Top videos
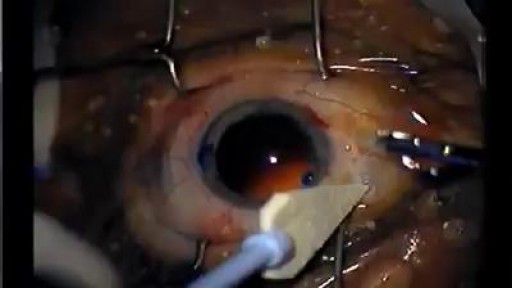
A cataract is a cloudiness of the normally transparent lens that is situated behind the iris. The lens focuses light rays on the retina at the back of the eye to produce a sharp image of what we see. When the lens becomes cloudy, the light rays cannot pass easily through it, and the image becomes blurry. It would be equivalent to having the lens in your camera becoming murky.
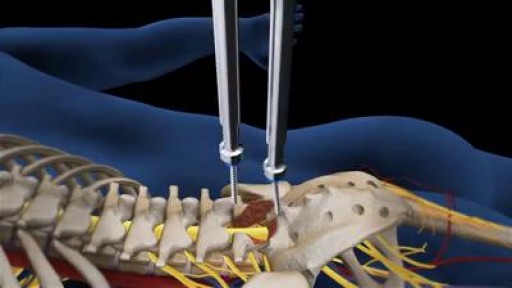
At each level of the spine, there is a disc space in the front and paired facet joints in the back. Working together, these structures define a motion segment (Fig. 1A). Back pain may result when injury or degenerative changes allow abnormal movement of the vertebrae to rub against one another, known as an unstable motion segment (Fig. 1B). Two vertebrae need to be fused to stop the motion at one segment. For example, an L4-L5 fusion is a one-level spinal fusion (Fig. 1C). A two-level fusion joins three vertebrae together and so on.
Spina bifida is a condition that affects the spine and is usually apparent at birth. It is a type of neural tube defect (NTD). Spina bifida can happen anywhere along the spine if the neural tube does not close all the way. When the neural tube doesn’t close all the way, the backbone that protects the spinal cord doesn’t form and close as it should. This often results in damage to the spinal cord and nerves. Spina bifida might cause physical and intellectual disabilities that range from mild to severe. The severity depends on: The size and location of the opening in the spine. Whether part of the spinal cord and nerves are affected.

houlder examination frequently appears in OSCEs. You’ll be expected to pick up the relevant clinical signs using your examination skills. This shoulder examination OSCE guide provides a clear step by step approach to examining the shoulder, with an included video demonstration.
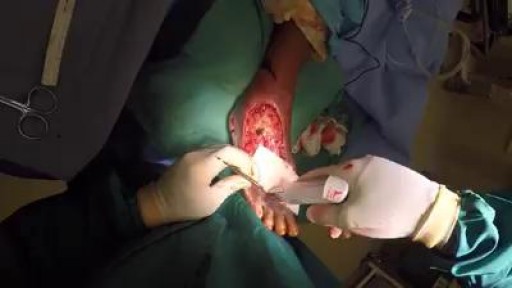
Compromise of the blood supply from microvascular disease, often in association with lack of sensation because of neuropathy, predisposes persons with diabetes mellitus to foot infections. These infections span the spectrum from simple, superficial cellulitis to chronic osteomyelitis. Diabetic foot infections typically take one of the following forms: Cellulitis Deep-skin and soft-tissue infections Acute osteomyelitis Chronic osteomyelitis Cellulitis Tender, erythematous, nonraised skin lesions are present, sometimes with lymphangitis Lymphangitis suggests group A streptococcal infection Bullae are typical of Staphylococcus aureus infection, but occasionally occur with group A streptococci
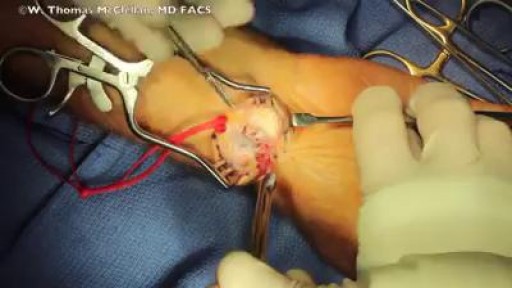
Surgery involves removing the cyst as well as part of the involved joint capsule or tendon sheath, which is considered the root of the ganglion. Even after excision, there is a small chance the ganglion will return. A ganglion cyst at the wrist is removed during a surgical procedure called excision.

Your baby measures about 20.7 inches from head to toe and weighs about 6 pounds. The baby may drop lower in your abdomen, usually assuming the head-down position to prepare for birth. The brain has been developing rapidly, and your baby is practicing blinking. Mom-to-be: Your uterus has grown bigger these last few weeks and is probably up under your ribs. But you're in the home stretch! After this week, you'll see your doctor weekly. You may switch between fatigue and extra bursts of energy. You may also have an achier back and feel heaviness and discomfort in your buttocks and pelvis. Tip of the Week: Start stocking your freezer with foods that can be easily popped into the oven or microwave after you bring your baby home. Chili, casseroles, and other simple dishes can be prepared and frozen ahead of time for use later.
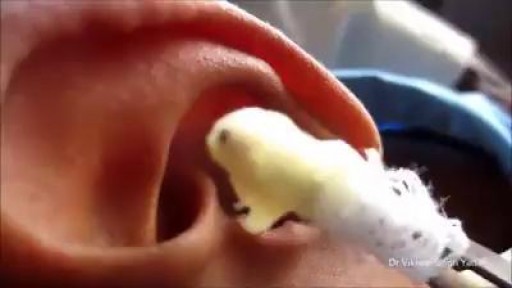
If your ear is leaking pus, you may have a hole in your eardrum.Your eardrum is stretched across the inner end of your ear canal. It vibrates when sound waves reach it, so you can hear. A hole in your eardrum can be caused by an ear infection. Fluid builds up behind the eardrum. The pressure of the fluid can tear the eardrum. Some people get a hole in the eardrum for other reasons, like hearing a very loud noise. If this happens, the ear may get infected because germs (bacteria) get through the hole. Ear infections happen to adults and children, but they're more common in children. Some things can make you more likely to get an ear infection with discharge. They include getting lots of colds and coughs, living in overcrowded housing, and eating a poor-quality diet
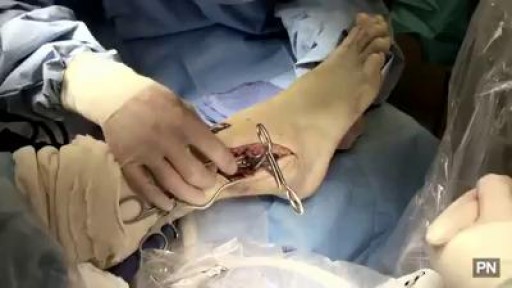
Depending on the fracture, the bone fragments may be fixed using screws, a plate and screws, or different wiring techniques. Because there is such a wide range of injuries, there is also a wide range of people's specific recovery time for ankle fracture surgery. It takes at least 6 weeks for the broken bones to heal.
Minimally invasive surgery has been shown to be feasible and safe in pediatric patients since 1975 when laparoscopic surgery was first used to treat a small bowel obstruction. Laparoscopy is an option for surgical repair of inguinal hernias in addition to the traditional open approach.
Vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to rejuvenate and tighten a woman’s vagina, by removing excess lining and repairing the surrounding soft tissues. It is designed to decrease the diameter of the vagina, resulting in increased friction during intercourse to make the experience more pleasurable for both partners.