Top videos
One of a series of films we produced to help patients, their families and carers learn more about some of the most common tests and procedures used to diagnose and treat blood diseases. Patients who have previously undergone these tests helped us to design the videos. Each film clearly explains what the procedure involves and addresses common issues and concerns including: Why your doctor recommended this procedure What you need to do to prepare What you can expect during the procedure What you need to do afterwards Not every patient will be referred for all of these tests and practice may differ slightly depending on where you are treated.

Pharyngitis is caused by swelling in the back of the throat (pharynx) between the tonsils and the voice box (larynx). Most sore throats are caused by colds, the flu, coxsackie virus or mono (mononucleosis). Bacteria that can cause pharyngitis in some cases: Strep throat is caused by group A streptococcus.

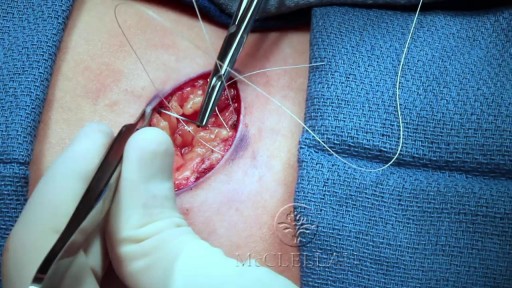
In this video, we show a sports hernia self treatment we give many of our clients. It is not the only part of treatment. Grabbing the skin around the region of the groin strain can reduce pain and stiffness with turning and twisting. Sports hernias are often misdiagnosed with hip labrum tears, hip impingement, adductor tendonitis and abdominal strains.
Want more information? We have a more detailed free webinar on our page here. https://bit.ly/37thtNF
Want some treatment or suggestions of exercises or stretches? Contact us! We have in-person and virtual sessions.
Costa Mesa CA 715-502-4243 www.p2sportscare.com
Sports Hernia Diagnosis
What Is A Sports Hernia?
A sports hernia is tearing of the transversalis fascia of the lower abdominal or groin region. A common misconception is that a sports hernia is the same as a traditional hernia. The mechanism of injury is rapid twisting and change of direction within sports, such as football, basketball, soccer and hockey.
The term “sports hernia” is becoming mainstream with more professional athletes being diagnosed. The following are just to name a few:
Torii Hunter
Tom Brady
Ryan Getzlaf
Julio Jones
Jeremy Shockey
If you follow any of these professional athletes, they all seem to have the same thing in common: Lingering groin pain. If you play fantasy sports, this is a major headache since it seems so minor, but it can land a player on Injury Reserve on a moments notice. In real life, it is a very frustrating condition to say the least. It is hard to pin point, goes away with rest and comes back after activity, but is hardly painful enough to make you want to stop. It lingers and is always on your mind. And if you’re looking for my step-by-step sports hernia rehab video course here it is.
One the best definitions of Sport hernias is the following by Harmon:
The phenomena of chronic activity–related groin pain that it is unresponsive to conservative therapy and significantly improves with surgical repair.”
This is truly how sports hernias behave in a clinical setting. It is not uncommon for a sports hernia to be unrecognized for months and even years. Unlike your typical sports injury, most sports medicine offices have only seen a handful of cases. It’s just not on most doctors’ radar. The purpose of this article is not only to bring awareness about sports hernias, but also to educate.
Will you find quick fixes in this article for sports hernia rehab?
Nope. There is no quick fix for this condition, and if someone is trying to sell you one, they are blowing smoke up your you-know-what.
Is there a way to decrease the pain related to sports hernias?
Yes. Proper rehab and avoidance of activity for a certain period of time will assist greatly, but this will not always stop it from coming back. Pain is the first thing to go and last thing to come. Do not be fooled when you become pain-free by resting it. Pain is only one measure of improvement in your rehab. Strength, change of direction, balance and power (just to name a few) are important, since you obviously desire to play your sport again. If you wanted to be a couch potato, you would be feeling better in no time. Watching Sports Center doesn’t require any movement.
Why is this article so long?
There is a lot of information on sports hernias available to you on the web. However, much of the information is spread out all over the internet and hard for athletes to digest due to complicated terminology. This article lays out the foundational terminology you will need to understand what options you have with your injury. We will go over anatomy, biomechanics, rehab, surgery, and even the fun facts. The information I am using is from the last ten years of medical research, up until 2016. We will be making updates overtime when something new is found as well. So link to this page and share with friends. This is the best source for information on sports hernias you will find.
Common Names (or Aliases?) for Sports Hernias
Sportsman’s Hernia
Athletic Pubalgia
Gilmore’s Groin
How Do You Know If You Have A Sports Hernia?
