Top videos

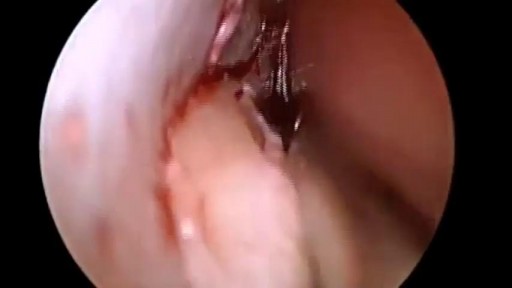
Traumatic penile injury can be due to multiple factors. Penile fracture, penile amputation, penetrating penile injuries, and penile soft tissue injuries are considered urologic emergencies and typically require surgical intervention. The goals of treatment for penile trauma are universal: preservation of penile length, erectile function, and maintenance of the ability to void while standing. Traumatic injury to the penis may concomitantly involve the urethra.[1, 2] Urethral injury and repair is beyond the scope of this article but details can be found in Urethral Trauma. Penile fracture Penile fracture is the traumatic rupture of the corpus cavernosum. Traumatic rupture of the penis is relatively uncommon and is considered a urologic emergency.[3] Sudden blunt trauma or abrupt lateral bending of the penis in an erect state can break the markedly thinned and stiff tunica albuginea, resulting in a fractured penis. One or both corpora may be involved, and concomitant injury to the penile urethra may occur. Urethral trauma is more common when both corpora cavernosa are injured.[4] Penile rupture can usually be diagnosed based solely on history and physical examination findings; however, in equivocal cases, diagnostic cavernosography or MRI should be performed. Concomitant urethral injury must be considered; therefore, preoperative retrograde urethrographic studies should generally be performed. See the images below.
The principal signs of cerebellar dysfunction are the following: Ataxia: unsteadiness or incoordination of limbs, posture, and gait. A disorder of the control of force and timing of movements leading to abnormalities of speed, range, rhythm, starting, and stopping.
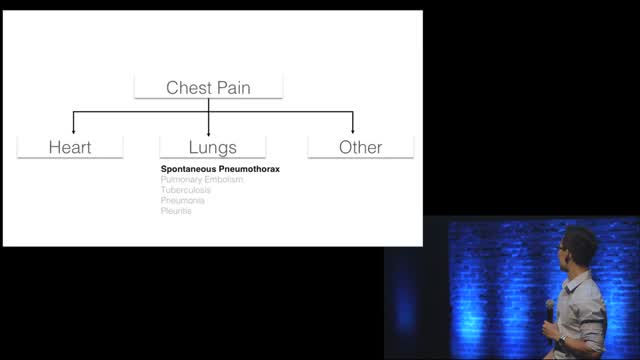
Chest pain is a frequent complaint of patients seeking urgent medical assistance, and accounts for an estimated 2-4 per cent of all A&E visits in the UK (Becker, 2000). Generally, acute chest pain should be considered cardiovascular in origin until proven otherwise and it is common in clinical practice to err on the conservative or ‘safe’ side when evaluating people with chest pain. Individuals with suspected ischaemic chest pain must be evaluated rapidly for several reasons: - Myocardial ischaemia, if prolonged and severe, can cause myocardial infarction (necrosis); - Treatment strategies that achieve myocardial salvage (thrombolytic therapy or primary coronary angioplasty) are available for patients with acute coronary syndromes and these treatments reduce morbidity and mortality;
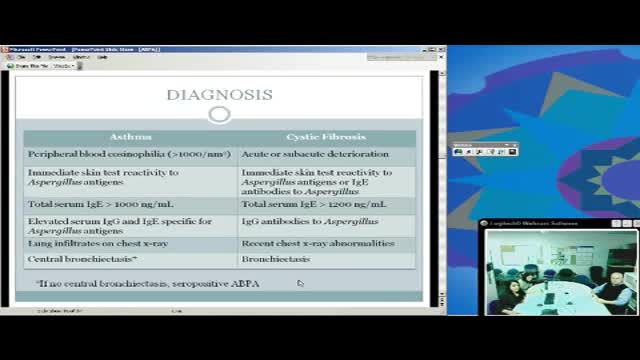
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a condition characterised by an exaggerated response of the immune system (a hypersensitivity response) to the fungus Aspergillus (most commonly Aspergillus fumigatus). It occurs most often in patients with asthma or cystic fibrosis.

Anemia is a medical condition in which the red blood cell count or hemoglobin is less than normal. The normal level of hemoglobin is generally different in males and females. For men, a normal hemoglobin level is typically defined as a level of more than 13.5 gram/100 ml, and in women as hemoglobin of more than 12.0 gram/100 ml. These definitions may vary slightly depending on the source and the laboratory reference used. Continue Reading

The majority of epileptic seizures are controlled by medication, particularly anticonvulsant drugs. The type of treatment prescribed will depend on several factors, including the frequency and severity of the seizures and the person's age, overall health, and medical history. An accurate diagnosis of the type of epilepsy is also critical to choosing the best treatment. Drug Therapy Many drugs are available to treat epilepsy. Although generic drugs are safely used for most medications, anticonvulsants are one category where doctors proceed with caution. Most doctors prefer to use brand-name anticonvulsants, but realize that many insurance companies will not cover the cost. As a result, it is acceptable to start taking a generic anticonvulsant medication, but if the desired control is not achieved, the patient should be switched to the brand-name drug.

