Top videos

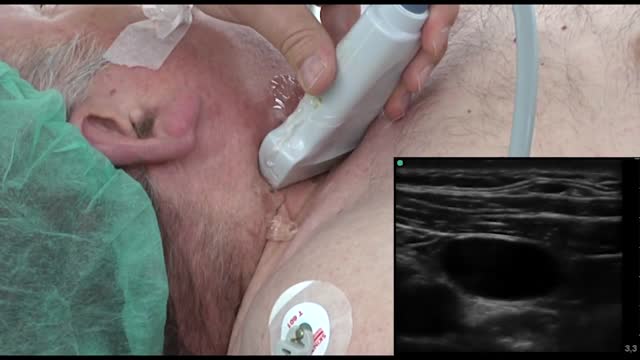
Pediatric surgeons at Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus perform general surgical procedures such as circumcisions, removal of foreign objects, hernia repair, and suturing of minor lacerations. While more complex surgeries take place at the Texas Children’s Main Campus, pre-operative and follow-up outpatient care for those procedures is available at the West Campus.
Everything about Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus is dedicated to the health and wellness of children. As greater Houston's first suburban hospital designed exclusively for children, we offer the expert care you've come to trust from Texas Children's Hospital coupled with a location that's convenient and accessible for area families. Our facility is located just off the westbound feeder road of the Katy Freeway (at I-10 and Barker Cypress).
For more information about Texas Children's Hospital West Campus, visit http://www.texaschildrens.org/....Locate/In-the-Commun
Meet Dr. Allen Milewicz, chief of community surgery at Texas Children's West Campus
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uMoCdipuKfA&index=16&list=PLiN68C9rloPBD-E9ChWhVy73h7V3SEMlm

When you’re depressed, it can feel like you’ll never get out from under a dark shadow. However, even the most severe depression is treatable. So, if your depression is keeping you from living the life you want to, don’t hesitate to seek help. Learning about your depression treatment options will help you decide what approach is right for you. From therapy to medication to healthy lifestyle changes, there are many effective treatments that can help you overcome depression and reclaim your life.
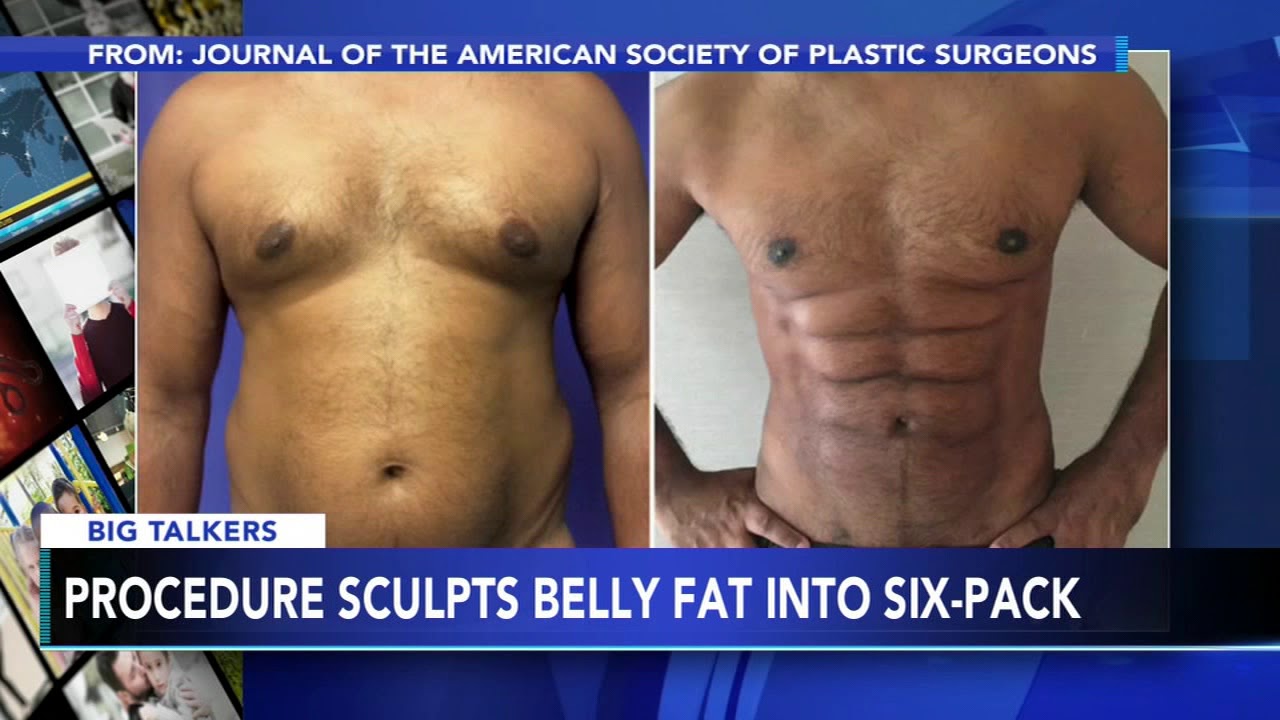
If you've always wanted six-pack abs, but can't seem to get to the gym - there's now a short-cut for that. Researchers at the University of Miami have developed a new plastic surgery technique called abdominal etching. It can reshape belly fat to make you look like you spend a lot of time at the gym.
READ MORE: https://6abc.cm/2Vv5Tu4
WARNING: Explicit and Educational Surgical Content.
Visage Clinic's Dr. Marc DuPéré - located in Toronto, Ontario, Canada discusses Liposuction (upper bra, back rolls, lower back rolls, love handles & abdomen) and "Tummy Tuck" (Abdominoplasty): Skin excision, muscle repair and umbilicoplasty.
For more info and to book a consultation visit www.VisageClinic.com/cosmetic-....surgery/mommy-makeov or call (416) 929-9800.

