Top videos
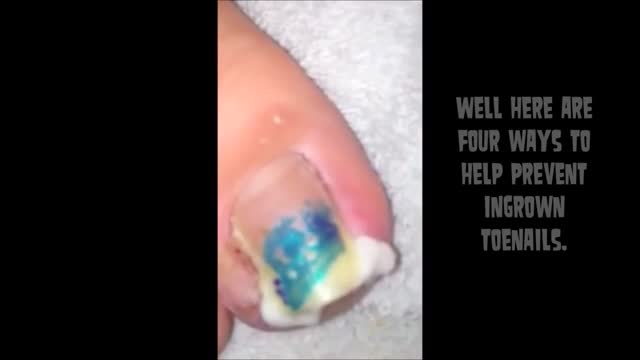
irregular, curved toenails. footwear that places a lot of pressure on the big toes, such as socks and stockings that are too tight or shoes that are too tight, narrow, or flat for your feet. toenail injury, including stubbing your toe, dropping something heavy on your foot, or kicking a ball repeatedly. poor posture. How can ingrowing toenails be prevented? Cut your nails straight across; do not cut them too short or too low at the sides. ... Keep your feet clean and dry. ... Avoid tight shoes and use cotton socks rather than synthetic. If you have diabetes, you should take extra care when cutting your nails:

Blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury.

An MRCP scan is a scan that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce pictures of the liver, bile ducts, gallbladder and pancreas. Note: the information below is a general guide only. The arrangements,and the way tests are performed, may vary between different hospitals.
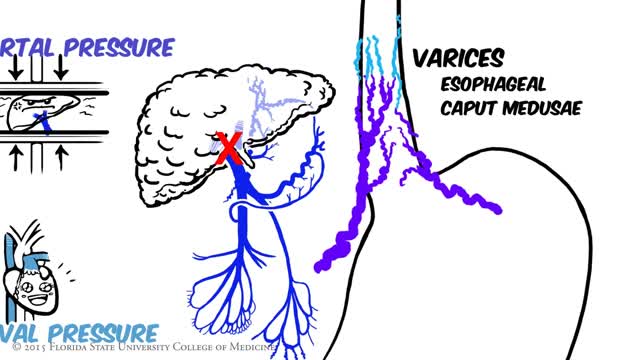
Portal hypertension is an increase in the blood pressure within a system of veins called the portal venous system. Veins coming from the stomach, intestine, spleen, and pancreas merge into the portal vein, which then branches into smaller vessels and travels through the liver.
The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.
A pneumothorax is usually caused by an injury to the chest, such as a broken rib or puncture wound. It may also occur suddenly without an injury. A pneumothorax can result from damage to the lungs caused by conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, cystic fibrosis, and pneumonia.
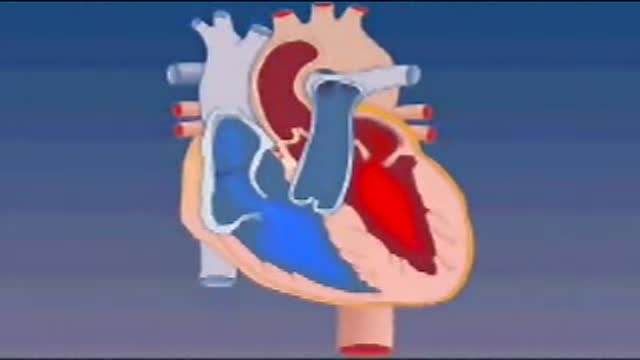
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
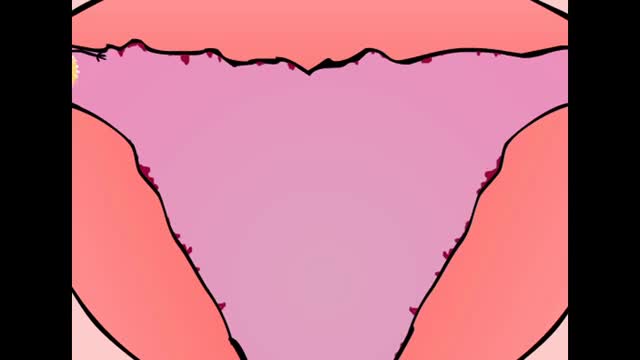
The menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system like the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy.

Bone pain: Pain is the most common sign of bone cancer, and may become more noticeable as the tumor grows. Bone pain can cause a dull or deep ache in a bone or bone region (e.g., back, pelvis, legs, ribs, arms). Early on, the pain may only occur at night, or when you are active.

Cushing's disease is a serious condition of an excess of the steroid hormone cortisol in the blood level caused by a pituitary tumor secreting adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH is a hormone produced by the normal pituitary gland. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) to produce cortisol, commonly referred to as the stress hormone.

Atherosclerosis is a process in which blood, fats such as cholesterol, and other substances build up on your artery walls. Eventually, deposits called plaques may form. The deposits may narrow — or block — your arteries. These plaques can also rupture, causing a blood clot.

Tongue and lip-tie are common causes of nipple pain, uneven breast drainage, slow weight gain and low milk supply. Many physicians do not properly assess for tongue or lip-tie or recognize their impact on the breastfeeding relationship, leaving babies vulnerable to early weaning. Ultrasound studies have shown that the tongue movements used by tongue-tied babies are qualitatively different from those used by by babies who are not tongue-tied. These movements are not as effective at removing milk from the breast and can cause significant pain and nipple damage. In these studies, tongue-tied babies also did not draw the nipple as deeply into the mouth as babies who were not tongue-tied.

Blind loop syndrome (BLS), commonly referred to in the literature as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) or bacterial overgrowth syndrome (BOS), is a state that occurs when the normal bacterial flora of the small intestine proliferates to numbers that cause significant derangement to the normal physiological ...