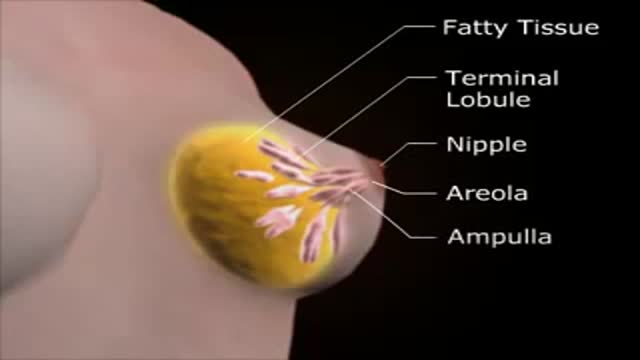
Top videos

Dr. Alex Campbell and Dr. Carolina Restrepo of Premium Care Plastic Surgery in Cartagena, Colombia perform a Mommy Makeover on an international patient. Watch the procedure as Dr. Campbell and Dr. Restrepo work together to offer this patient more surgery in less time, which leads to a quicker recovery and better results.

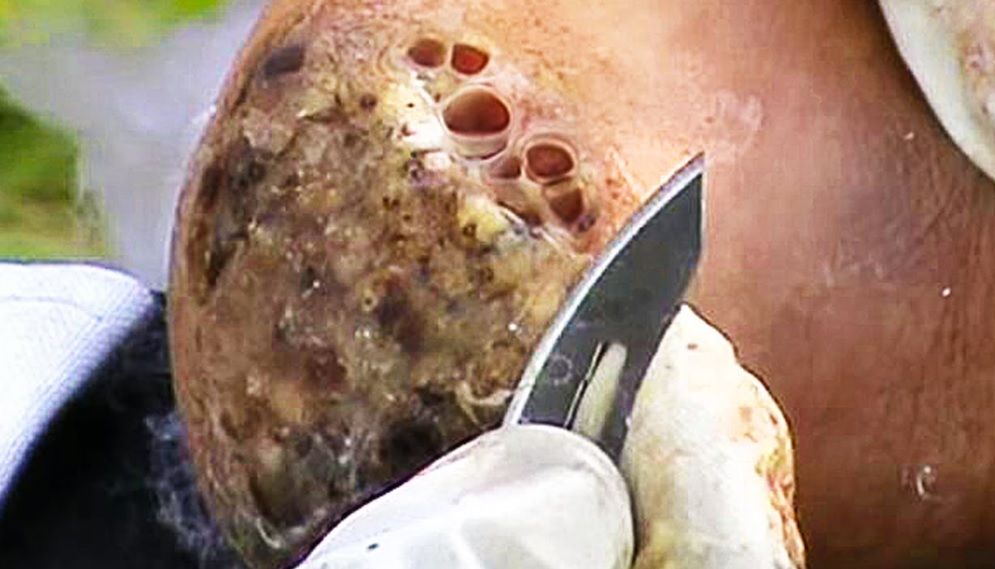
Video shows another patient on the second day of surgery by Dr. Desarda technique of inguinal hernia repair without mesh.
“Complete cure from groin hernia is now possible with Dr.Desarda's repair technique.......”
Mesh is a foreign body. Therefore, its use in hernia repairs is known to cause all sorts of complications like pain, recurrence, infection etc. We have developed an innovative new technique of inguinal hernia repair without mesh. It uses your own body muscle for repair and gives virtually complete cure from inguinal hernia problem. An undetached strip of the external oblique aponeurosis is stitched on the weak area between the muscle arch and the inguinal ligament to form a new, strong and physiologically dynamic posterior wall that gives protection and prevents re-herniation. Normally patient goes home in a day after surgery and can drive car and go to office in 3-4 days time. This "Dr.Desarda's hernia repair" is now followed in many countries all over the world. We are surprised to see the enquiries from many patients in the developed countries asking for this repair in their country. This is because this operation does not use any foreign body like mesh for repair and therefore there are no complications that are seen in mesh repairs. A visit to Topix or other hernia forums show thousands of posts showing sufferings of many patients due to mesh repairs. But still why surgeons from developed countries are interested in mesh repairs is a big question for us.
Please visit our website for more details: http://herniasurgery.tripod.com Our cell number: +91 9373322178

