Top videos
Bulimia (boo-LEE-me-uh) nervosa, commonly called bulimia, is a serious, potentially life-threatening eating disorder. People with bulimia may secretly binge — eating large amounts of food — and then purge, trying to get rid of the extra calories in an unhealthy way. For example, someone with bulimia may force vomiting or engage in excessive exercise. Sometimes people purge after eating only a small snack or a normal-size meal.
Bell's palsy is a form of facial paralysis resulting from damage or trauma to the facial nerves. The facial nerve-also called the 7th cranial nerve-travels through a narrow, bony canal (called the Fallopian canal) in the skull, beneath the ear, to the muscles on each side of the face. For most of its journey, the nerve is encased in this bony shell. Each facial nerve directs the muscles on one side of the face, including those that control eye blinking and closing, and facial expressions such as smiling and frowning. Additionally, the facial nerve carries nerve impulses to the lacrimal or tear glands, the saliva glands, and the muscles of a small bone in the middle of the ear called the stapes. The facial nerve also transmits taste sensations from the tongue. When Bell's palsy occurs, the function of the facial nerve is disrupted, causing an interruption in the messages the brain sends to the facial muscles. This interruption results in facial weakness or paralysis. Bell's palsy is named for Sir Charles Bell, a 19th century Scottish surgeon who described the facial nerve and its connection to the condition. The disorder, which is not related to stroke, is the most common cause of facial paralysis. Generally, Bell's palsy affects only one of the paired facial nerves and one side of the face, however, in rare cases, it can affect both sides.
Middle cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the middle cerebral artery (MCA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the lateral aspects of frontal, temporal and parietal lobes, the corona radiata, globus pallidus, caudate and putamen. The MCA is the most common site for the occurrence of ischemic stroke.[1] Depending upon the location and severity of the occlusion, signs and symptoms may vary within the population affected with MCA syndrome. More distal blockages tend to produce milder deficits due to more extensive branching of the artery and less ischemic response. In contrast, the most proximal occlusions result in widespread effects that can lead to significant cerebral edema, increased intracranial pressure, loss of consciousness and could even be fatal.[1] In such occasions, mannitol (osmotic diuretic) or hypertonic saline are given to draw fluid out of the oedematus cerebrum to minimise secondary injury. Hypertonic saline is better than mannitol, as mannitol being a diuretic will decrease the mean arterial pressure and since cerebral perfusion is mean arterial pressure minus intracranial pressure, mannitol will also cause a decrease in cerebral perfusion. Contralateral hemiparesis and hemisensory loss of the face, upper and lower extremities is the most common presentation of MCA syndrome.[1] Lower extremity function is more spared than that of the faciobrachial region.[2] The majority of the primary motor and somatosensory cortices are supplied by the MCA and the cortical homunculus can, therefore, be used to localize the defects more precisely.it is important to note that middle cerebral artery lesions mostly affect the dominant hemisphere i.e. the left cerebral hemisphere.
Today, hair transplant physicians are able to make use of different techniques to extract and transplant large numbers of hair follicles (follicular units). There are two primary techniques for hair transplantation currently in use. The FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and the FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) methods. They differ primarily in the way hair follicles are extracted from the donor area. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) The FUT process involves removing a small strip of tissue from the back of the head, from which the donor hair follicles will be extracted. The hair follicles are harvested from the strip by a skilled clinical team before being individually transplanted to the recipient areas. In most cases, and especially cases of advanced hair loss, FUT is the preferred method because it allows the physician to fully utilize the scalp area to deliver results consistent with patient expectations. FUT typically allows for the greatest number of grafts to be transplanted in a single session. Pain Management Some patients report higher levels of discomfort with FUT procedures compared to FUE due the potential swelling in the area where the strip of tissue was removed, but both methods have a very manageable recovery period and pain medication can be prescribed by your physician if needed. Both techniques of hair transplantation are relatively simple. Hair transplantation procedures are outpatient surgeries with some patients going back to work as soon as the very next day. Scarring The FUT strip extraction method typically results in a very narrow linear scar in the back of the head (typically 1mm in