Top videos
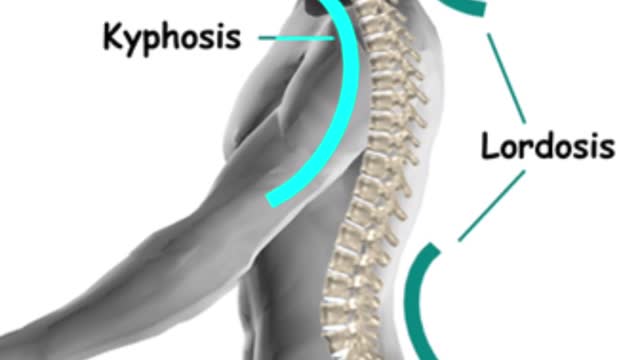
If you look at someone’s back, you’ll see that the spine runs straight down the middle. When a person has scoliosis, their backbone curves to the side. The angle of the curve may be small, large or somewhere in between. But anything that measures more than 10 degrees is considered scoliosis. Doctors may use the letters “C” and “S” to describe the curve of the backbone. You probably don’t look directly at too many spines, but what you might notice about someone with scoliosis is the way they stand. They may lean a little or have shoulders or hips that look uneven. What Causes Scoliosis? In as many as 80% of cases, doctors don’t find the exact reason for a curved spine. Scoliosis without a known cause is what doctors call “idiopathic.” Some kinds of scoliosis do have clear causes. Doctors divide those curves into two types -- structural and nonstructural. In nonstructural scoliosis, the spine works normally, but looks curved. Why does this happen? There are a number of reasons, such as one leg’s being longer than the other, muscle spasms, and inflammations like appendicitis. When these problems are treated, this type of scoliosis often goes away.

NTIS refers to a syndrome found in seriously ill or starving patients with low fT3, usually elevated RT3, normal or low TSH, and if prolonged, low fT4. It is found in a high proportion of patients in the ICU setting, and correlates with a poor prognosis if TT4 is <4ug/dl. The patho-physiology includes suppression of TRH release, reducedT3 and T4 turnover, reduction in liver generation of T3, increased formation of RT3, and tissue specific down-regulation of deiodinases, transporters, and TH receptors. Although long debated, tissue TH levels are definitely reduced, and tissue hypothyroidism is presumably present. This is often not clinically evident because of the brief duration, and reduced but not absent tissue levels of TH. Although recognized for nearly 4 decades, interpretation of the syndrome is contested, because of lack of data. Some observes, totally without data, argue that it is a protective response and should not be treated. Other observers (as in this review) present available data suggesting, but not proving, that thyroid hormone replacement is appropriate, not harmful, and may be beneficial. The best form of treatment (TRH,TSH,or T3+T4) and possible accompanying treatments (GHRH, Cortisol, nutrition, insulin) lack consensus. In this review current data are laid out for reader’s review and judgment.

The vast majority of glucocorticoid activity in most mammals is from cortisol, also known as hydrocortisone. Corticosterone, the major glucocorticoid in rodents, is another glucocorticoid. Cortisol binds to the glucocorticoid receptor in the cytoplasm and the hormone-receptor complex is then translocated into the nucleus, where it binds to its DNA response element and modulates transcription from a battery of genes, leading to changes in the cell's phenotype. Only about 10% of circulating cortisol is free. The remaining majority circulates bound to plasma proteins, particularly corticosteroid-binding globulin (transcortin). This protein binding likely decreases the metabolic clearance rate of glucocorticoids and, because the bound steroid is not biologically active, tends to act as a buffer and blunt wild fluctuations in cortisol concentration.

