Top videos

Here we’ll explain the symptoms of pancreatitis, how alcohol causes the condition and the other health problems it can lead to. You probably don’t pay much attention to your pancreas. But that small, tadpole-shaped organ behind your stomach and below your ribcage is pretty important. It produces two essential substances: digestive juices which your intestines use to break down food, and hormones that are involved in digestion, such as insulin, which regulates your blood sugar levels. Pancreatitis is when your pancreas becomes inflamed and its cells are damaged. Heavy drinking can cause pancreatitis. But if you drink within the government’s low risk unit guidelines, you should avoid upsetting this important organ.

Of the many factors that affect your compatibility with a man, one of the biggest (or smallest) is in his pants. As with humour, interests or habits, the wrong fit can leave you cold. Or traumatised. In a study of 1,661 penises, Dr Debby Herbenick, author of Sex Made Easy, found an almost nine-inch difference in erection size: from 1.6 inches to 10.2. And since absolutely nothing outside the package tells you what to expect with the package, you have to test compatibility the hard way. Sometimes you hit your jackpot, sometimes it's just fine, and sometimes he's the guy on either end of that erection spectrum. These writers have been there, so here's what they learned - and how you can deal (without the gasp reflex).
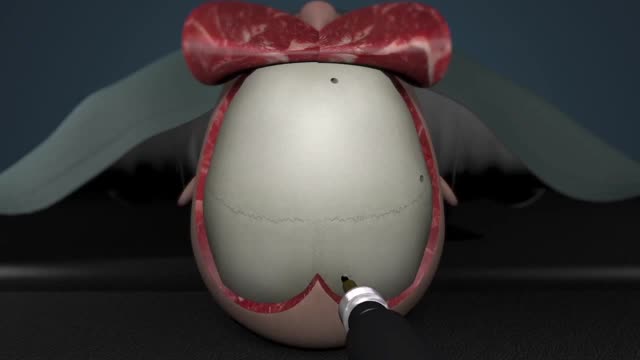
A craniotomy is the surgical removal of part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain. Specialized tools are used to remove the section of bone called the bone flap. The bone flap is temporarily removed, then replaced after the brain surgery has been done.
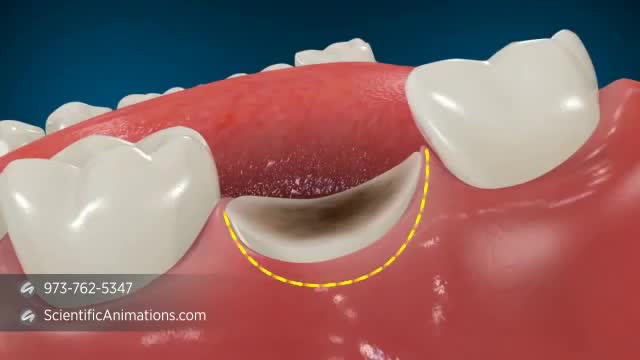
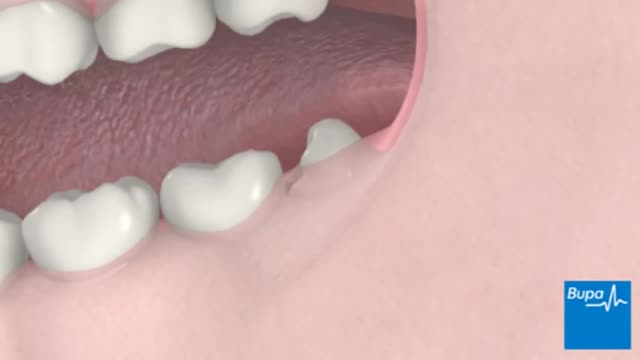
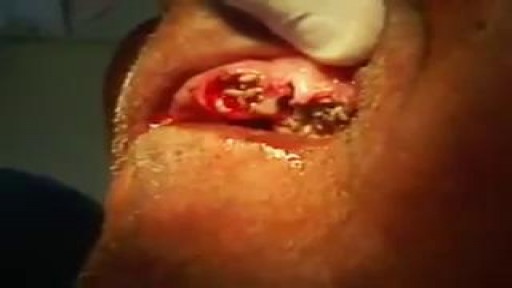
A palatal view of a maxillary premolar during a crown lengthening procedure. Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically.

Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a rare systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the classic triad of persistent high spiking fevers, joint pain, and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash. The disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion.

Trisomy 18, also called Edwards syndrome, is a chromosomal condition associated with abnormalities in many parts of the body. Individuals with trisomy 18 often have slow growth before birth (intrauterine growth retardation) and a low birth weight. Affected individuals may have heart defects and abnormalities of other organs that develop before birth. Other features of trisomy 18 include a small, abnormally shaped head; a small jaw and mouth; and clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Due to the presence of several life-threatening medical problems, many individuals with trisomy 18 die before birth or within their first month. Five to 10 percent of children with this condition live past their first year, and these children often have severe intellectual disability.

Rheum is made up of mucus, skin cells, oils and dust. The rheum that comes from the eyes and forms eye boogers is called gound, which you may know as eye sand, eye gunk, sleep dust, sleep sand, sleep in your eyes, or eye shnooters. When you're awake, gound doesn't cause any problems.
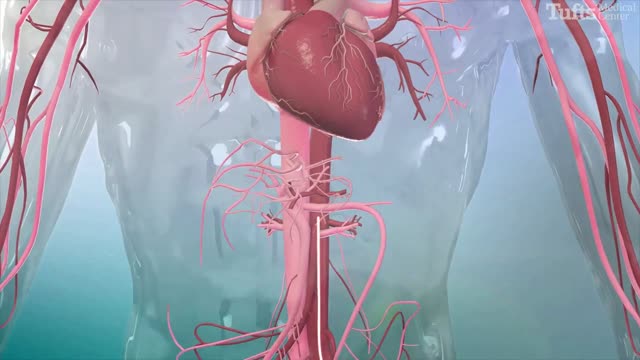
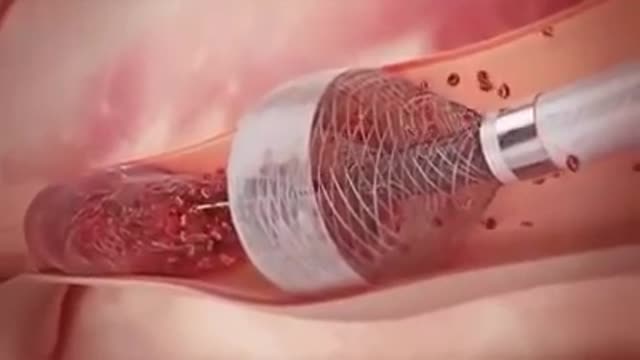
Alcohol septal ablation (ASA, TASH, Sigwart procedure) is a percutaneous, minimally-invasive treatment performed by an interventional cardiologist to relieve symptoms and improve functional status in severely symptomatic patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) who meet strict clinical, anatomic and physiologic ...
Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants.

With so many antibiotics available, it isn't possible to list all of them here. But common antibiotics that are generally considered safe during pregnancy include penicillins (such as amoxicillin and ampicillin), cephalosporins (such as cephalexin), and erythromycin.

Pain in the affected bone is the most common complaint of patients with bone cancer. At first, the pain is not constant. It may be worse at night or when the bone is used (for example, leg pain when walking). As the cancer grows, the pain will be there all the time. The pain increases with activity and the person might limp if a leg is involved.