Top videos
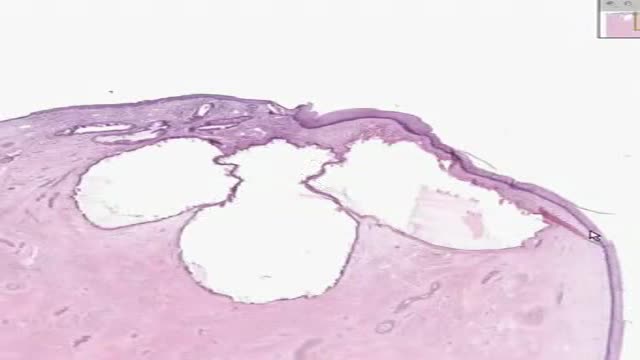
Teratomas are tumors made up of tissues, such as hair, muscle, and bone. They occur most often in the ovaries in women, and the testicles in men. They may be benign or malignant. Symptoms vary depending on the location. A painful lump or swelling may be apparent. Some babies have a mass that can be seen on an ultrasound before birth. Treatment often involves surgery. In rare cases when a teratoma is malignant, chemotherapy or radiation may be needed.

The arm and leg muscles are affected later. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease — a disease that occurs when the immune system attacks the body's own tissues. In MG, that attack interrupts the connection between nerve and muscle — the neuromuscular junction.
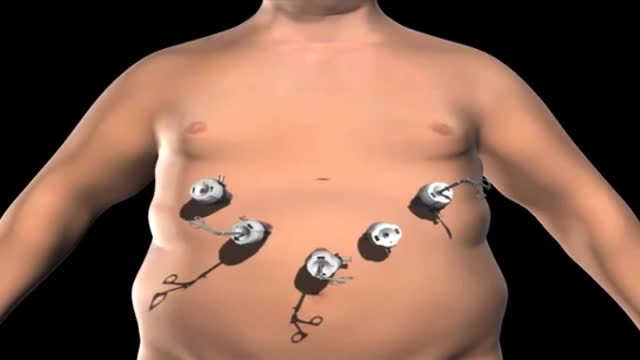
Super Obese individuals (people with a Body Mass Index over 45) have an increased risk during any surgery. And the longer the time under anesthesia, the greater the risk. Gastric bypass surgery can last over 2 hours. Duodenal switch surgery often takes over 4 hours. That’s a long time to be under anesthesia.
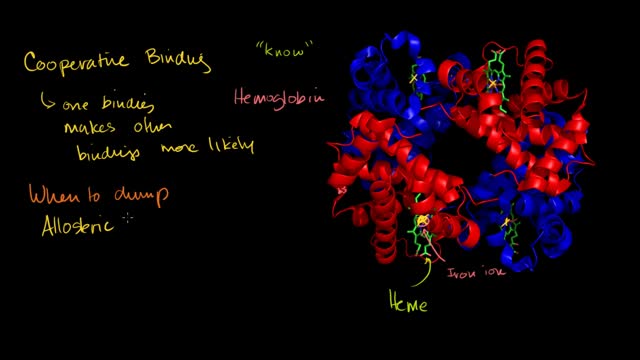
Hemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs. Hemoglobin is made up of four protein molecules (globulin chains) that are connected together.

During in vitro fertilization (IVF), eggs and sperm are brought together in a laboratory glass dish to allow the sperm to fertilize an egg. With IVF, you can use any combination of your own eggs and sperm and donor eggs and sperm. After IVF, one or more fertilized eggs are placed in the uterus .
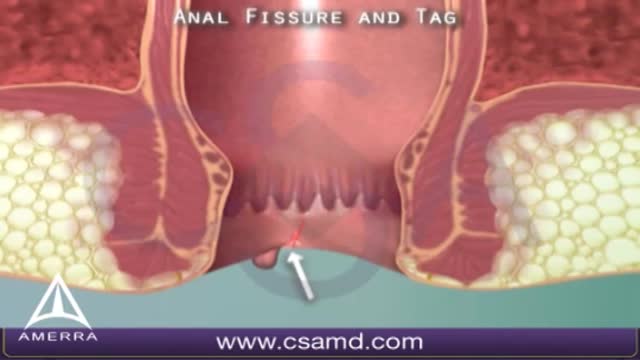
An anal fissure is a small tear in the thin, moist tissue (mucosa) that lines the anus. An anal fissure may occur when you pass hard or large stools during a bowel movement. Anal fissures typically cause pain and bleeding with bowel movements. You also may experience spasms in the ring of muscle at the end of your anus (anal sphincter). Anal fissures are very common in young infants but can affect people of any age. Most anal fissures get better with simple treatments, such as increased fiber intake or sitz baths. Some people with anal fissures may need medication or, occasionally, surgery.

