Top videos
A craniotomy is the surgical removal of part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain. Specialized tools are used to remove the section of bone called the bone flap. The bone flap is temporarily removed, then replaced after the brain surgery has been done.
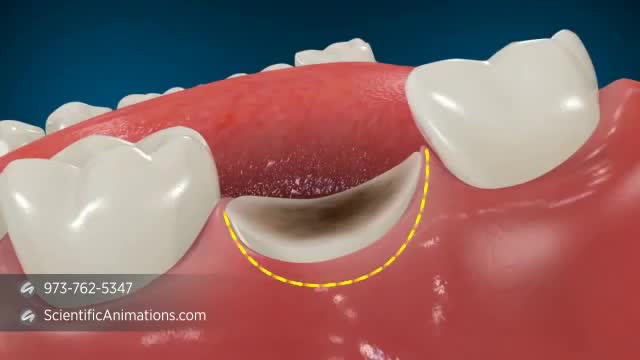
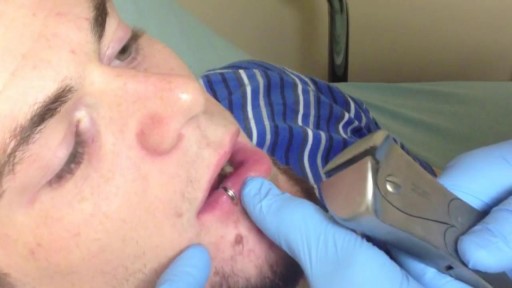
A palatal view of a maxillary premolar during a crown lengthening procedure. Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically.
Breast Implant Surgery - exchanging the breast implants. In this video you can see a Plastic Surgeon performing an exchange of breast implant surgery.As breast implants become more popular more breast implant exchange procedures are being performed. This video shows breast implant removal followed by insertion of a larger breast implant.

Behcet's (beh-CHETS) disease, also called Behcet's syndrome, is a rare disorder that causes blood vessel inflammation throughout your body. The disease can lead to numerous signs and symptoms that may seem unrelated at first. They may include mouth sores, eye inflammation, skin rashes and lesions, and genital sores. The effects of Behcet's disease vary from person to person and may clear up on their own. Treatment involves medications to reduce the signs and symptoms of Behcet's disease and to prevent serious complications, such as blindness.

Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a rare systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the classic triad of persistent high spiking fevers, joint pain, and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash. The disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion.

Trisomy 18, also called Edwards syndrome, is a chromosomal condition associated with abnormalities in many parts of the body. Individuals with trisomy 18 often have slow growth before birth (intrauterine growth retardation) and a low birth weight. Affected individuals may have heart defects and abnormalities of other organs that develop before birth. Other features of trisomy 18 include a small, abnormally shaped head; a small jaw and mouth; and clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Due to the presence of several life-threatening medical problems, many individuals with trisomy 18 die before birth or within their first month. Five to 10 percent of children with this condition live past their first year, and these children often have severe intellectual disability.

The most common symptoms of pneumoconiosis are cough and shortness of breath. The risk is generally higher when people have been exposed to mineral dusts in high concentrations and/or for long periods of time. Inadequate or inconsistent use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirators (specially fitted protective masks) is another risk factor since preventing dusts from being inhaled will also prevent pneumoconiosis. Pneumoconiosis does not generally occur from environmental (non-workplace) exposures since dust levels in the environment are much lower.

Rheum is made up of mucus, skin cells, oils and dust. The rheum that comes from the eyes and forms eye boogers is called gound, which you may know as eye sand, eye gunk, sleep dust, sleep sand, sleep in your eyes, or eye shnooters. When you're awake, gound doesn't cause any problems.