Visualization of the larynx by direct or indirect means is referred to as laryngoscopy and is the principal aim during airway management for passage of a tracheal tube. This paper presents a brief background regarding the development and practice of laryngoscopy and examines the equipment and techniques for both direct and indirect methods. Patient evaluation during the airway examination is discussed, as are predictors for difficult intubation. Laryngoscope blade design, newer intubating techniques, and a variety of indirect laryngoscopic technologies are reviewed, as is the learning curve for these techniques and devices.
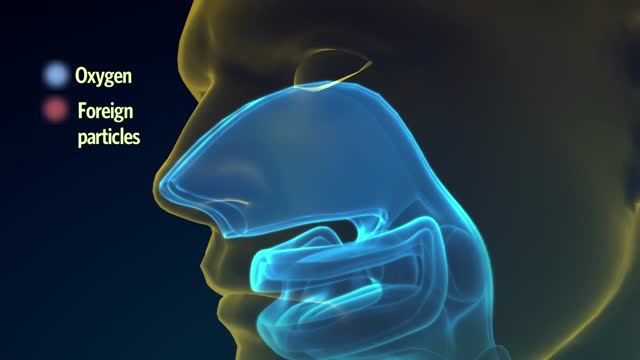
The lungs and respiratory system allow oxygen in the air to be taken into the body, while also enabling the body to get rid of carbon dioxide in the air breathed out. Respiration is the term for the exchange of oxygen from the environment for carbon dioxide from the body's cells.

The superior sagittal sinus (also known as the superior longitudinal sinus), within the human head, is an unpaired area along the attached margin of falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of anterior cerebral hemispheres to the confluence of sinuses.

-Korsakoff's syndrome is a common and preventable sequel of Wernicke's encephalopathy. Thiamine, if given during the stage of Wernicke's encephalopathy, can prevent the onset of Korsakoff's psychosis. The administration of glucose prior to thiamine can precipitate Korsakoff's syndrome, as seen in this case. In such patients, brain MRI frequently shows abnormal enhancement of the mammillary bodies & thallamus

Cerebral palsy refers to brain damage that occurs before a child is five years old. Therefore, adults cannot develop cerebral palsy. However, cerebral palsy does not get better or worse with age, so when a child has the condition, he or she will continue to have the condition into adulthood.
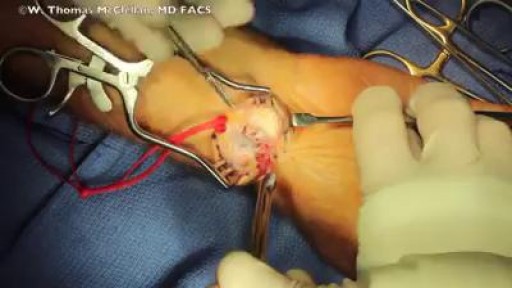
Surgery involves removing the cyst as well as part of the involved joint capsule or tendon sheath, which is considered the root of the ganglion. Even after excision, there is a small chance the ganglion will return. A ganglion cyst at the wrist is removed during a surgical procedure called excision.

