Top videos
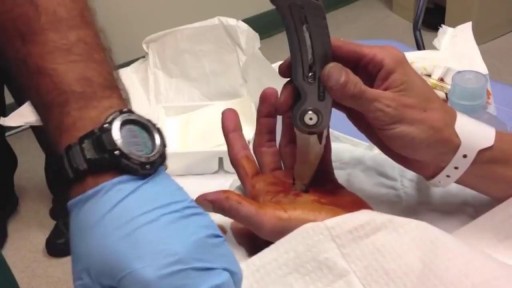
This video may contain images of a medical doctor providing emergency care for a patient.
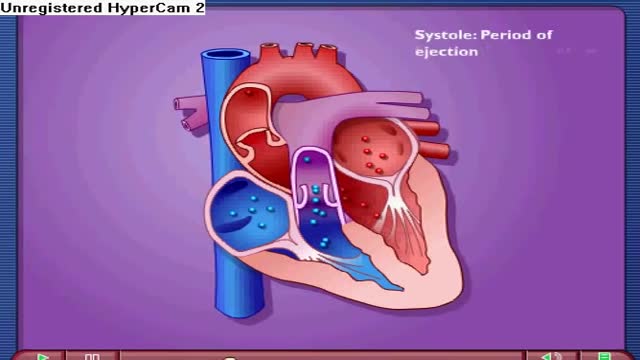
Near the end of diastole, the ventricles nearly fill with blood, and then the atria contract, adding even more volume to the ventricles. The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole is referred to as the end-diastolic volume. The other phase of the cardiac cycle is called systole.
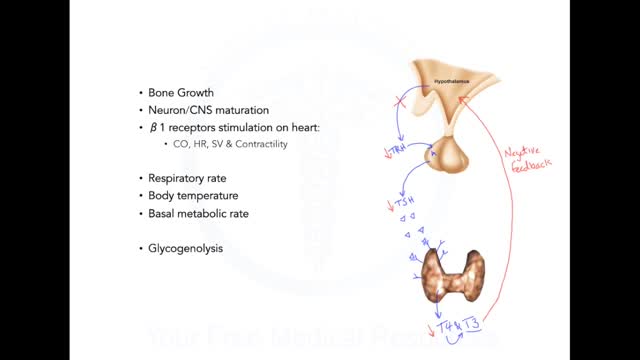
Graves' disease is an immune system disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism). Although a number of disorders may result in hyperthyroidism, Graves' disease is a common cause. Because thyroid hormones affect a number of different body systems, signs and symptoms associated with Graves' disease can be wide ranging and significantly influence your overall well-being. Although Graves' disease may affect anyone, it's more common among women and before the age of 40. The primary treatment goals are to inhibit the overproduction of thyroid hormones and lessen the severity of symptoms.
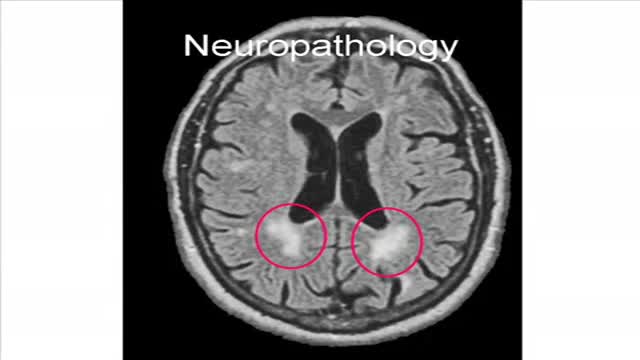
Binswanger's disease is a type of vascular dementia that involves white matter infarcts. Patients with this disease usually present with apathy, agitation, and bilateral corticospinal or bulbar signs
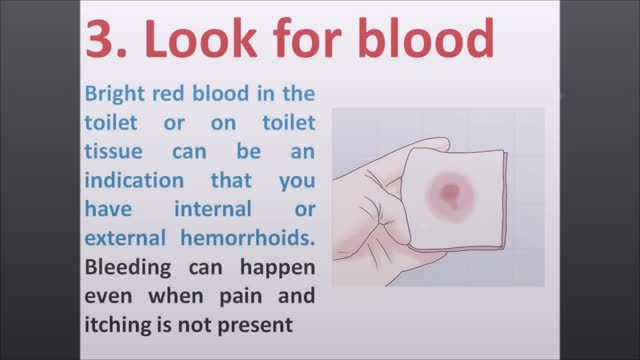
Most of the time, treatment for hemorrhoids involves steps that you can take on your own, such as lifestyle modifications. But sometimes medications or surgical procedures are necessary. Medications If your hemorrhoids produce only mild discomfort, your doctor may suggest over-the-counter creams, ointments, suppositories or pads. These products contain ingredients, such as witch hazel or hydrocortisone, that can relieve pain and itching, at least temporarily. Don't use an over-the-counter cream or other product for more than a week unless directed by your doctor. These products can cause side effects, such as skin rash, inflammation and skin thinning. Minimally invasive procedures If a blood clot has formed within an external hemorrhoid, your doctor can remove the clot with a simple incision, which may provide prompt relief. For persistent bleeding or painful hemorrhoids, your doctor may recommend another minimally invasive procedure. These treatments can be done in your doctor's office or other outpatient setting. Rubber band