A small spontaneous pneumothorax may resolve without treatment; a pneumothorax arising as a result of lung disease or injury requires immediate treatment. Treatment may include insertion of a chest tube or aspiration of the free air in the chest cavity.Feb 19, 2016
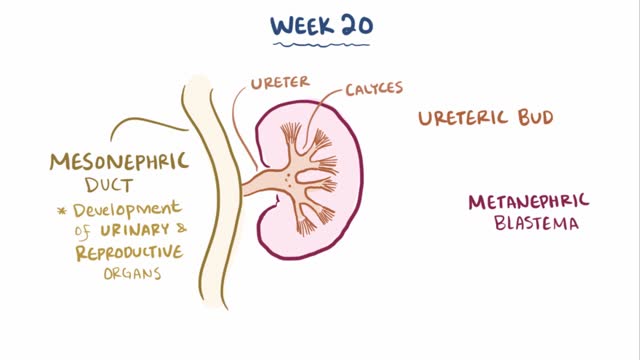
Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants.

http://plantar-fasciitis-solution.info-pro.co Foot Arch Pain, Sharp Pain In Heel, Pain In Foot, Achilles Heel Pain, Chronic Plantar Fasciitis What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a common injury that affects the heel of a person’s foot. The arches of the feet are supported by a tough and fibrous tissue known as the plantar fascia and when this tissue is used repetitively, injury may occur. It can be easy to overuse the feet, especially when participating in activities such as sporting events. Hence, plantar fasciitis is more commonly found in athletes or others who are constantly using their feet for long durations. With excessive use, the planar fascia will eventually give in and this condition may also be progressive. Runners and those who are known to participate in similar activities need to ensure that they do not damage this important band of tissue. In addition, body weight could be a factor that leads to the occurrence of plantar fasciitis. If a person is overweight, the feet and subsequently the plantar fascia tissue could become overwhelmed. Improper footwear could also cause a strain on the plantar fascia tissue and this could gradually become severe over time. plantar fasciitis relief in 7 days click here. http://plantar-fasciitis-solution.info-pro.co
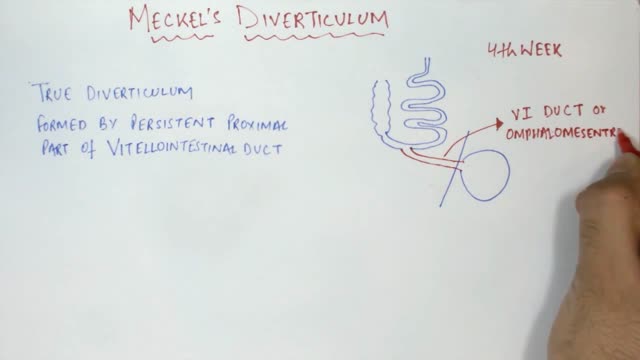
The differential diagnosis for this child's painless hematochezia includes Meckel's diverticulum as well as vascular malformations. Meckel's diverticulum results from a failure of the vitelline duct to obliterate during the first 8 weeks of gestation, leaving behind a blind pouch often containing ectopic gastric tissue. Meckel's diverticulum classically affects children age ~:2 but can also occur in older children or even adults. Young children are more likely to experience painless bleeding due to mucosal irritation from gastric acid; adolescents and adults are more likely to have signs of obstruction. A technetium-99 nuclear scan will identify the diverticulum, which is usually located in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen within 2 feet of the ileocecal valve. Technetium-99 concentrates in the parietal cells of the diverticulum and stomach. The scan is also known as "Meckel's scan" due to its high specificity. A symptomatic Meckel's diverticulum is generally treated with surgical resection.

Pain in the affected bone is the most common complaint of patients with bone cancer. At first, the pain is not constant. It may be worse at night or when the bone is used (for example, leg pain when walking). As the cancer grows, the pain will be there all the time. The pain increases with activity and the person might limp if a leg is involved.

Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in rare cases) eye movement, acquired in infancy or later in life, that may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes"
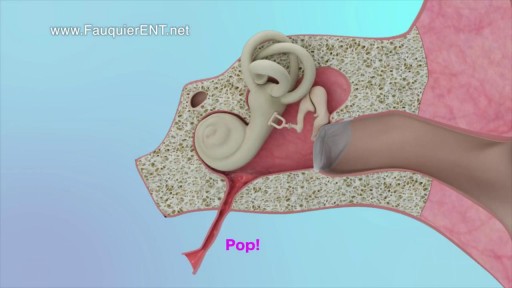
This video demonstrates why ears become clogged and why ear popping helps. The video also explains why ear popping may become difficult resulting in a persistent clogged or muffled ear especially after an ear infection.

How do you assess cerebellar function? Ask them to do this as fast as possible while you slowly move your finger. Repeat the test with the other hand. Perform the heel-to-shin test. Have the patient lying down for this and get them to run the heel of one foot down the shin of the other leg, and then to bring the heel back up to the knee and start again.