Typical athlete characteristics:
Male, age mid-20s
Common sports: soccer, hockey, tennis, football, field hockey
Motions involved: cutting, pivoting, kicking and sharp turns
Gradual onset
How A Sports Hernia Develops
Chronic groin pain typically happens over time, which is why with sports hernias, we do not hear many stories of feeling a “pop” or a specific moment of injury. It is the result of “overuse” mechanics stemming from a combination of inadequate strength and endurance, lack of dynamic control, movement pattern abnormalities, and discoordination of motion in the groin area.
#sportsherniadiagnosisselftreatment #sportshernia #california
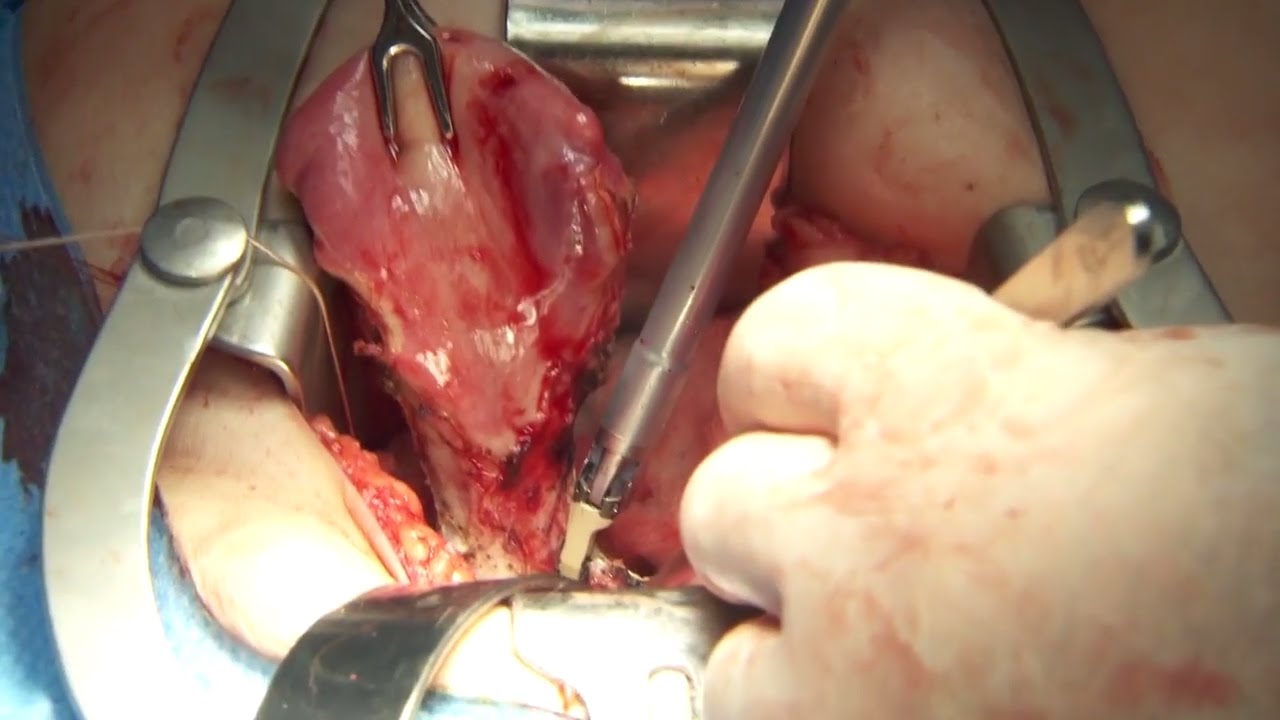
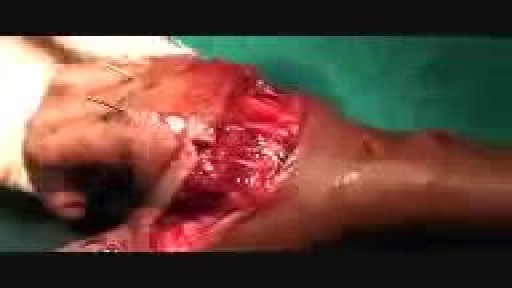
Olympus has extended the value of its award-winning combined surgical energy device, THUNDERBEAT, to open surgical procedures. Watch Dr. Francois Blaudeau master use of THUNDERBEAT Open Extended Jaw (OEJ) in a total abdominal hysterectomy.