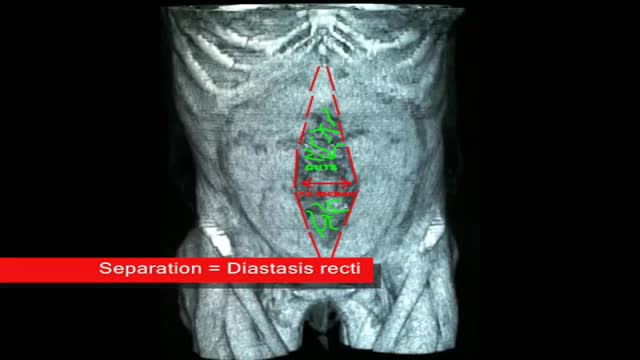
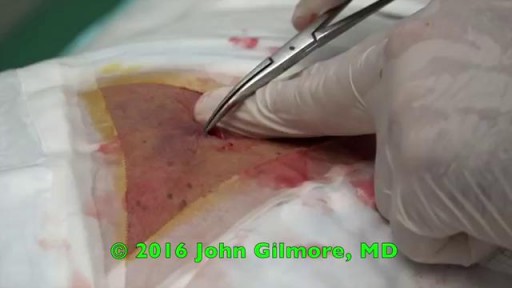
Diastasis recti often occurs during pregnancy and can persist after pregnancy. It affects core strength and the appearance of the abdominal muscles.
Dr. Erick Sanchez repairs the abdominal muscles with every tummy tuck. This short video shows the muscle repair portion of the surgery with a bonus after photo at the end!
To request a consultation with Dr. Sanchez, visit sanchezplasticsurgery.com and click Request a Consultation. Fill out the form and someone will get in touch with you to answer all your questions.
Expected cost can be found at the bottom of each procedure page on our website.

It’s not tummy tuck procedure.. it’s liposuction only.. don’t get confused with both procedure..
#beforeandafter #kmc #nose #aesthetic #antiaging #beauty #drhabibhairtransplant #peshawar #nose #islamabad #swat #kohat #nowshehra #karakin #mardan
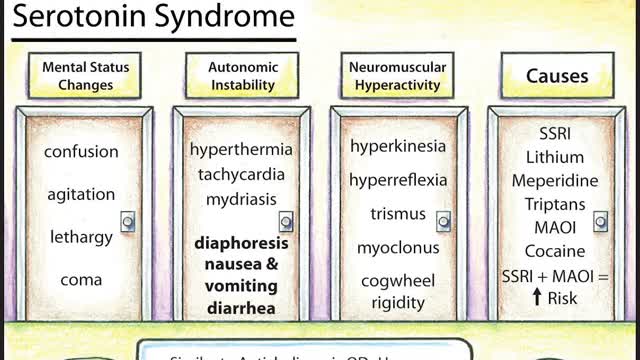
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include a classic triad of mental status changes (eg, anxiety, delirium, confusion, restlessness), autonomic dysregulation (eg, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, diarrhea, mydriasis), and neuromuscular hyperactivity (eg, hyperreflexia, tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, ocular clonus). Serotonin syndrome is clinically diagnosed and laboratory tests are used to rule out other etiologies. It usually occurs due to inadvertent interactions between drugs, therapeutic use of multiple serotonergic agents, or serotonergic medication overdose. Treatment involves discontinuation of serotonergic drugs, supportive measures, and sedation with benzodiazepines. In severe cases, a serotonin antagonist (cyproheptadine) may be used.

You can now test your knowledge with a free lesson quiz on NURSING.com!
Click here for your free quiz: https://bit.ly/3HwJr8t
Stoma Care- Changing a Colostomy Bag (Nursing Skills)
FREE Nursing School Cheat Sheets at: http://www.NURSING.com
Get the full lesson on Stoma Care here:
05.01 Stoma Care (Colostomy bag) | NURSING.com
Check out our new Nurse Care Plan Lessons here:
https://bit.ly/3BPRfPL
Watch the Nursing Skills Course Introduction here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-00-01-course-int
Get Access to Thousands of Lessons here:
https://nursing.com/courses/
Welcome to the NURSING Family, we call it the most supportive nursing cohort on the planet.
At NURSING.com, we want to help you remove the stress and overwhelm of nursing school so that you can focus on becoming an amazing nurse.
Check out our freebies and learn more at: (http://www.nursing.com)
Stoma Care- Changing a Colostomy Bag (Nursing Skills)
In this video, we’re going to talk about stoma care. Now, the wafer and bag for an ostomy only NEEDS to be changed every 3 days, or if it’s leaking. But, you still need to be able to assess the stoma itself. In this case we’re going to show you how to replace the bag and clean and assess the stoma. Start by putting a towel under the patient on the side of the stoma. We love you guys! Go out and be your best selves today! And, as always, happy nursing!
Bookmarks:
0.05 Introduction to Stoma Care
0:20 Assessing the stoma
0:47 Cleaning the stoma
1:12 Inspecting the stoma
1:25 Measuring and cutting the stoma
2:00 Applying and sealing the bag
2:35 Documentation
2:41 Outro
Visit us at https://nursing.com/medical-disclaimer/ for disclaimer information.
NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, INC. and hold no affiliation with NURSING.com.