Top videos

An MRCP scan is a scan that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce pictures of the liver, bile ducts, gallbladder and pancreas. Note: the information below is a general guide only. The arrangements,and the way tests are performed, may vary between different hospitals.
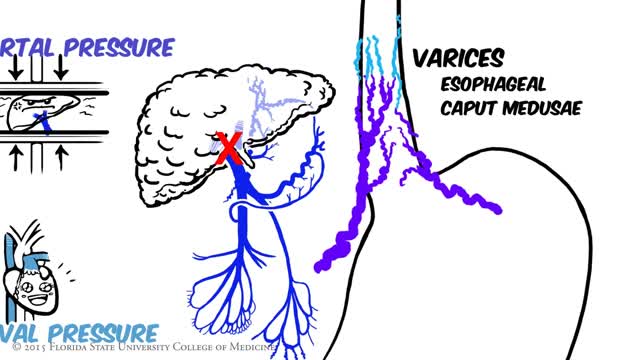
Portal hypertension is an increase in the blood pressure within a system of veins called the portal venous system. Veins coming from the stomach, intestine, spleen, and pancreas merge into the portal vein, which then branches into smaller vessels and travels through the liver.
Dysfunction in the sacroiliac joint, also called the SI joint, can sometimes cause lower back and/or leg pain. Leg pain from sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be particularly difficult to differentiate from radiating leg pain caused by a lumbar disc herniation (sciatica) as they can feel quite similar.
The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.
A pneumothorax is usually caused by an injury to the chest, such as a broken rib or puncture wound. It may also occur suddenly without an injury. A pneumothorax can result from damage to the lungs caused by conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, cystic fibrosis, and pneumonia.
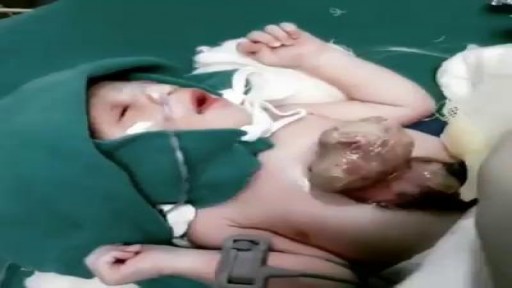
Ectopia cordis is a rare genetic defect. During a baby’s development in utero, their chest wall doesn’t form correctly. It also doesn’t fuse together as it normally would. This prevents the heart from developing where it should, leaving it defenseless and exposed outside of the protection of the chest wall. The defect affects about one in 126,000 births. In partial ectopia cordis, the heart is located outside the chest wall, but just under the skin. The heart can be seen beating through the skin.
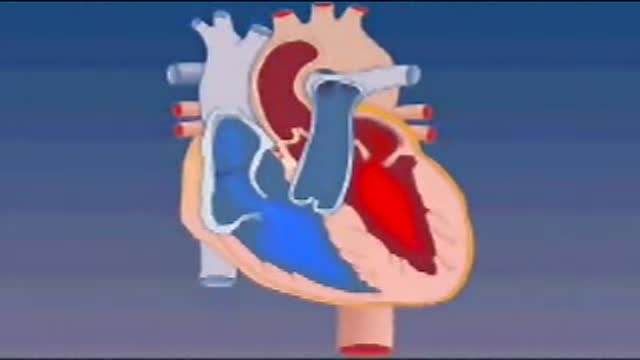
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.

The procedure was performed under wrist block regional anesthesia with tourniquet control. A single Chinese finger trap was used on the thumb with 5 to 8 lb of ongitudinal traction. The arm was held down with wide tape around the tourniquet securing it to the hand table to serve as countertraction. A shoulder holder, rather than a traction tower, was used to facilitate fluoroscopic intervention more easily. The Trapeziometacarpal joint was detected by palpation. Joint distension was achieved by injecting 1 to 3 mL of normal saline (Fig. 1). It is important to distally direct the needle approximately 20 degrees to clear the dorsal flare of the metacarpal base and enter the joint capsule. This course should be reproduced upon entering with arthroscopic sleeve/ trocar assembly to minimize iatrogenic cartilage injury. Fluid distention is important to facilitate this. The incision for the 1-R (radial) portal, used for proper assessment of the dorsoradial ligament, posterior oblique ligament, and ulnar collateral ligament, was placed just volar to the abductor pollicis longus tendon. The incision for the 1-U (ulnar) portal, for better evaluation of the anterior oblique ligament and ulnar collateral ligament, was made just ulnar to the extensor pollicis brevis tendon. A short-barrel, 1.9-mm, 30- degree inclination arthroscope was used for complete visualization of the CMC joint surfaces, capsule, and ligaments, and then appropriate management was done, as dictated by the stage of the arthritis detected (Fig. 2A). A full-radius mechanical shaver with suction was used in all the cases, particularly for initial debridement and visualization. Most of the cases were augmented with radiofrequency ablation to perform a thorough synovectomy and radiofrequency was also used to perform chondroplasty in the cases with focal articular cartilage wear or fibrillation. Chondroplasty refers to thedebridement of the fibrillated cartilage to improve vascularity of the cartilage and enhance the growth of fibrocartilage. Ligamentous laxity and capsular attenu- ation were treated with thermal capsulorraphy using a radiofrequency shrinkage probe. We were careful to avoid thermal necrosis; hence, a striping technique was used to tighten the capsule of the lax joints. The striping technique refers to thermal shrinkage performed in longitudinal stripes on the lax capsule, so as to leave vascular zones between the stripes; hence, thermal necrosis is prevented. Arthroscopic stage I disease was characterized by synovitis without any cartilage wear, wherein a synovectomy coupled with thermal capsulor- raphy as described was performed.
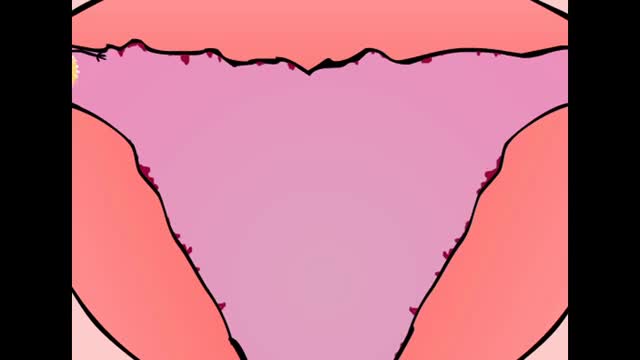
The menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system like the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy.