Your baby measures about 20.7 inches from head to toe and weighs about 6 pounds. The baby may drop lower in your abdomen, usually assuming the head-down position to prepare for birth. The brain has been developing rapidly, and your baby is practicing blinking. Mom-to-be: Your uterus has grown bigger these last few weeks and is probably up under your ribs. But you're in the home stretch! After this week, you'll see your doctor weekly. You may switch between fatigue and extra bursts of energy. You may also have an achier back and feel heaviness and discomfort in your buttocks and pelvis. Tip of the Week: Start stocking your freezer with foods that can be easily popped into the oven or microwave after you bring your baby home. Chili, casseroles, and other simple dishes can be prepared and frozen ahead of time for use later.
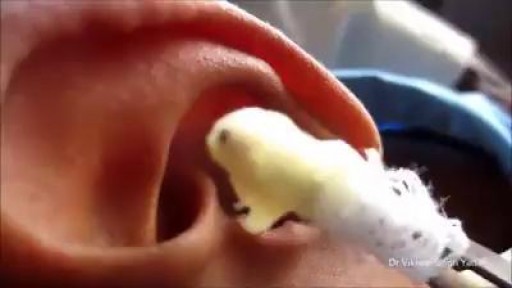
If your ear is leaking pus, you may have a hole in your eardrum.Your eardrum is stretched across the inner end of your ear canal. It vibrates when sound waves reach it, so you can hear. A hole in your eardrum can be caused by an ear infection. Fluid builds up behind the eardrum. The pressure of the fluid can tear the eardrum. Some people get a hole in the eardrum for other reasons, like hearing a very loud noise. If this happens, the ear may get infected because germs (bacteria) get through the hole. Ear infections happen to adults and children, but they're more common in children. Some things can make you more likely to get an ear infection with discharge. They include getting lots of colds and coughs, living in overcrowded housing, and eating a poor-quality diet
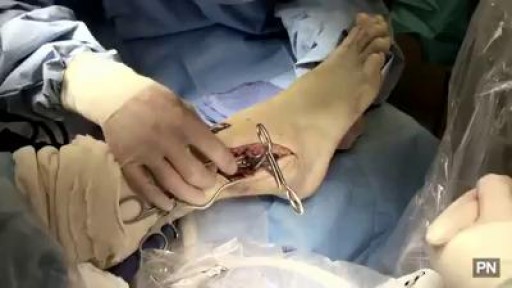
Depending on the fracture, the bone fragments may be fixed using screws, a plate and screws, or different wiring techniques. Because there is such a wide range of injuries, there is also a wide range of people's specific recovery time for ankle fracture surgery. It takes at least 6 weeks for the broken bones to heal.
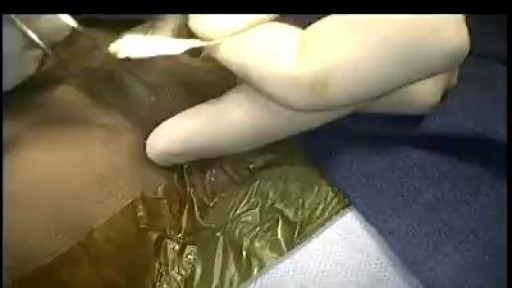
Minimally invasive surgery has been shown to be feasible and safe in pediatric patients since 1975 when laparoscopic surgery was first used to treat a small bowel obstruction. Laparoscopy is an option for surgical repair of inguinal hernias in addition to the traditional open approach.

A burn is tissue damage that results from scalding, overexposure to the sun or other radiation, contact with flames, chemicals or electricity, or smoke inhalation. Is it a major or minor burn? Call 911 or seek immediate care for major burns, which: Are deep Cause the skin to be dry and leathery May appear charred or have patches of white, brown or black Are larger than 3 inches (about 8 centimeters) in diameter or cover the hands, feet, face, groin, buttocks or a major joint A minor burn that doesn't require emergency care may involve: Superficial redness similar to a sunburn Pain Blisters An area no larger than 3 inches (about 8 centimeters) in diameter Treating major burns Until emergency help arrives: Protect the burned person from further harm. If you can do so safely, make sure the person you're helping is not in contact with the source of the burn. For electrical burns, make sure the power source is off before you approach the burned person. Make certain that the person burned is breathing. If needed, begin rescue breathing if you know how. Remove jewelry, belts and other restrictive items, especially from around burned areas and the neck. Burned areas swell rapidly. Cover the area of the burn. Use a cool, moist bandage or a clean cloth. Don't immerse large severe burns in water. Doing so could cause a serious loss of body heat (hypothermia). Elevate the burned area. Raise the wound above heart level, if possible. Watch for signs of shock. Signs and symptoms include fainting, pale complexion or breathing in a notably shallow fashion. Treating minor burns For minor burns: Cool the burn. Hold the burned area under cool (not cold) running water or apply a cool, wet compress until the pain eases. Remove rings or other tight items from the burned area. Try to do this quickly and gently, before the area swells. Don't break blisters. Fluid-filled blisters protect against infection. If a blister breaks, clean the area with water (mild soap is optional). Apply an antibiotic ointment. But if a rash appears, stop using the ointment. Apply lotion. Once a burn is completely cooled, apply a lotion, such as one that contains aloe vera or a moisturizer. This helps prevent drying and provides relief. Bandage the burn. Cover the burn with a sterile gauze bandage (not fluffy cotton). Wrap it loosely to avoid putting pressure on burned skin. Bandaging keeps air off the area, reduces pain and protects blistered skin. If needed, take an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve) or acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).