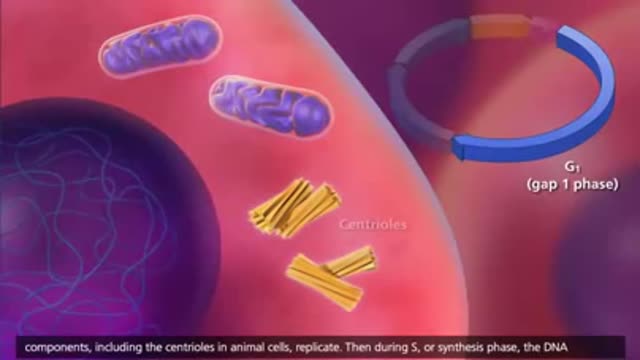
Top videos
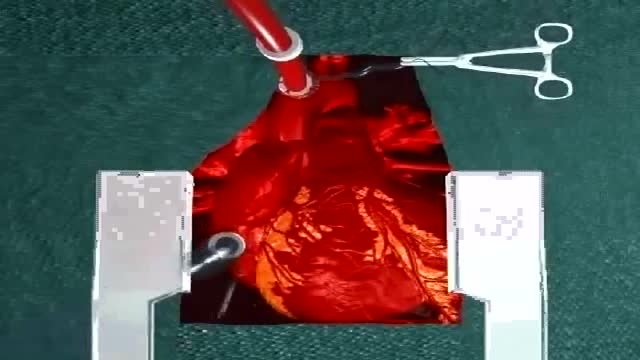
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a type of surgery that improves blood flow to the heart. Surgeons use CABG to treat people who have severe coronary heart disease (CHD). CHD is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque (plak) builds up inside the coronary arteries.

Here we’ll explain the symptoms of pancreatitis, how alcohol causes the condition and the other health problems it can lead to. You probably don’t pay much attention to your pancreas. But that small, tadpole-shaped organ behind your stomach and below your ribcage is pretty important. It produces two essential substances: digestive juices which your intestines use to break down food, and hormones that are involved in digestion, such as insulin, which regulates your blood sugar levels. Pancreatitis is when your pancreas becomes inflamed and its cells are damaged. Heavy drinking can cause pancreatitis. But if you drink within the government’s low risk unit guidelines, you should avoid upsetting this important organ.

Diabetes is a growing global health concern, as is obesity. Diabetes and obesity are intrinsically linked: obesity increases the risk of diabetes and also contributes to disease progression and cardiovascular disease. Although the benefits of weight loss in the prevention of diabetes and as a critical component of managing the condition are well established, weight reduction remains challenging for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to a host of metabolic and psychological factors. For many patients, lifestyle intervention is not enough to achieve weight loss, and alternative options, such as pharmacotherapy, need to be considered. However, many traditional glucose-lowering medications may lead to weight gain. This article focuses on the potential of currently available pharmacological strategies and on emerging approaches in development to support the glycemic and weight-loss goals of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Two pharmacotherapy types are considered: those developed primarily for blood glucose control that have a favorable effect on body weight and those developed primarily to induce weight loss that have a favorable effect on blood glucose control. Finally, the potential of combination therapies for the management of obese patients with type 2 diabetes is discussed.

Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed: Donepezil (Aricept) is approved to treat all stages of Alzheimer's. Rivastigmine (Exelon) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Galantamine (Razadyne) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer's. But drug and non-drug treatments may help with both cognitive and behavioral symptoms. Researchers are looking for new treatments to alter the course of the disease and improve the quality of life for people with dementia. ... Medications for Memory Loss.
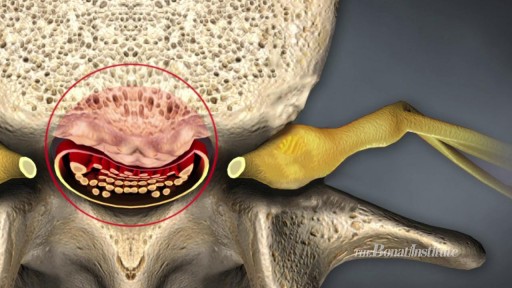
Watch Spinal Stenosis Videos Spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal cord in the neck (cervical spine) or the spinal nerve roots in the lower back (lumbar spine) are compressed. Symptoms of lumbar stenosis often include leg pain (sciatica) and leg tingling, weakness, or numbness. Arm pain is a typical symptom of cervical spinal stenosis. For cervical spinal stenosis with myelopathy, difficulty with coordination often occurs. Stenosis treatment may include non-surgical options (exercise, anti-inflammatory medication, epidural injections, and activity modification) or back surgery.
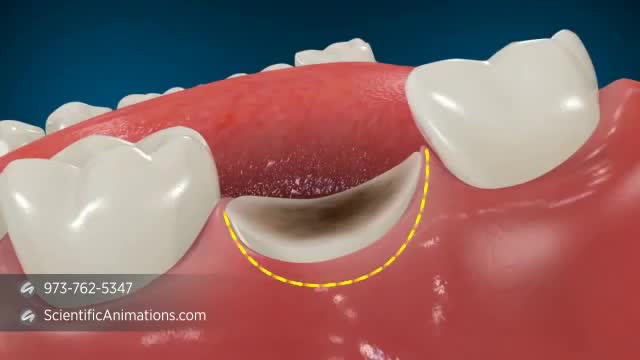
A palatal view of a maxillary premolar during a crown lengthening procedure. Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically.
In vitro fertilization, or IVF, is the most common and effective type of assisted reproductive technology to help women become pregnant. It involves fertilizing an egg outside the body, in a laboratory dish, and then implanting it in a woman's uterus. By 2016, some 6.5 million babies had been born using in-vitro fertilization (IVF). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 1.6 percent of babies born in the United States each year are conceived through assisted reproductive technology (ART).

Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a rare systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the classic triad of persistent high spiking fevers, joint pain, and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash. The disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion.

Trisomy 18, also called Edwards syndrome, is a chromosomal condition associated with abnormalities in many parts of the body. Individuals with trisomy 18 often have slow growth before birth (intrauterine growth retardation) and a low birth weight. Affected individuals may have heart defects and abnormalities of other organs that develop before birth. Other features of trisomy 18 include a small, abnormally shaped head; a small jaw and mouth; and clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Due to the presence of several life-threatening medical problems, many individuals with trisomy 18 die before birth or within their first month. Five to 10 percent of children with this condition live past their first year, and these children often have severe intellectual disability.

Rheum is made up of mucus, skin cells, oils and dust. The rheum that comes from the eyes and forms eye boogers is called gound, which you may know as eye sand, eye gunk, sleep dust, sleep sand, sleep in your eyes, or eye shnooters. When you're awake, gound doesn't cause any problems.
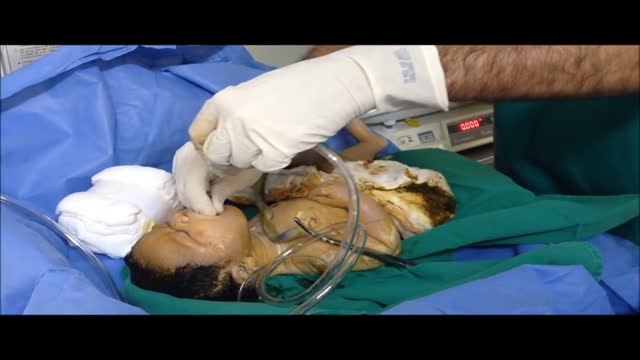
The following guidelines are an interpretation of the evidence presented in the 2010 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations1). They apply primarily to newly born infants undergoing transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life, but the recommendations are also applicable to neonates who have completed perinatal transition and require resuscitation during the first few weeks to months following birth. Practitioners who resuscitate infants at birth or at any time during the initial hospital admission should consider following these guidelines. For the purposes of these guidelines, the terms newborn and neonate are intended to apply to any infant during the initial hospitalization. The term newly born is intended to apply specifically to an infant at the time of birth.
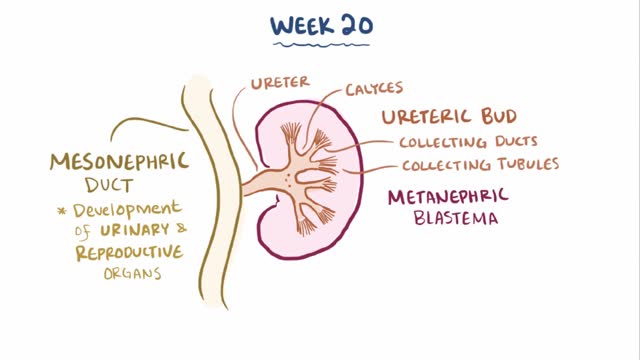
Renal agenesis is a condition in which a newborn is missing one or both kidneys. Unilateral renal agenesis (URA) is the absence of one kidney. Bilateral renal agenesis (BRA) is the absence of both kidneys. Both types of renal agenesis occur in fewer than 1 percent of births annually, according to the March of Dimes. Fewer than 1 in every 1,000 newborns has URA. BRA is much rarer, occurring in about 1 in every 3,000 births.
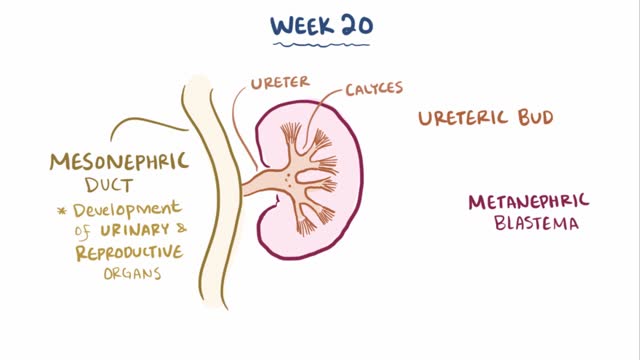
Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants.

Modern treatment of seizures started in 1850 with the introduction of bromides, which was based on the theory that epilepsy was caused by an excessive sex drive. In 1910, phenobarbital (PHB), which then was used to induce sleep, was found to have antiseizure activity and became the drug of choice for many years. A number of medications similar to PHB were developed, including primidone.

Pain in the affected bone is the most common complaint of patients with bone cancer. At first, the pain is not constant. It may be worse at night or when the bone is used (for example, leg pain when walking). As the cancer grows, the pain will be there all the time. The pain increases with activity and the person might limp if a leg is involved.