Bone pain: Pain is the most common sign of bone cancer, and may become more noticeable as the tumor grows. Bone pain can cause a dull or deep ache in a bone or bone region (e.g., back, pelvis, legs, ribs, arms). Early on, the pain may only occur at night, or when you are active.

Cushing's disease is a serious condition of an excess of the steroid hormone cortisol in the blood level caused by a pituitary tumor secreting adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH is a hormone produced by the normal pituitary gland. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) to produce cortisol, commonly referred to as the stress hormone.

Pediatric Surgery Day Unit (PSDU)
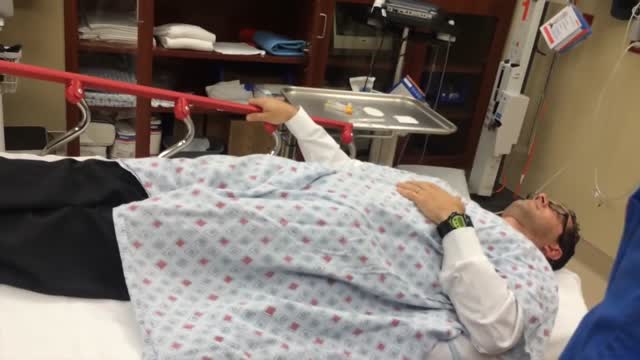
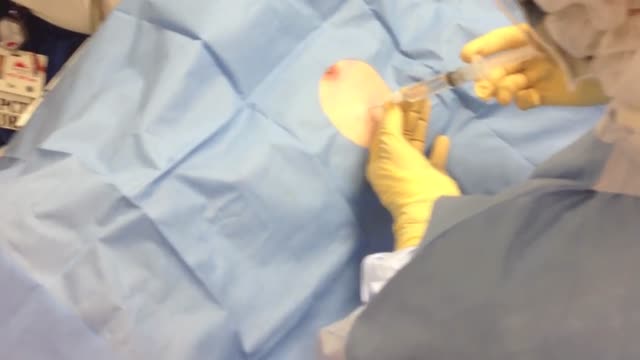
Welcome to Harley Street state-of-the-art Pediatric Surgery Day Unit! We are thrilled to have the opportunity to provide exceptional care and support for our young patients and their families. At our unit, we understand the unique needs and concerns associated with pediatric surgery, and we strive to create a safe and comforting environment for everyone involved.
Compassionate Care by Dedicated Professionals
Lead by Consultant Pediatric Surgeon, Dr. Niall Martin Jones, we will ensure your baby is looked after to the highest possible standards. Our dedicated team and support staff is committed to delivering the highest quality of care. All procedures are performed with local anesthetic and sucrose for comfort. Usually, your baby is so comfortable that she/he will be asleep by the end of the treatment.
Advanced Technology and Safety Measures
Patient safety is our utmost priority. We have implemented rigorous infection control measures to ensure a sterile environment. Our operating rooms are equipped with advanced technology and monitoring systems to ensure the highest standards of safety and precision during surgery. Our anesthesiologists are experienced in administering anesthesia to children, ensuring a smooth and comfortable experience.
learn more https://www.hsmc.ae/our-clinic....s/pediatric-surgery-
#pediatricsurgery #pediatrics #childhealthcare

Blind loop syndrome (BLS), commonly referred to in the literature as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) or bacterial overgrowth syndrome (BOS), is a state that occurs when the normal bacterial flora of the small intestine proliferates to numbers that cause significant derangement to the normal physiological ...