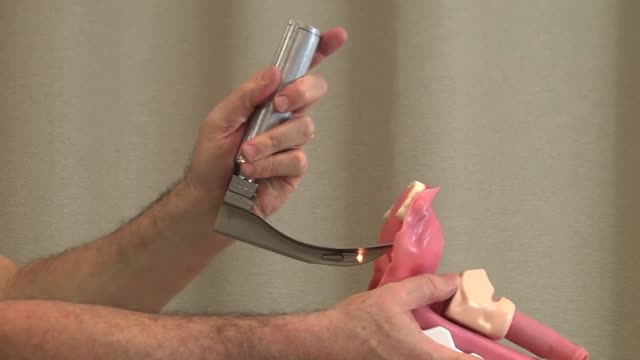
Top videos

An MRCP scan is a scan that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce pictures of the liver, bile ducts, gallbladder and pancreas. Note: the information below is a general guide only. The arrangements,and the way tests are performed, may vary between different hospitals.
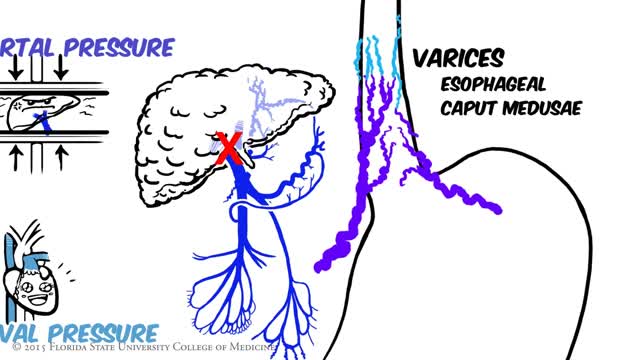
Portal hypertension is an increase in the blood pressure within a system of veins called the portal venous system. Veins coming from the stomach, intestine, spleen, and pancreas merge into the portal vein, which then branches into smaller vessels and travels through the liver.
The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.
A pneumothorax is usually caused by an injury to the chest, such as a broken rib or puncture wound. It may also occur suddenly without an injury. A pneumothorax can result from damage to the lungs caused by conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, cystic fibrosis, and pneumonia.

http://combatir-la-ansiedad.good-info.co/ --- Trastorno De Ansiedad Generalizada, Medicamentos Para La Ansiedad, Que Tomar Para La Ansiedad. Obteniendo el estado interior perfecto... ¿Listo para acceder a los métodos, los cuales te van a permitir decirle adios a las preocupaciones y a la ansiedad? Si quieres tener acceso a estos métodos exclusivos los cuales han ayudado a muchos a eliminar la ansiedad facilmente, tan solo entra aqui: http://combatir-la-ansiedad.good-info.co Muchas personas han comenzado a vivir tranquilamente siguiendo lo que aqui venimos a mostrarte. personas que tenian que medicarse para sentirse mejor y que no podian sanarse en absoluto. Lo mejor es que con estos métodos no es necesario que sepas mucho sobre ejercicios de relajación o meditación. ya que cualquiera podra ver una gran mejora en poco tiempo. curar tu ansiedad de forma definitiva y de forma natural. haciendo click aqui. http://combatir-la-ansiedad.good-info.co
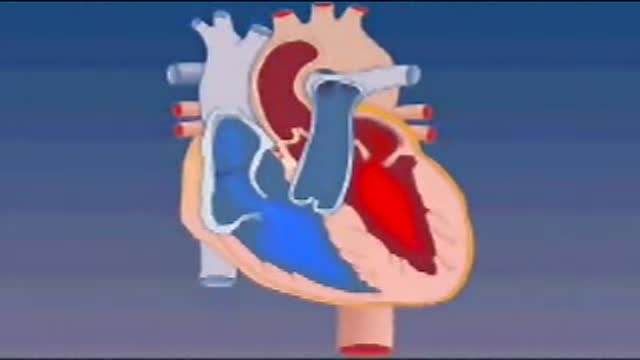
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.

Transcript: Body Restoration (http://stalbertphysiotherapy.com/) has treated over 12,400 patients since it opened its doors in 1992. While embracing new technology and techniques they have not left behind the basic tenets of hands-on healing. If you are injured or have chronic pain, the mission is to help you live pain-free. Relief is a click or a phone call away. Come in for your no obligation exam and find out what will work for you.

Systemic lupus erythematous is an autoimmune condition characterised by damage to organ systems due to autoantibodies and immune complex deposition. Genes, epigenetic changes and environment play a role in its pathogenesis. SLE is a truly multi system disease causing widespread clinical manifestations in almost all organ systems. Autoantibodies in SLE are numerous and mainly include ANA, dsDNA, Sm and others.

Frostbite is an injury caused by freezing of the skin and underlying tissues. First your skin becomes very cold and red, then numb, hard and pale. Frostbite is most common on the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin. Exposed skin in cold, windy weather is most vulnerable to frostbite. But frostbite can occur on skin covered by gloves or other clothing. Frostnip, the first stage of frostbite, doesn't cause permanent skin damage. You can treat very mild frostbite with first-aid measures, including rewarming your skin. All other frostbite requires medical attention because it can damage skin, tissues, muscle and bones. Possible complications of severe frostbite include infection and nerve damage.

A growing number of patients having total knee replacement surgery are 55 or younger. Surgeons at Sunnybrook's Holland Centre perform more than 1,000 total knee replacements each year. Read more: http://sunnyview.sunnybrook.ca..../2011/11/snap-crackl
The menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system like the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy.

Cushing's disease is a serious condition of an excess of the steroid hormone cortisol in the blood level caused by a pituitary tumor secreting adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH is a hormone produced by the normal pituitary gland. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) to produce cortisol, commonly referred to as the stress hormone.
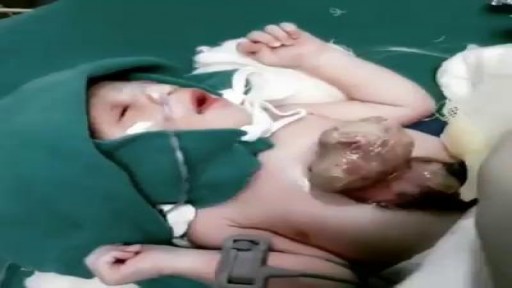
Ectopia cordis is a rare genetic defect. During a baby’s development in utero, their chest wall doesn’t form correctly. It also doesn’t fuse together as it normally would. This prevents the heart from developing where it should, leaving it defenseless and exposed outside of the protection of the chest wall. The defect affects about one in 126,000 births. In partial ectopia cordis, the heart is located outside the chest wall, but just under the skin. The heart can be seen beating through the skin.

Blind loop syndrome (BLS), commonly referred to in the literature as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) or bacterial overgrowth syndrome (BOS), is a state that occurs when the normal bacterial flora of the small intestine proliferates to numbers that cause significant derangement to the normal physiological ...