diameter or less in size). Since the scar is very thin, it’s easily concealed by all but the shortest of haircut styles. A short to moderate crop setting on most clippers is sufficient to conceal the scar for the majority of patients, and over time the scar will become less noticeable as it fades. Costs The industry norm for pricing is on a per-graft basis. This allows each individual to pay for only what they need and receive in number of grafts, and not a flat rate that in the end may cost you more. The per-graft cost of a FUT procedure is generally lower than that of a FUE procedure. Lately however, in response to the rising popularity of the FUE technique, many hair transplantation clinics have started lowering the per graft cost on FUE procedures, so that the cost difference between the two types of procedure are not as much as most people think. The costs of medical procedures always vary by patients’ conditions, needs and objectives. For the most accurate assessment of your hair loss and the associated cost of your hair restoration, you will need to speak to a physician. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) In an FUE hair transplantation, each follicular unit is individually taken directly from the scalp with no strip of tissue being removed. Hair follicles are removed in a random fashion and the result is less density in the donor area that many say is not even noticeable. This is the main difference between FUE & FUT. Since follicles are removed one at a time, fewer follicles can be harvested during a typical session, making FUE a better option to restore hair in smaller cases (number of grafts) compared to the traditional FUT method. FUE is constantly evolving and what was once utilized for only smaller cases is now being utilized for larger and larger cases. Some people that prefer the FUE method may have the option of splitting their procedure into two days in order to complete their recommended transplantation goals. Pain Management With no stitches required and no linear scar left to heal, FUE procedures do have a faster healing time and less post-procedure discomfort compared to the traditional FUT procedure. Scarring Since FUE procedures involve removing hairs individually from the scalp, there is no linear scar left behind. However, there will be tiny 1mm in diameter or less puncture marks that tend to heal by themselves after scabbing-over in the days following the procedure. These tiny wounds typically heal within three to seven days. Costs Since the physician must remove each hair follicle individually, the time-sensitive nature of an FUE procedure typically makes it more expensive than an FUT procedure. As stated earlier, FUE technology is improving as well as gaining popularity and many hair restoration practices (including Bosley) have started to lower the cost per graft price for FUE procedures. Nowadays, the cost difference between a FUE and a FUT procedures is less disparate.
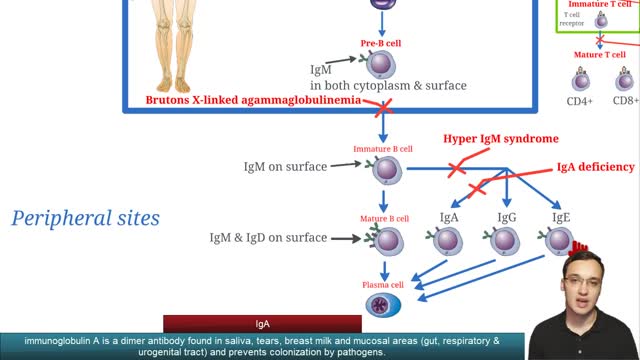
Selective immunoglobulin A deficiency (SIgAD) is a primary immunodeficiency disease and is the most common of the primary antibody deficiencies.[1] Total immunoglobulin A deficiency (IgAD) is defined as an undetectable serum immunoglobulin A (IgA) level at a value < 5 mg/dL (0.05 g/L) in humans. Partial IgAD refers to detectable but decreased IgA levels that are more than 2 standard deviations below normal age-adjusted means.[2, 3] IgAD is commonly associated with normal B lymphocytes in peripheral blood, normal CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and, usually, normal neutrophil and lymphocyte counts. Anti-IgA autoantibodies of the IgG and/or IgE isotype may be present. Peripheral blood may also be affected by autoimmune cytopenias, eg, autoimmune thrombocytopenia,[4, 5] and patients may have other autoimmune phenomena. IgA was first identified by Graber and Williams in 1952; ten years later, the first patients with IgAD were described. IgAD is a heterogeneous disorder, and the results of intensive study are beginning to elucidate genetic loci and molecular pathogenesis that contribute to various subtypes of this disorder. Several lines of evidence suggest that, in many cases, IgAD and common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) have a common pathogenesis, which is discussed further in Pathophysiology. Other data indicate different genetic risk factors. Family studies show variable inheritance patterns. Familial inheritance of IgAD occurs in approximately 20% of cases,[6] and, within families, IgAD and CVID are associated.[7, 8] Many IgAD patients are asymptomatic (ie, "normal" blood donors) and are identified by finding a laboratory abnormality, without any apparent associated clinical disease. Some patients with IgAD may have the following associated conditions: (1) deficits in one or more immunoglobulin G (IgG) subclasses (this accounts for 20-30% of IgA-deficient patients, many of whom may have total IgG levels within the normal range) or (2) a deficient antibody response to pneumococcal immunization (specific polysaccharide antibody deficiency [SPAD]). Some patients with IgAD later develop CVID, and family members of patients with CVID may have only selective IgAD. Characterization of the receptor for the transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI), encoded by the gene TNFRSF13B ( tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13B), suggests that people with the C104, A181E, and ins204A variants may be at risk for IgAD that progresses to CVID.