Top videos
Ellie was born with a rare condition which stopped her jawbones from growing properly. At first, her parents didn't realize there was a problem, apart from the fact that her teeth were not aligned. But when she went to have braces fitted to straighten her teeth when she was 14, orthodontist Joy Hickman realized her jaw had not grown since she was eight. Over the next six years Hickman worked with a maxillofacial surgeon to transform Ellie's looks. Ellie, who is now 20, said the surgery was painful but paid almost immediate dividends. "About six months after it was my year 11 prom and it looked good." Ellie told the Daily Post the change in her appearance has been matched by an increase in confidence.
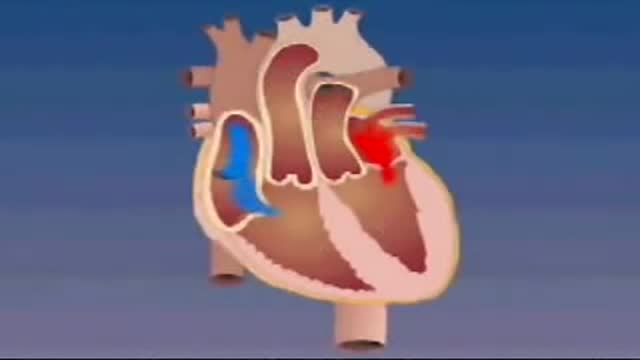
Transposition of the great arteries is a serious but rare heart defect present at birth (congenital), in which the two main arteries leaving the heart are reversed (transposed). Transposition of the great arteries changes the way blood circulates through the body, leaving a shortage of oxygen in blood flowing from the heart to the rest of the body. Without an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood, the body can't function properly and your child faces serious complications or death without treatment.

Obstetrical emergencies of pregnancy ECTOPIC PREGNANCY. ... PLACENTAL ABRUPTION. ... PLACENTA PREVIA. ... ECTOPIC PREGNANCY. ... PLACENTAL ABRUPTION. ... PLACENTA PREVIA. ... Amniotic fluid — The liquid in the placental sac that cushions the fetus and regulates temperature in the placental environment.

Surfactant. Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, and dispersants.
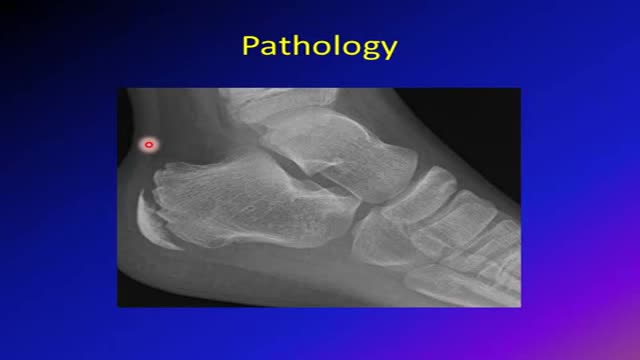
Sever's disease (also known as calcaneal apophysitis) is a type of bone injury in which the growth plate in the lower back of the heel, where the Achilles tendon (the heel cord that attaches to the growth plate) attaches, becomes inflamed and causes pain.
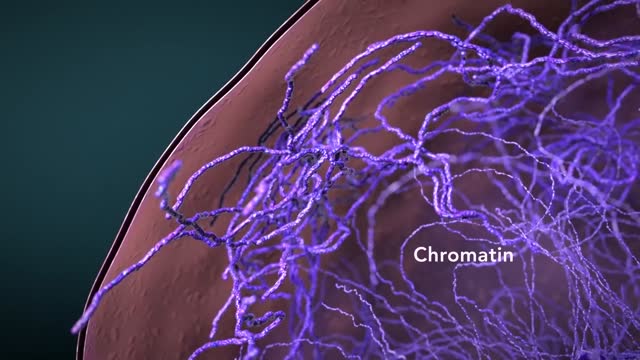
Cytoplasmic organelles are "little organs" that are suspended in the cytoplasm of the cell. Each type of organelle has a definite structure and a specific role in the function of the cell. Examples of cytoplasmic organelles are mitochondrion, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.