Rheum is made up of mucus, skin cells, oils and dust. The rheum that comes from the eyes and forms eye boogers is called gound, which you may know as eye sand, eye gunk, sleep dust, sleep sand, sleep in your eyes, or eye shnooters. When you're awake, gound doesn't cause any problems.

Genes are the building blocks of heredity. They are passed from parent to child. They hold DNA, the instructions for making proteins. Proteins do most of the work in cells. They move molecules from one place to another, build structures, break down toxins, and do many other maintenance jobs. Sometimes there is a mutation, a change in a gene or genes. The mutation changes the gene's instructions for making a protein, so the protein does not work properly or is missing entirely. This can cause a medical condition called a genetic disorder. You can inherit a gene mutation from one or both parents. A mutation can also happen during your lifetime.
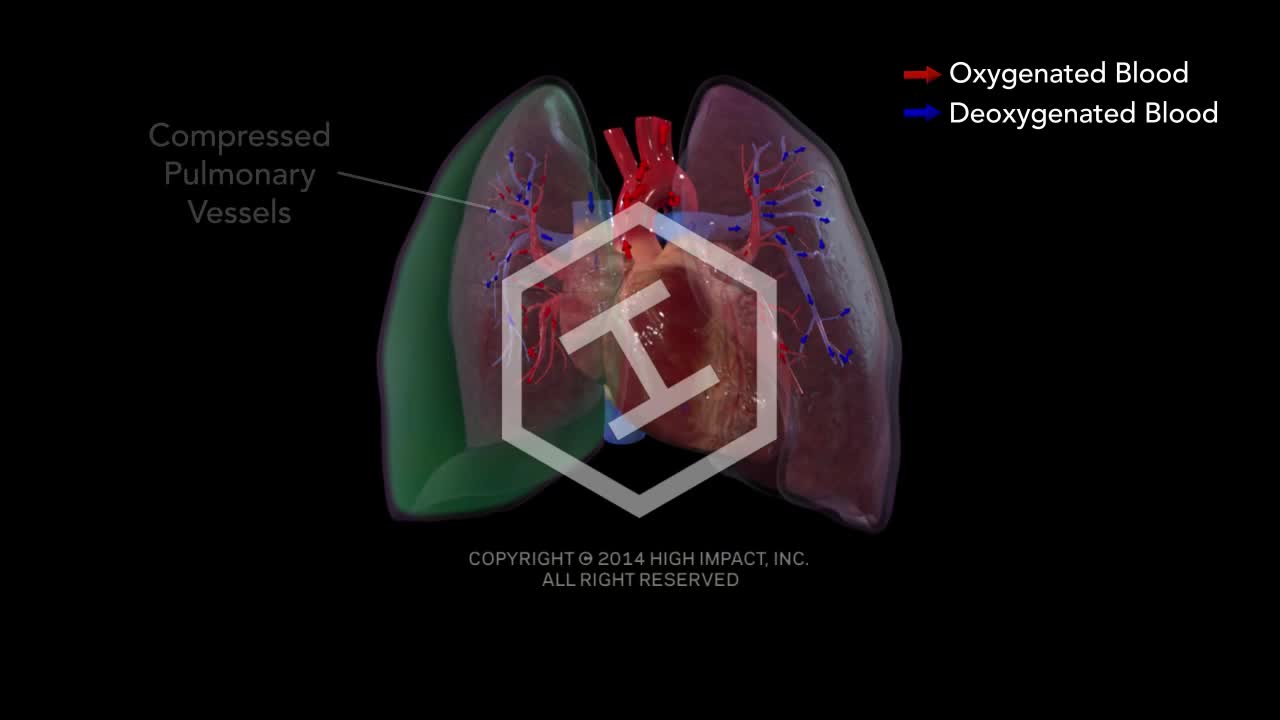
Tension pneumothorax develops when a lung or chest wall injury is such that it allows air into the pleural space but not out of it (a one-way valve). As a result, air accumulates and compresses the lung, eventually shifting the mediastinum, compressing the contralateral lung, and increasing intrathoracic pressure enough to decrease venous return to the heart, causing shock. These effects can develop rapidly, particularly in patients undergoing positive pressure ventilation.

Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS) is obstruction of blood flow through the superior vena cava (SVC). It is a medical emergency and most often manifests in patients with a malignant disease process within the thorax. A patient with SVCS requires immediate diagnostic evaluation and therapy.
Renal artery stenosis is a narrowing of arteries that carry blood to one or both of the kidneys. Most often seen in older people with atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), renal artery stenosis can worsen over time and often leads to hypertension (high blood pressure) and kidney damage.