[9] Primary IgAD is permanent, and below-normal levels have been noted to remain static and persist after 20 years of observation.[10] A recent report documents a rare case of reversion.[11] Environmental factors such as drugs or infections can cause IgAD, but this form is reversible in more than half the cases (see Causes). Although individuals with IgAD have largely been considered healthy, recent studies indicate a higher rate of symptoms. A 20-year follow-up study that compared 204 healthy blood donors with incidentally identified IgAD to 237 healthy subjects with normal IgA levels demonstrated that 80% of IgAD donors and 50% of control subjects had episodes of infections, drug allergy, or autoimmune or atopic disease. Severe respiratory tract infections occurred in 26% of IgAD subjects, in 24% of subjects with decreased IgA levels, and in 8% of control subjects; however, the incidence of life-threatening infections was not increased. IgAD is more common in adult patients with chronic lung disease than in healthy age-matched control subjects.[12] Patients with IgAD are at some increased risk of developing severe reactions after receiving blood products.[13, 14, 15] IgG anti-IgA antibodies may cause severe transfusion reactions if patients with IgAD are given whole blood; therefore, IgA-poor blood or washed red cells are preferred for those patients. IgA-deficient patients with immunoglobulin E (IgE)–class anti-IgA antibodies are at risk for anaphylaxis if they receive blood or intravenous immunoglobulin, but this situation is extremely rare. Individuals with such an unusual profile should receive only low IgA intravenous immunoglobulin preparations. However, caution must be used when administering IGIV to patients with IgAD if their anti-IgA status is unknown. A history devoid of previous blood product administration does not exclude the possibility of anti-IgA antibodies or adverse reactions. Fortunately, appropriate precautions can significantly reduce morbidity (see Treatment). Blood banks can use a simple ELISA screening approach to establish an IgAD blood donor poo
Rapid cycling is a pattern of frequent, distinct episodes in bipolar disorder. In rapid cycling, a person with the disorder experiences four or more episodes of mania or depression in one year
http://destructeur-de-poids.info-pro.co Perdre Des Cuisses, Astuces Pour Maigrir, Objectif Ventre Plat, Exercice Pour Perdre Du Poids. Boire de l’eau est relié au gain de poids Ceci peut sembler vraiment étrange... Mais boire de l'eau serait la raison pourquoi la plupart d'entre nous avons des problèmes à perdre du poids ? Une découverte récente démontre que c'est vrai et que pour perdre du poids... il faut connaître exactement la quantité d'eau à boire... basé sur votre propre corps. En utilisant ce truc simple, les gens ont perdu 15, 20, 25 kilos même, en moins de 2 mois. Découvrez combien d'eau vous avez besoin et commencez à perdre du poids. http://destructeur-de-poids.info-pro.co http://astuce-ventre-plat.blogspot.com/
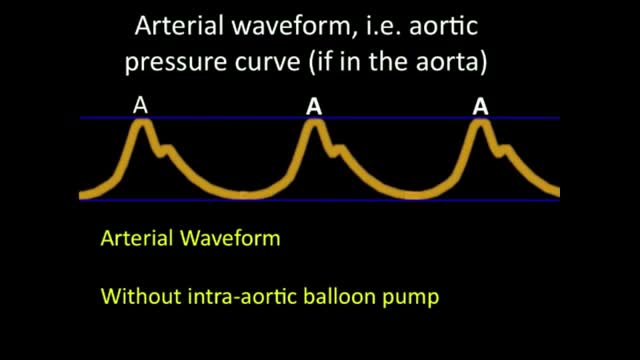
An intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) is a mechanical device that helps the heart pump blood. This device is inserted into the aorta, the body's largest artery. It is a long, thin tube called a catheter with a balloon on the end of it. If you are hospitalized, your doctor may insert an IABP. Your doctor will numb an area of your leg and thread the IABP through the femoral artery in your leg into your aorta. He or she then positions the IABP at the center of your aorta, below your heart. The doctor will use an X-ray machine during this procedure to help accurately position the IABP. Why is it used? An IABP might be used to stabilize a person who is in the hospital for acute mitral valve regurgitation or severe heart failure. An IABP is only used for a short period of time (hours to days). A long-term treatment will likely be needed, such as valve surgery or the insertion of a left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
The term "miniaturization" is widely accepted in our vernacular as a positive step in product development. Reducing components to create less space, product footprint and more affordable medical devices are ongoing objectives for manufacturers today. Jabil strives to integrate new innovative technologies into product design and manufacturing as continual miniaturization of medical devices is a focus of the healthcare thought process. Miniaturization is a constantly moving target. Once a novel, new technology sets a higher bar for miniaturization standards, the next ambitious goal is to achieve an even thinner and smaller device. Industry trends, including minimally invasive surgical devices and home health care delivery, demand more sophisticated medical portable devices and easy-to-use electronics which may not be a core competency of medical device manufacturers.
