سرفہرست ویڈیوز
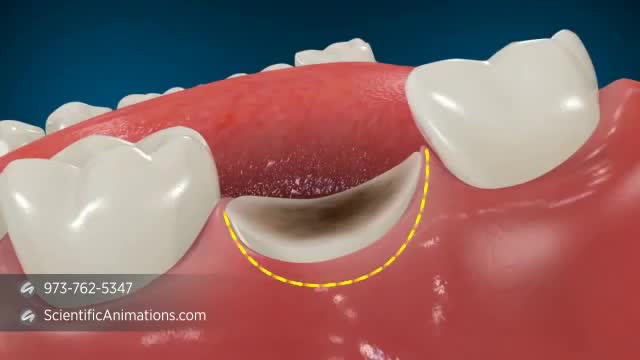
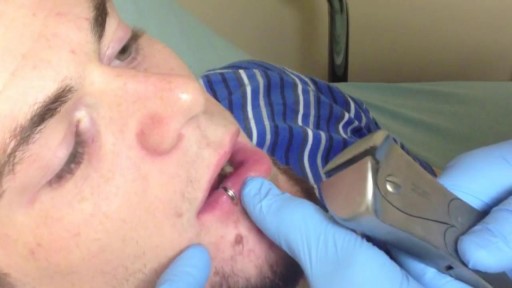
A palatal view of a maxillary premolar during a crown lengthening procedure. Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically.
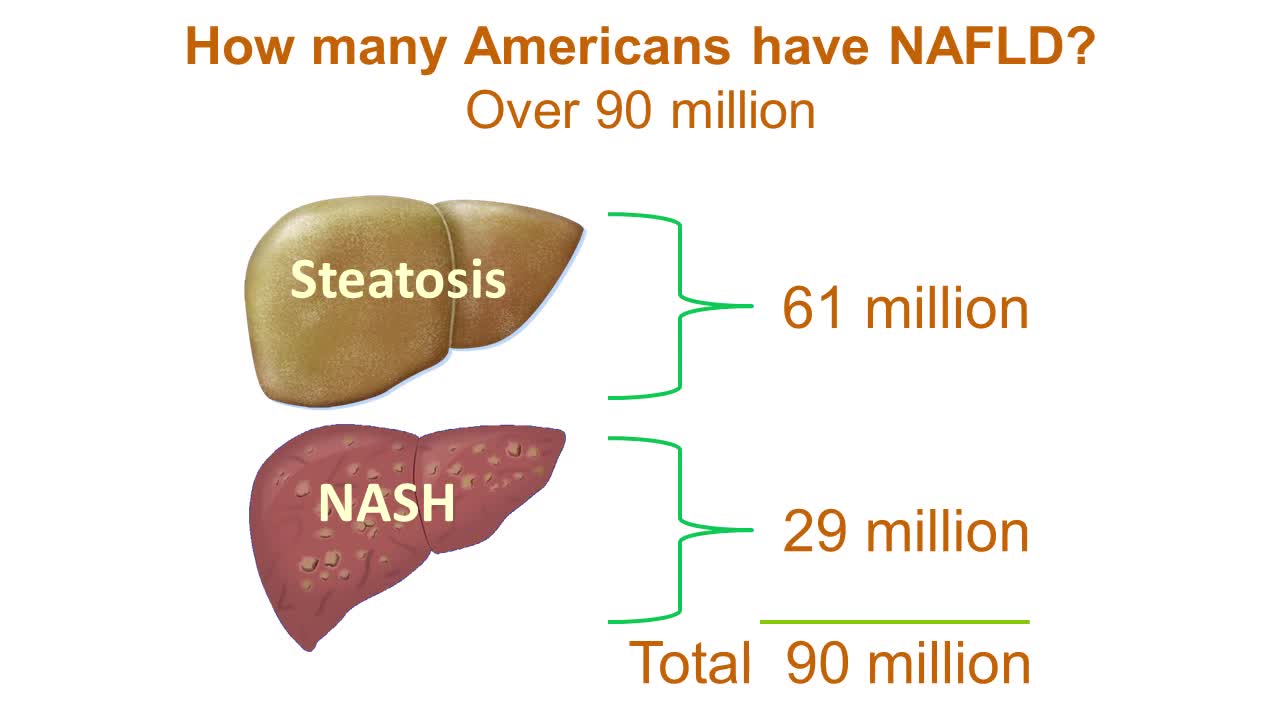
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is an umbrella term for a range of liver conditions affecting people who drink little to no alcohol. As the name implies, the main characteristic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is too much fat stored in liver cells. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a potentially serious form of the disease, is marked by liver inflammation, which may progress to scarring and irreversible damage. This damage is similar to the damage caused by heavy alcohol use. At its most severe, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is increasingly common around the world, especially in Western nations. In the United States, it is the most common form of chronic liver disease, affecting an estimated 80 to 100 million people. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease occurs in every age group but especially in people in their 40s and 50s who are at high risk of heart disease because of such risk factors as obesity and type 2 diabetes. The condition is also closely linked to metabolic syndrome, which is a cluster of abnormalities including increased abdominal fat, poor ability to use the hormone insulin, high blood pressure and high blood levels of triglycerides, a type of fat. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease care at Mayo Clinic Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic Symptoms & causes Aug. 23, 2016 Print Share on: Facebook Twitter References Related Magnetic resonance elastography Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Overview Symptoms & causes Diagnosis & treatment Diagnosis Treatment Departments & specialties Expertise & rankings Locations, travel & lodging Clinical trials Research Costs & insurance Preparing for your appointment Self-management More about In-Depth Multimedia Resources News from Mayo Clinic Advertisement
Breast Implant Surgery - exchanging the breast implants. In this video you can see a Plastic Surgeon performing an exchange of breast implant surgery.As breast implants become more popular more breast implant exchange procedures are being performed. This video shows breast implant removal followed by insertion of a larger breast implant.

Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a rare systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the classic triad of persistent high spiking fevers, joint pain, and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash. The disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion.

Trisomy 18, also called Edwards syndrome, is a chromosomal condition associated with abnormalities in many parts of the body. Individuals with trisomy 18 often have slow growth before birth (intrauterine growth retardation) and a low birth weight. Affected individuals may have heart defects and abnormalities of other organs that develop before birth. Other features of trisomy 18 include a small, abnormally shaped head; a small jaw and mouth; and clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Due to the presence of several life-threatening medical problems, many individuals with trisomy 18 die before birth or within their first month. Five to 10 percent of children with this condition live past their first year, and these children often have severe intellectual disability.

Rheum is made up of mucus, skin cells, oils and dust. The rheum that comes from the eyes and forms eye boogers is called gound, which you may know as eye sand, eye gunk, sleep dust, sleep sand, sleep in your eyes, or eye shnooters. When you're awake, gound doesn't cause any problems.

http://plantar-fasciitis-solution.info-pro.co Foot Arch Pain, Sharp Pain In Heel, Pain In Foot, Achilles Heel Pain, Chronic Plantar Fasciitis What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a common injury that affects the heel of a person’s foot. The arches of the feet are supported by a tough and fibrous tissue known as the plantar fascia and when this tissue is used repetitively, injury may occur. It can be easy to overuse the feet, especially when participating in activities such as sporting events. Hence, plantar fasciitis is more commonly found in athletes or others who are constantly using their feet for long durations. With excessive use, the planar fascia will eventually give in and this condition may also be progressive. Runners and those who are known to participate in similar activities need to ensure that they do not damage this important band of tissue. In addition, body weight could be a factor that leads to the occurrence of plantar fasciitis. If a person is overweight, the feet and subsequently the plantar fascia tissue could become overwhelmed. Improper footwear could also cause a strain on the plantar fascia tissue and this could gradually become severe over time. plantar fasciitis relief in 7 days click here. http://plantar-fasciitis-solution.info-pro.co
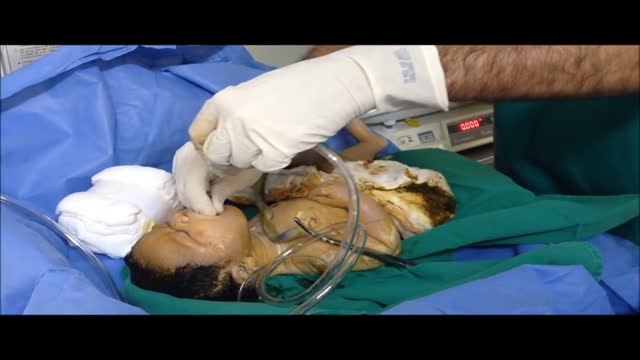
The following guidelines are an interpretation of the evidence presented in the 2010 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations1). They apply primarily to newly born infants undergoing transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life, but the recommendations are also applicable to neonates who have completed perinatal transition and require resuscitation during the first few weeks to months following birth. Practitioners who resuscitate infants at birth or at any time during the initial hospital admission should consider following these guidelines. For the purposes of these guidelines, the terms newborn and neonate are intended to apply to any infant during the initial hospitalization. The term newly born is intended to apply specifically to an infant at the time of birth.