ligation. Your doctor places one or two tiny rubber bands around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its circulation. The hemorrhoid withers and falls off within a week. This procedure — called rubber band ligation — is effective for many people. Hemorrhoid banding can be uncomfortable and may cause bleeding, which might begin two to four days after the procedure but is rarely severe. Injection (sclerotherapy). In this procedure, your doctor injects a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid tissue to shrink it. While the injection causes little or no pain, it may be less effective than rubber band ligation. Coagulation (infrared, laser or bipolar). Coagulation techniques use laser or infrared light or heat. They cause small, bleeding, internal hemorrhoids to harden and shrivel. While coagulation has few side effects, it's associated with a higher rate of hemorrhoids coming back (recurrence) than is the rubber band treatment. Surgical procedures If other procedures haven't been successful or you have large hemorrhoids, your doctor may recommend a surgical procedure. Surgery can be performed on an outpatient basis or you may need to stay in the hospital overnight. Hemorrhoid removal. During a hemorrhoidectomy, your surgeon removes excessive tissue that causes bleeding. Various techniques may be used. The surgery may be done with a local anesthetic combined with sedation, a spinal anesthetic or a general anesthetic. Hemorrhoidectomy is the most effective and complete way to treat severe or recurring hemorrhoids. Complications may include temporary difficulty emptying your bladder and urinary tract infections associated with this problem. Most people experience some pain after the procedure. Medications can relieve your pain. Soaking in a warm bath also may help. Hemorrhoid stapling. This procedure, called stapled hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy, blocks blood flow to hemorrhoidal tissue. Stapling generally involves less pain than hemorrhoidectomy and allows an earlier return to regular activities. Compared with hemorrhoidectomy, however, stapling has been associated with a greater risk of recurrence and rectal prolapse, in which part of the rectum protrudes from the anus. Talk with your doctor about what might be the best option for you.
Dr. Arthur Handal explains how and why your surgeon might suggest less or more than the procedure you originally planned for.