http://medical.olympusamerica.com/products/thunderbeat?utm_source=youtube&utm_campaign=Total%20Abdominal%20Hysterectomy%20Surgery%20-%20THUNDERBEAT&utm_medium=description&utm_term=energy&utm_content=surgical
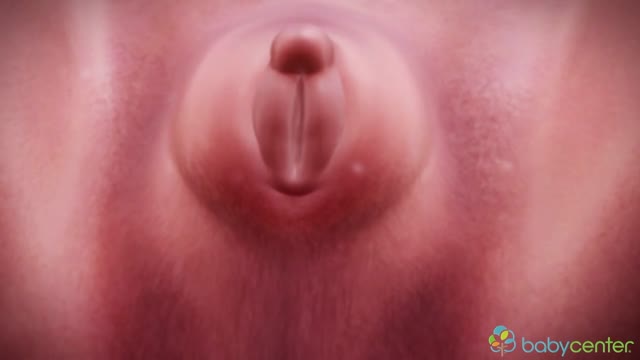
Your baby's sex is set at conception. At around 7 weeks, your baby's internal sex organs – such as ovaries and testes – begin to form in the abdomen. Male and female sex organs and genitalia look the same at this stage because they're derived from the same structures. At around 9 weeks, boys and girls begin to develop differently. In girls, a tiny bud emerges between the tissue of the legs. This bud will become the clitoris. The membrane that forms a groove below the bud separates to become the labia minora and the vaginal opening. By 22 weeks, the ovaries are completely formed and move from the abdomen to the pelvis. They already contain a lifetime supply of 6 million eggs. In boys, the bud develops into the penis and starts to elongate at around 12 weeks. The outer membrane grows into the scrotal sac that will later house the testicles. By 22 weeks, the testes have formed in the abdomen. They already contain immature sperm. Soon they'll begin their descent to the scrotum, but it's a long journey. They'll reach their destination late in pregnancy, or for some boys, after birth. If you're eager to find out whether you're having a girl or a boy, you'll have to wait until you're at least 17 weeks pregnant. That's when the genitals have developed enough to be seen on an ultrasound.
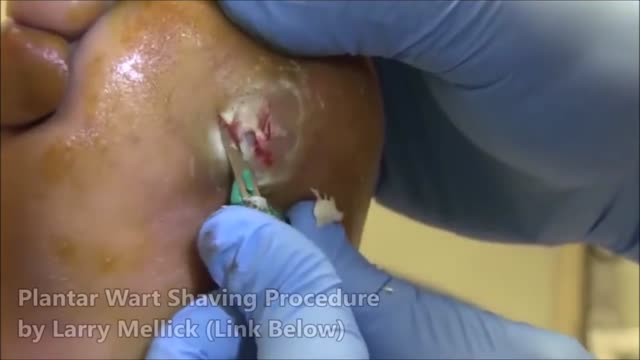
Plantar warts are hard, grainy growths that usually appear on the heels or balls of your feet, areas that feel the most pressure. This pressure also may cause plantar warts to grow inward beneath a hard, thick layer of skin (callus). Plantar warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus enters your body through tiny cuts, breaks or other weak spots on the bottom of your feet. Most plantar warts aren't a serious health concern and may not require treatment. But plantar warts can cause discomfort or pain. If self-care treatments for plantar warts don't work, you may want to see your doctor to have them removed.
Site enhancement oil, often called "santol" or "synthol" (no relation to the Synthol mouthwash brand), refers to oils injected into muscles to increase the size or change the shape. Some bodybuilders, particularly at the professional level, inject their muscles with such mixtures to mimic the appearance of developed muscle where it may otherwise be disproportionate or lagging. This is known as "fluffing".Synthol is 85% oil, 7.5% lidocaine, and 7.5% alcohol. It is not restricted, and many brands are available on the Internet. The use of injected oil to enhance muscle appearance is common among bodybuilders, despite the fact that synthol can cause pulmonary embolisms, nerve damage, infections, sclerosing lipogranuloma,[60] stroke,[55] and the formation of oil-filled granulomas, cysts or ulcers in the muscle. Rare cases might require surgical intervention to avoid further damage to the muscle and/or to prevent loss of life. Sesame oil is often used in such mixtures, which can cause allergic reactions such as vasculitis.

When you’re depressed, it can feel like you’ll never get out from under a dark shadow. However, even the most severe depression is treatable. So, if your depression is keeping you from living the life you want to, don’t hesitate to seek help. Learning about your depression treatment options will help you decide what approach is right for you. From therapy to medication to healthy lifestyle changes, there are many effective treatments that can help you overcome depression and reclaim your life.