Appareil Pour La Cellulite, Creme Anti Cellulite Efficace, Anti Cellulite Maison, Café Cellulite--- http://perdre-sa-cellulite.plus101.com --- Cellulite Des Cuisses, Que Faire? Comment Eliminer Vite Sa Cellulite Des Cuisses Avec Des Exercices et L'alimentation cellulite-cuissesMême si la plupart des gens se mettent continuellement à la chasse de la cellulite, jusqu’à ce jour, il n’y a pas encore eu de remèdes miracles. Elle est particulièrement causée par le manque d’activités physiques et une alimentation non équilibrée. Elle apparaît souvent sur les fesses, les hanches et principalement sur les cuisses. Ainsi, pour se débarrasser de la cellulite surtout celle des cuisses, il est important d’avoir une alimentation équilibrée et de pratiquer des exercices sportifs. Il vous suffit de suivre les recommandations dans la vidéo ci-dessous qui vous aideront à tonifier vos jambes de manière efficaces, ainsi réduisant la présence de la cellulite sur les fesses, hanches et cuisses pour une silhouette plus attirante.CLIQUEZ ICI: http://perdre-sa-cellulite.plus101.com
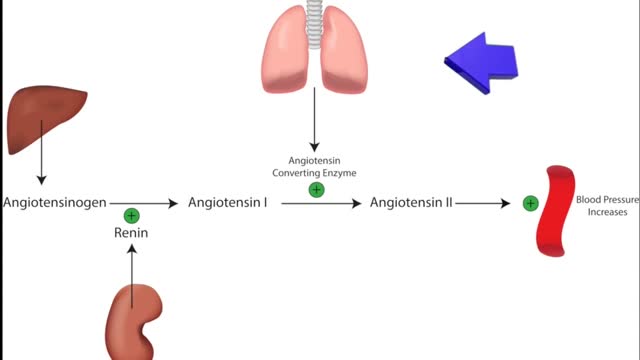
ACE inhibitors Email this page to a friend Print Facebook Twitter Google+ Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are medicines. They treat heart, blood vessel, and kidney problems. How ACE inhibitors help ACE inhibitors are used to treat heart disease. These medicines make your heart work less hard by lowering your blood pressure. This keeps some kinds of heart disease from getting worse. Most people who have heart failure take these medicines. These medicines treat high blood pressure, strokes, or heart attacks. They may help lower your risk for stroke or heart attack. They are also used to treat diabetes and kidney problems. This can help keep your kidneys from getting worse. If you have these problems, ask your health care provider if you should be taking these medicines.
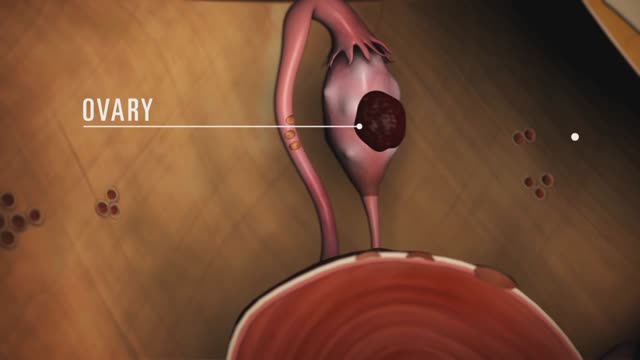
Endometriosis (en-doe-me-tree-O-sis) is an often painful disorder in which tissue that normally lines the inside of your uterus — the endometrium — grows outside your uterus. Endometriosis most commonly involves your ovaries, fallopian tubes and the tissue lining your pelvis. Rarely, endometrial tissue may spread beyond pelvic organs.
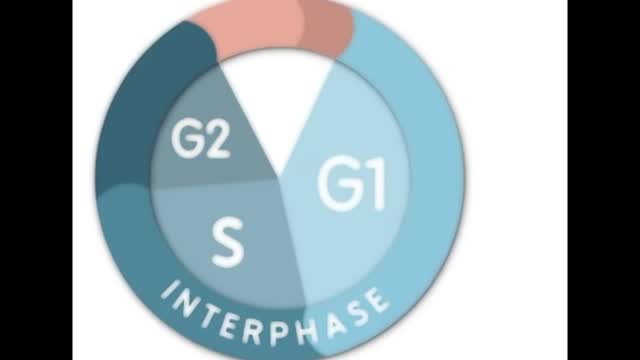
Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell nucleus splits in two, followed by division of the parent cell into two daughter cells. The word "mitosis" means "threads," and it refers to the threadlike appearance of chromosomes as the cell prepares to divide.

Experts do not know the exact cause of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. About 25 to 30 percent of gastrinomas are caused by an inherited genetic disorder called multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). MEN1 causes hormone-releasing tumors in the endocrine glands and the duodenum.

A febrile seizure is a convulsion in a child that may be caused by a spike in body temperature, often from an infection. Your child's having a febrile seizure can be alarming, and the few minutes it lasts can seem like an eternity. Febrile seizures represent a unique response of a child's brain to fever, usually the first day of a fever. Fortunately, they're usually harmless and typically don't indicate an ongoing problem. You can help by keeping your child safe during a febrile seizure and by comforting him or her afterward.