Top videos

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the levatores ani and coccygei, with which may be included the parietal pelvic fascia on their upper and lower aspects. The pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity above from the perineal region (including perineum) below.
The right and left levator ani lie almost horizontally in the floor of the pelvis, separated by a narrow gap that transmits the urethra, vagina, and anal canal. The levator ani is usually considered in three parts: pubococcygeus, puborectalis, and iliococcygeus. The pubococcygeus, the main part of the levator, runs backward from the body of the pubis toward the coccyx and may be damaged during parturition. Some fibers are inserted into the prostate, urethra, and vagina. The right and left puborectalis unite behind the anorectal junction to form a muscular sling . Some regard them as a part of the sphincter ani externus. The iliococcygeus, the most posterior part of the levator ani, is often poorly developed.
The coccygeus, situated behind the levator ani and frequently tendinous as much as muscular, extends from the ischial spine to the lateral margin of the sacrum and coccyx.
The pelvic cavity of the true pelvis has the pelvic floor as its inferior border (and the pelvic brim as its superior border.) The perineum has the pelvic floor as its superior border.
Some sources do not consider “pelvic floor” and “pelvic diaphragm” to be identical, with the “diaphragm” consisting of only the levator ani and coccygeus, while the “floor” also includes the perineal membrane and deep perineal pouch. However, other sources include the fascia as part of the diaphragm. In practice, the two terms are often used interchangeably.
Inferiorly, the pelvic floor extends into the anal triangle.

Amniotomy is the official term for artificially breaking the bag of waters during labor. It is believed that breaking the bag of waters will help to speed up an otherwise slow labor. Amniotomy is part of the Active Management of Labor practiced in some hospitals. Amniotomy is performed by a midwife or doctor. A long, thin instrument with a hook on the end is inserted into the vagina and through the cervix so it can catch and rip the bag of waters. To perform an amniotomy, the cervix must be dilated enough to allow the instrument through the cervix, generally at least a two. Why choose Amniotomy? Unlike other medical methods of starting labor, amniotomy does not add synthetic hormones to your labor. Instead it seems to stimulate your body’s own labor process. Amniotomy allows the use of an internal electronic fetal monitor. How effective is Amniotomy? Amniotomy alone is unpredictable, it may take hours for labor to start with amniotomy. Because amniotomy increases the risk for infection, most caregivers use amniotomy in combination with synthetic oxytocin. Birth does happen faster when amniotomy is combined with synthetic oxytocin than when amniotomy is used alone. Risks of Amniotomy Risks for Mother Increases the risk for infection. This risk is increased with length of time the waters are broken and with vaginal exams. Because of the infection risk, a time limit is given by which the mother must give birth. As the time limit approaches attempts to progress labor will become more aggressive. The fore waters equalize pressure on the cervix so it will open uniformly. When they are broken, the mother increases her chances of having uneven dilation. Risks for Baby Increases the risk of umbilical cord compression. The fore waters equalize pressure on the baby’s head as it presses against the cervix. When they are broken, the pressure on the baby’s head may be uneven causing swelling in some parts.
When both mucosa and stroma are parts of the suspect lesion, a deep biopsy is needed. The Cervicore is designed to harvest samples from the cervix and vagina with minimal collateral injury to the surrounding tissues. The procedure is easy with minimal discomfort to the patient.