#abdomenliposuction #laserskintightening #drprashantyadav #cosmeticsurgery #plasticsurgery #dezireclinicindia #weightloss #shorts #360degreeabdomenliposuction #lowerbackliposuction
Weight Loss After 360° Abdomen liposuction result, Abdomen Liposuction, lower back liposuction, 360 degree abdomen liposuction
☎️ For more info:
WhatsApp Your Details to know the Cost
Delhi - 8956880644, 9717470550, Pune - 9222122122, Bangalore- 8971224700, Gurugram - 9272007896, Ahmedabad - 9711162746
Why choose Dezire Clinic For Your Cosmetic and plastic surgery treatment ?
Dezire Clinic is a top searched clinic surgical and nonsurgical cosmetic procedure in India when comes to “Cosmetic, Skin ,Laser and Hair transplantation”.
Like and Share the video if you find it useful. Do not forget to Subscribe to our channel to get more updates.
Subscribe on YouTube https://youtube.com/dezireclin....ic?sub_confirmation=
https://youtube.com/dezireplas....ticsurgerycenter?sub
🎦 https://www.youtube.com/dezireclinic
🎦 https://www.youtube.com/DezirePlasticSurgeryCenter
👍🏻 https://www.facebook.com/drprashantmch/
👍🏻 https://www.facebook.com/dezireclinic
📸 https://www.instagram.com/drprashantdezireclinic/
📸 https://www.instagram.com/dezireclinics/
🐥 https://twitter.com/drprashantmch
👍🏻 https://www.linkedin.com/in/drprashantyadav/
🌐 Website: https://www.dezireclinic.in/
📧 dezireclinicindia@gmail.com
📧 info@dezireclinic.in
Dr. Prashant Yadav (M.S., M.Ch. Plastic Surgery ) & Founder of Dezire Clinic
Disclaimer: The content of this channel is for informational and educational purposes only. This content should not be considered a substitute for advice provided by a certified plastic or cosmetic surgeon. Patients must be properly diagnosed by a healthcare professional on an individual basis in order to achieve the desired results. There is no guarantee of getting the results and outcomes shown in videos, as the results can vary at the end. We will not be held liable for any harm caused by someone misusing our name.
#plasticsurgery #cosmeticsurgery #dezireclinic #drprashantyadav
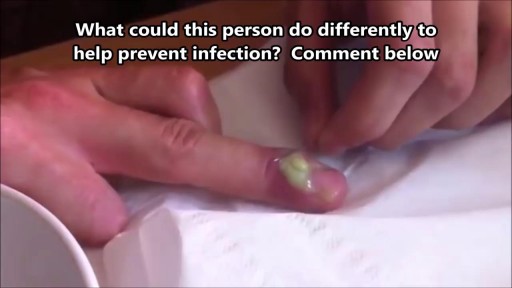
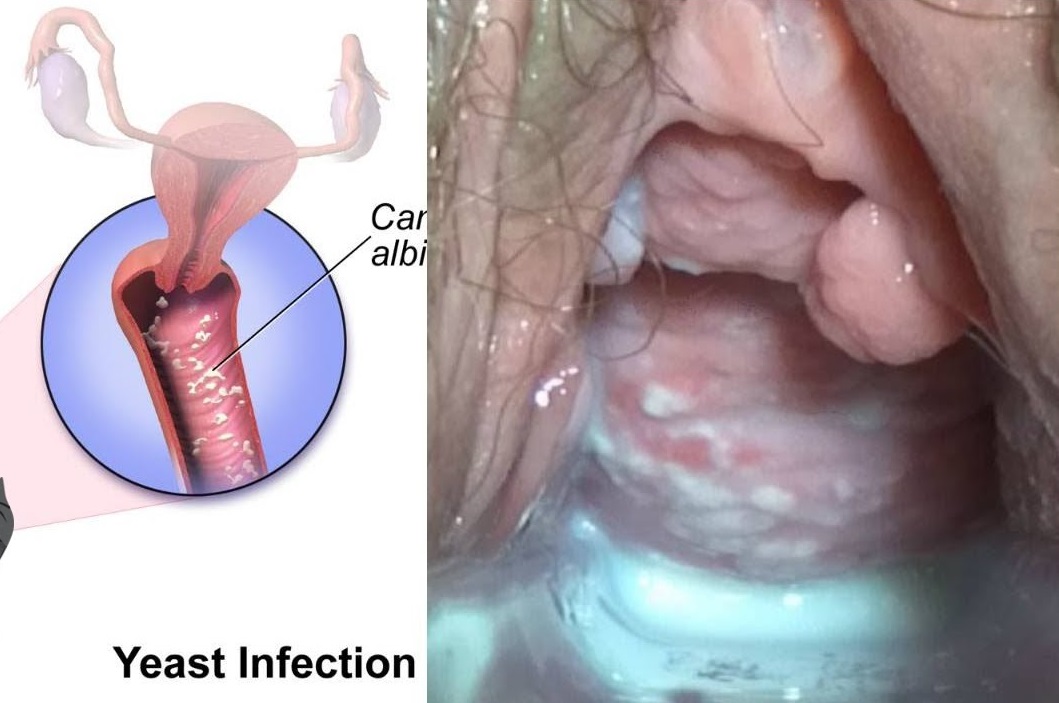
What Is a Paronychia (Nail Infection)? An infection that develops along the edge of the fingernail or toenail is called a paronychia (pear-ah-NIK-ee-ah). It is the most common hand infection and, if left untreated, can progress to a more severe infection of the entire finger or toe. Paronychia is distinguished from other infections such as onychomycosis and herpetic whitlow by its location and appearance.
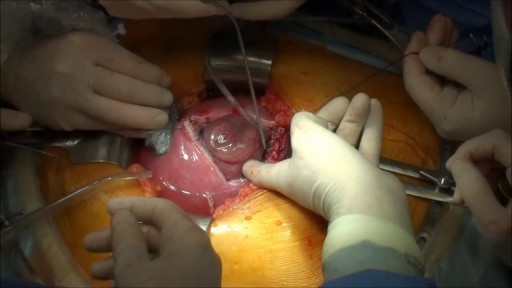
Prenatal repair of myelomeningocele (MMC), the most common and severe form of spina bifida, is a delicate surgical procedure where fetal surgeons open the uterus and close the opening in the baby's back while they are still in the womb.

