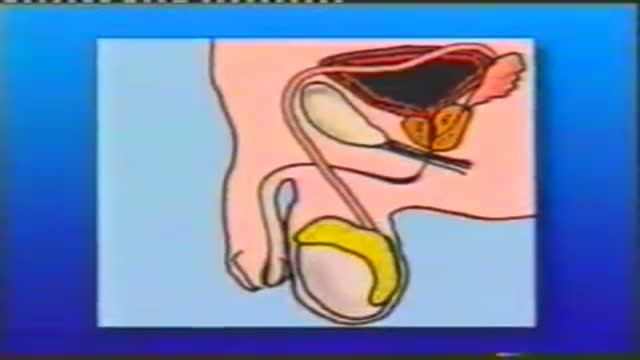
Your baby's sex is set at conception. At around 7 weeks, your baby's internal sex organs – such as ovaries and testes – begin to form in the abdomen. Male and female sex organs and genitalia look the same at this stage because they're derived from the same structures. At around 9 weeks, boys and girls begin to develop differently. In girls, a tiny bud emerges between the tissue of the legs. This bud will become the clitoris. The membrane that forms a groove below the bud separates to become the labia minora and the vaginal opening. By 22 weeks, the ovaries are completely formed and move from the abdomen to the pelvis. They already contain a lifetime supply of 6 million eggs. In boys, the bud develops into the penis and starts to elongate at around 12 weeks. The outer membrane grows into the scrotal sac that will later house the testicles. By 22 weeks, the testes have formed in the abdomen. They already contain immature sperm. Soon they'll begin their descent to the scrotum, but it's a long journey. They'll reach their destination late in pregnancy, or for some boys, after birth. If you're eager to find out whether you're having a girl or a boy, you'll have to wait until you're at least 17 weeks pregnant. That's when the genitals have developed enough to be seen on an ultrasound.

Piles Treatment
contact : drjamil79@yahoo.com
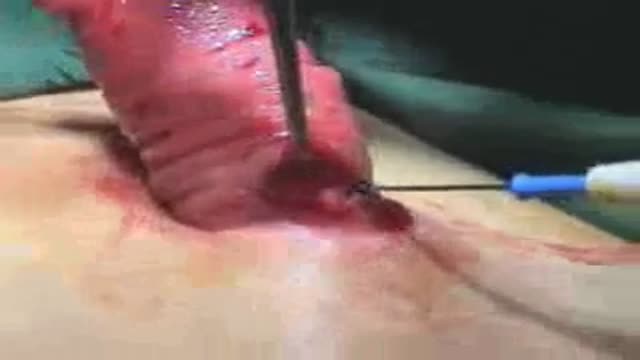
Rubber band application around the pile is a pain free procedure.Patient is put to sleep for a few minutes and can go home after a few hours.In this procedure anal fissure was also treated with the transparent anoscope that comes with the PPH gun set.
Piles Treatment piles: HAL Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation new fast and painless treatment of haemorrhoids dr jamil ahmad hashmi -PainlessRubber band application around the pile is pain free procedure.Patient put to sleep for few minutes can go home after hours.In this procedure anal fissure was also treated with transparent anoscope that comes PPH gun set. Category: health

The Combitube is a twin lumen device designed for use in emergency situations and difficult airways. It can be inserted without the need for visualization into the oropharynx, and usually enters the esophagus. It has a low volume inflatable distal cuff and a much larger proximal cuff designed to occlude the oro- and nasopharynx.
If the tube has entered the trachea, ventilation is achieved through the distal lumen as with a standard ETT. More commonly the device enters the esophagus and ventilation is achieved through multiple proximal apertures situated above the distal cuff. In the latter case the proximal and distal cuffs have to be inflated to prevent air from escaping through the esophagus or back out of the oro- and nasopharynx.

Pharyngitis is caused by swelling in the back of the throat (pharynx) between the tonsils and the voice box (larynx). Most sore throats are caused by colds, the flu, coxsackie virus or mono (mononucleosis). Bacteria that can cause pharyngitis in some cases: Strep throat is caused by group A streptococcus.

Surgery to treat men with prostate cancer is often followed by months of difficulty controlling urine flow, a condition known as urinary incontinence. But new research suggests that this problem may go away more quickly if the men perform certain exercises to strengthen their pelvic floor muscles.
Researchers from the Kaiser Permanente Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, found that men who were taught how to perform pelvic floor exercises before and after surgery were more likely to have regained continence three months later.
Men Doing Pelvic Exercises Recover Earlier
In the current study, the researchers randomly assigned 38 men scheduled for radical prostatectomy to either a treatment group or a control group. The men in the treatment group were referred to a physical therapist. They were instructed how to do Pelvic Floor Exercises both before and after surgery, using biofeedback to ensure they were using the proper muscles. The control group did not receive any formal instruction. All of the men completed questionnaires regarding bladder function at regular intervals over the next year.
Overall, 82% of the patients had regained continence (defined as not needing to use any absorbent pads) by the end of the year, including about equal numbers in both groups. But on average the men who had been educated about Pelvic exercises regained continence about one month earlier than those in the control group (at 12 weeks vs. 16 weeks).
Most of the men who did not regain continence within a year were still using at least three absorbent pads a day, indicating continued severe incontinence. The study authors explained that these men probably had extensive damage to the bladder sphincter or severe dysfunction of the bladder after surgery, and the exercises alone were unable to compensate for this.
But the exercises seemed to be effective. Pelvic floor exercise and education initiated prior to surgery is an effective noninvasive intervention useful for improving early return of urinary continence, the authors concluded. It would certainly have a positive impact on our patients undergoing radical prostatectomy in an effort to improve quality of life after major urological surgery.
The results of the study were published in the Journal of Urology (Vol. 170, No. 1: 130-133)