An excellent video demonstrating how a laparoscopy is performed to evaluate the uterus (note a small fibroid appearing as a bulge in the uterus), fallopian tubes and ovaries. Blue dye is injected into the uterus, entering the fallopian tubes and spilling from the end of the tubes into the abdominal cavity, confirming that both tubes are open
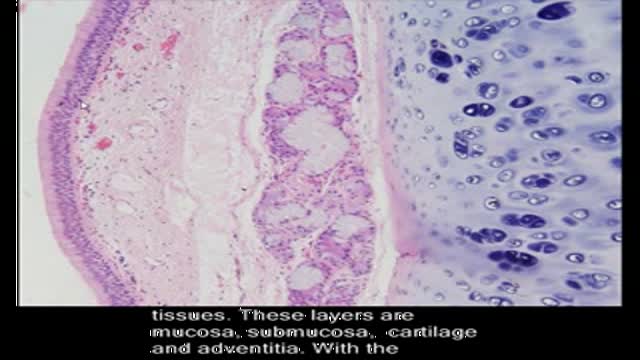
Bronchiectasis is an abnormal dilation of the proximal and medium-sized bronchi (>2 mm in diameter) caused by weakening or destruction of the muscular and elastic components of the bronchial walls. Affected areas may show a variety of changes, including transmural inflammation, edema, scarring, and ulceration, among other findings. Distal lung parenchyma may also be damaged secondary to persistent microbial infection and frequent postobstructive pneumonia. Bronchiectasis can be congenital but is most often acquired.[9] Congenital bronchiectasis usually affects infants and children. These cases result from developmental arrest of the bronchial tree. Acquired forms occur in adults and older children and require an infectious insult, impairment of drainage, airway obstruction, and/or a defect in host defense. The tissue is also damaged in part by the host response of neutrophilic proteases, inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide, and oxygen radicals. This results in damage to the muscular and elastic components of the bronchial wall. Additionally, peribronchial alveolar tissue may be damaged, resulting in diffuse peribronchial fibrosis.[12] The result is abnormal bronchial dilatation with bronchial wall destruction and transmural inflammation. The most important functional finding of altered airway anatomy is severely impaired clearance of secretions from the bronchial tree. Impaired clearance of secretions causes colonization and infection with pathogenic organisms, contributing to the purulent expectoration commonly observed in patients with bronchiectasis. The result is further bronchial damage and a vicious cycle of bronchial damage, bronchial dilation, impaired clearance of secretions, recurrent infection, and more bronchial damage
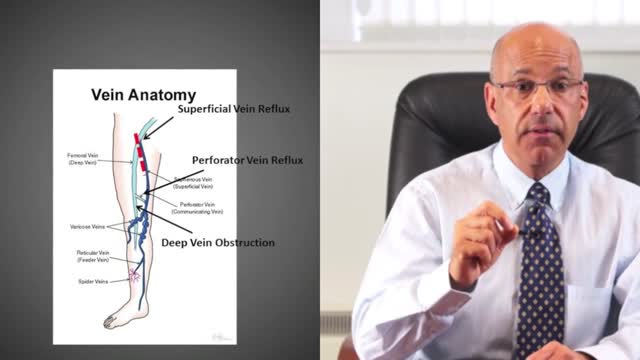
A leg ulcer is simply a break in the skin of the leg, which allows air and bacteria to get into the underlying tissue. This is usually caused by an injury, often a minor one that breaks the skin. In most people such an injury will heal up without difficulty within a week or two. However, when there is an underlying problem the skin does not heal and the area of breakdown can increase in size. This is a chronic leg ulcer.

EART (Health Education and Rescue Training) Wilderness First Aid is an intensive course that covers patient examination and evaluation, body systems and anatomy, wound care, splinting, environmental emergencies, and backcountry medicine. Hands-on simulations provide first-hand training in treating patients. This is an excellent course taught by experienced Wilderness First Responders and Emergency Medical Technicians and is highly recommended to all wilderness travelers. People who pass the courses will receive a Wilderness First Aid certification from the Emergency Care and Safety Institute (ECSI) which is good for 2 years. Participants who successfully pass CPR and HEART Wilderness First Aid will have met the First Aid requirements for OA Leader Training.

A Pap smear (Papanicolau smear; also known as the Pap test) is a screening test for cervical cancer. The test itself involves collection of a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the uterus that extends into the vagina) during a routine pelvic exam

Symptoms Burning stomach pain Feeling of fullness, bloating or belching Fatty food intolerance Heartburn Nausea The most common peptic ulcer symptom is burning stomach pain. Stomach acid makes the pain worse, as does having an empty stomach. The pain can often be relieved by eating certain foods that buffer stomach acid or by taking an acid-reducing medication, but then it may come back. The pain may be worse between meals and at night. Nearly three-quarters of people with peptic ulcers don't have symptoms. Less often, ulcers may cause severe signs or symptoms such as: Vomiting or vomiting blood — which may appear red or black Dark blood in stools, or stools that are black or tarry Trouble breathing Feeling faint Nausea or vomiting Unexplained weight loss Appetite changes