Vaginal discharge serves an important housekeeping function in the female reproductive system. Fluid made by glands inside the vagina and cervix carries away dead cells and bacteria. This keeps the vagina clean and helps prevent infection. Most of the time, vaginal discharge is perfectly normal. The amount can vary, as can odor and hue (its color can range from clear to a milky white-ish), depending on the time in your menstrual cycle. For example, there will be more discharge if you are ovulating, breastfeeding, or are sexually aroused. The smell may be different if you are pregnant or you haven't been diligent about your personal hygiene. None of those changes is cause for alarm. However, if the color, smell, or consistency seems significantly unusual, especially if it accompanied by vaginal itching or burning, you could be noticing an infection or other condition. What causes abnormal discharge? Any change in the vagina's balance of normal bacteria can affect the smell, color, or discharge texture. These are a few of the things that can upset that balance:

Diabetic retinopathy involves changes to retinal blood vessels that can cause them to bleed or leak fluid, distorting vision. Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of vision loss among people with diabetes and a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults.

Remedios Caseros Para La Migraña, Causas De Dolores De Cabeza, Como Controlar La Migraña
http://Curar-Dolor-De-Cabeza.Good-Info.Co
Un Millón De Maneras De Adquirir Un Dolor De Cabeza
Y Cómo Curarlos A Todos
Hoy En Día, Hay Un Montón De Maneras, Un Millón De Hecho, Para Adquirir Un Dolor De Cabeza.
Usted Puede Obtener Un Dolor De Cabeza Cuando Se Golpea Su Cabeza Con Algo, Cuando Se Le Olvida Su Consumo De Cafeína, Cuando Come Un Helado Demasiado Rápido, Cuando Está Demasiado Estresado, Demasiado Cansado, O Cuando Se Enferma.
Sólo En Los Estados Unidos, Aproximadamente 1 De Cada 6 Personas Sufre De Dolores De Cabeza Crónicos Y Migrañas. Ellos Sufren De Forma Infrecuente,
for more information
http://Curar-Dolor-De-Cabeza.Good-Info.Co
subscribe to our channel
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DGcvq5u9TXQ
Visit our Blog
Remedios Caseros Para La Migraña, Causas De Dolores De Cabeza, Como Controlar La Migraña, dolor del cuero cabelludo, para dolores de cabeza, dolores fuertes de cabeza, remedios para dolores de cabeza, muchos dolores de cabeza, dolor lado izquierdo cabeza, porque duele la cabeza cuando tomas, medicina para la cabeza, dolor cabeza nuca, molestias en el cuero cabelludo, dolor cabeza lado izquierdo, dolor de cabez, remedio para la migraña, como aliviar el dolor,

Cardiac tamponade is a medical emergency that requires urgent drainage of the pericardial fluid. Preferably, patients should be monitored in an intensive care unit. All patients should receive the following: Oxygen Volume expansion with blood, plasma, dextran, or isotonic sodium chloride solution, as necessary, to maintain adequate intravascular volume - Sagristà-Sauleda et al noted significant increase in cardiac output after volume expansion [24] (see the Cardiac Output calculator) Bed rest with leg elevation - This may help increase venous return Positive-pressure mechanical ventilation should be avoided because it may decrease venous return and aggravate signs and symptoms of tamponade. Inpatient care After pericardiocentesis, leave the intrapericardial catheter in place after securing it to the skin using sterile procedure and attaching it to a closed drainage system via a 3-way stopcock. Periodically check for reaccumulation of fluid, and drain as needed. The catheter can be left in place for 1-2 days and can be used for pericardiocentesis. Serial fluid cell counts can be useful for helping to discover an impending bacterial catheter infection, which could be catastrophic. If the white blood cell (WBC) count rises significantly, the pericardial catheter must be removed immediately. A Swan-Ganz catheter can be left in place for continuous monitoring of hemodynamics and to assess the effect of reaccumulation of pericardial fluid. A repeat echocardiogram and a repeat chest radiograph should be performed within 24 hours.
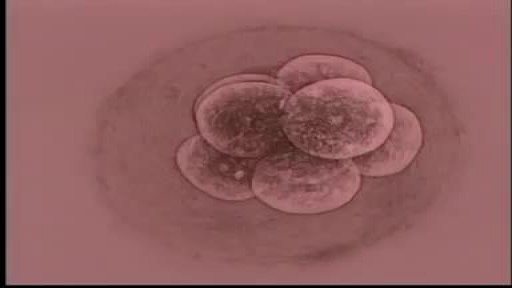
Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exception is sperm or eggs which are produced by a different type of cell division called meiosis. During fertilization the sperm and egg unite to form a single cell called the zygote which contains chromosomes from both the sperm and egg.