Cancer Patient Dances in OR before her Surgery
Best Position for Getting Pregnant Fast
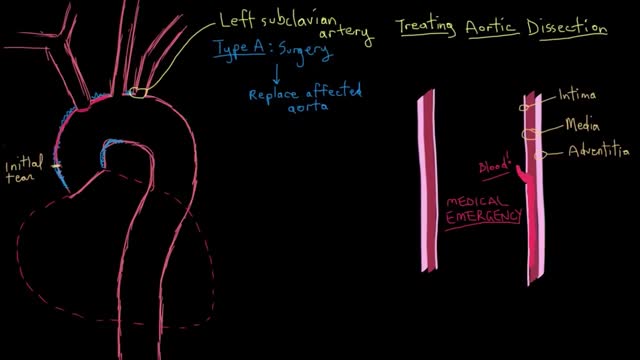
Acute aortic dissection can be treated surgically or medically. In surgical treatment, the area of the aorta with the intimal tear is usually resected and replaced with a Dacron graft. Emergency surgical correction is the preferred treatment for Stanford type A (DeBakey type I and II) ascending aortic dissection. It is also preferred for complicated Stanford type B (DeBakey type III) aortic dissections with clinical or radiologic evidence of the following conditions: Propagation (increasing aortic diameter) Increasing size of hematoma Compromise of major branches of the aorta Impending rupture Persistent pain despite adequate pain management Bleeding into the pleural cavity Development of saccular aneurysm
Specific treatment for menorrhagia is based on a number of factors, including: Your overall health and medical history The cause and severity of the condition Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures or therapies The likelihood that your periods will become less heavy soon Your future childbearing plans Effects of the condition on your lifestyle Your opinion or personal preference Drug therapy for menorrhagia may include: Iron supplements. If you also have anemia, your doctor may recommend that you take iron supplements regularly. If your iron levels are low but you're not yet anemic, you may be started on iron supplements rather than waiting until you become anemic. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen (Aleve), help reduce menstrual blood loss. NSAIDs have the added benefit of relieving painful menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea). Tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid (Lysteda) helps reduce menstrual blood loss and only needs to be taken at the time of the bleeding. Oral contraceptives. Aside from providing birth control, oral contraceptives can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce episodes of excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding. Oral progesterone. When taken for 10 or more days of each menstrual cycle, the hormone progesterone can help correct hormone imbalance and reduce menorrhagia. The hormonal IUD (Mirena). This intrauterine device releases a type of progestin called levonorgestrel, which makes the uterine lining thin and decreases menstrual blood flow and cramping. If you have menorrhagia from taking hormone medication, you and your doctor may be able to treat the condition by changing or stopping your medication.
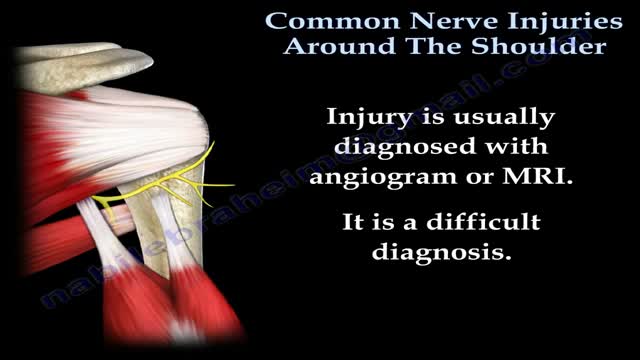
The shoulder and arm receives its nerve supply through the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus is a complex network of nerves which come out of the neck, passes down to the front of the shoulder and then splits into many separate nerves to travel to different muscles and parts of the skin. Normally an arm movement is produced by initially thinking of the movement, then a message passes from the brain, down through the spinal cord to the appropriate nerve. Then the instruction to move is conveyed along the nerve to the specific arm muscle which then contracts and moves the arm.
Inserting the Enlite Sensor with insulin pump
Overactive bladder syndrome is common. Symptoms include an urgent feeling to go to the toilet, going to the toilet frequently and sometimes leaking urine before you can get to the toilet (urge incontinence). Treatment with bladder training often cures the problem. Sometimes medication may be advised in addition to bladder training to relax the bladder.
It flattens the natural curve of the spine, which can lead to lower back pain. Sleeping all night with the head turned to one side also strains the neck. If this is the preferred position, try using pillows to gradually train the body to sleep on one side
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), in which there is a persistent communication between the descending thoracic aorta and the pulmonary artery that results from failure of normal physiologic closure of the fetal ductus (see image below), is one of the more common congenital heart defects.
New Treatment for sinusitis. Yamik procedure
Swelling is a typical symptom of lymphedema and commonly affects legs and arms. Compression stockings work to encourage the movement of lymph out of an affected limb. Lymphedema is incurable. However, treatment can help reduce the swelling and pain
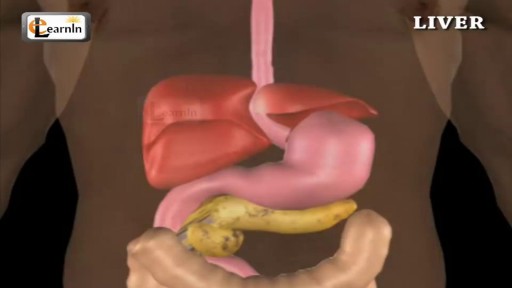
The liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes a product called bile. ... Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion. Production of certain proteins for blood plasma.