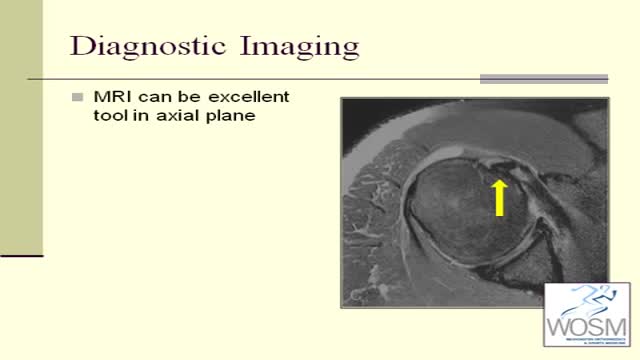
Biceps tendonitis, also called bicipital tendonitis, is inflammation in the main tendon that attaches the top of the biceps muscle to the shoulder. The most common cause is overuse from certain types of work or sports activities.
What Your Handwriting Says About You
In this educational clip, dr hosnani's rhinoplasty video is shown
Too much cholesterol in the blood can lead to cardiovascular disease. Heart disease is the No. 1 cause of death in the United States. Over 2,100 Americans die of cardiovascular disease each day, an average of one death every 40 seconds. The good news is, you can lower your cholesterol and reduce your risk of heart disease and stroke. Working with your doctor is key. It takes a team to develop and maintain a successful health program. You and your healthcare professionals each play an important role in maintaining and improving your heart health. Work with your doctor to determine your risk and the best approach to manage it. In all cases, lifestyle changes are important to reduce your risk for heart attack and stroke. In some cases, cholesterol-lowering statin medicines may also provide benefit. Learn how to make diet and lifestyle changes easy and lasting. Also make sure you understand instructions for taking medication because it won't work if you don't take it as directed. Lifestyle Changes Your diet, weight, physical activity and exposure to tobacco smoke all affect your cholesterol level. Know Your Fats Knowing which fats raise LDL cholesterol and which ones don't is the first step in lowering your risk of heart disease.
This video narrates the story of a girl who travels to Iran for doing a nose surgery.
baby wrapping
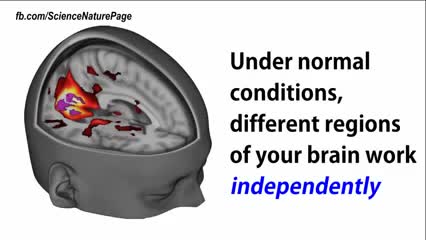
Scientists reveal how LSD alters your mind.
Blackheads, Cysts & Pimples
Chemokuren geven neuropathische pijnen. Behandeling met het supplement palmitoylethanolamide en topicale analgetische creme geven het volgende resultaat
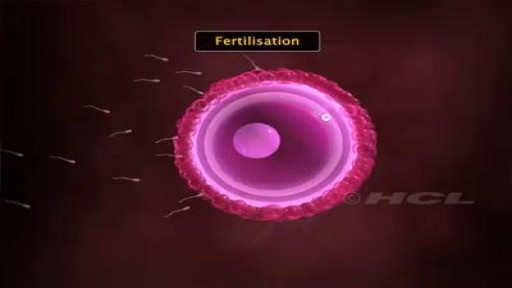
Millions of sperms are deposited into the vagina during sexual intercourse. The sperms make their way through the cervix into the uterus and then on to the fallopian tubes. As they swim along this way their numbers decline. Only a few hundred sperm will get close to the egg. During the trip, sperm prepare themselves to meet the egg by subtle alterations of their heads and movement patterns. Once inside the fallopian tube, the sperm attracts the egg by releasing a chemical. The egg is surrounded by a protective covering called the zona pellucida, which allows only one sperm to penetrate it. Once inside the egg, the head of the fertilizing sperm releases its genetic contents, which fuses with the nucleus of the egg. Fertilisation is now complete. Sperm are able to survive for 2-3 days within the female's reproductive tract. The length of the time that a woman's egg can be fertilized by a man's sperm ranges from 12-24 hours.