Mysterious massage from East Asia(CHINA).it can cure cure Erectile dysfunction,can let their life better.This video from mainland of China,so the language is Chinese mandarin.but you can see English show on the video too.Tiedang gong means kongfu of Iron penis&balls.
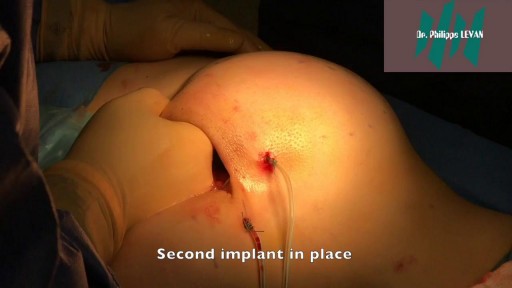
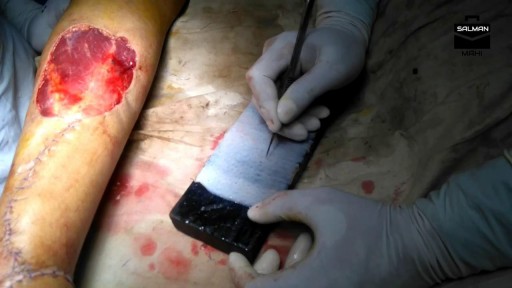
Butt implants are a popular plastic surgery procedure among those who wish to enhance the appearance, shape, and size of their rear ends. Buttock augmentation involves the surgical insertion of artificial body implants into a patient’s buttocks to create a larger, shapelier, and more sensuous rear end. Patients who have underdeveloped buttocks can achieve a more proportionate figure with butt implants. Women who wish to achieve an “hour glass” figure or are unhappy with the size of their buttocks can benefit from female butt implants. Men with flat or poorly developed buttocks can enhance the shape of the area to their liking with male butt implants. Many buttock augmentation patients say that their clothes fit better, they feel more attractive, and their confidence levels have improved.

Diastasis recti often occurs during pregnancy and can persist after pregnancy. It affects core strength and the appearance of the abdominal muscles.
Dr. Erick Sanchez repairs the abdominal muscles with every tummy tuck. This short video shows the muscle repair portion of the surgery with a bonus after photo at the end!
To request a consultation with Dr. Sanchez, visit sanchezplasticsurgery.com and click Request a Consultation. Fill out the form and someone will get in touch with you to answer all your questions.
Expected cost can be found at the bottom of each procedure page on our website.