The most common symptoms of pneumoconiosis are cough and shortness of breath. The risk is generally higher when people have been exposed to mineral dusts in high concentrations and/or for long periods of time. Inadequate or inconsistent use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirators (specially fitted protective masks) is another risk factor since preventing dusts from being inhaled will also prevent pneumoconiosis. Pneumoconiosis does not generally occur from environmental (non-workplace) exposures since dust levels in the environment are much lower.
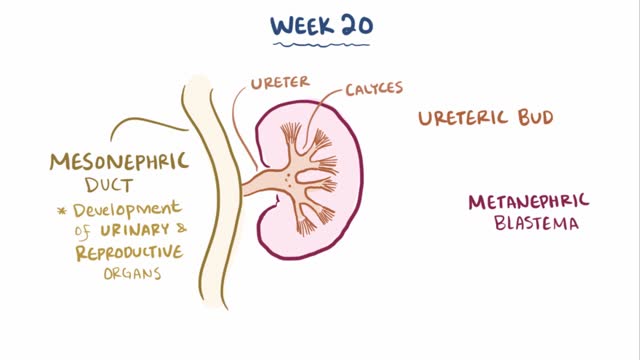
Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants.

Pain in the affected bone is the most common complaint of patients with bone cancer. At first, the pain is not constant. It may be worse at night or when the bone is used (for example, leg pain when walking). As the cancer grows, the pain will be there all the time. The pain increases with activity and the person might limp if a leg is involved.
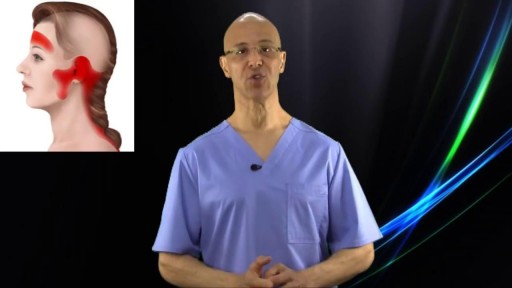
The majority of all headaches are tension related headaches. The blockage of blood circulation along with contraction/shortening of muscles is what causes this condition. This simple technique can take away most tension related headaches in seconds.

A small spontaneous pneumothorax may resolve without treatment; a pneumothorax arising as a result of lung disease or injury requires immediate treatment. Treatment may include insertion of a chest tube or aspiration of the free air in the chest cavity.Feb 19, 2016

Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in rare cases) eye movement, acquired in infancy or later in life, that may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes"

The goal of COPD management is to improve a patient’s functional status and quality of life by preserving optimal lung function, improving symptoms, and preventing the recurrence of exacerbations. Currently, no treatments aside from lung transplantation have been shown to significantly improve lung function or decrease mortality; however, oxygen therapy (when appropriate) and smoking cessation may reduce mortality. Once the diagnosis of COPD is established, it is important to educate the patient about the disease and to encourage his or her active participation in therapy.

Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a rare autosomal dominant metabolic disorder affecting the production of heme, the oxygen-binding prosthetic group of hemoglobin. It is characterized by a deficiency of the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase.