Top videos

Genes are the building blocks of heredity. They are passed from parent to child. They hold DNA, the instructions for making proteins. Proteins do most of the work in cells. They move molecules from one place to another, build structures, break down toxins, and do many other maintenance jobs. Sometimes there is a mutation, a change in a gene or genes. The mutation changes the gene's instructions for making a protein, so the protein does not work properly or is missing entirely. This can cause a medical condition called a genetic disorder. You can inherit a gene mutation from one or both parents. A mutation can also happen during your lifetime.

Weight loss is the most effective nonpharmacologic measure to decrease blood pressure in overweight individuals. Weight loss with other nonpharmacologic measures can prevent or delay the onset of hypertension and reduce the overall risk of cardiovascular events in such patients. In some patients with established hypertension, lifestyle changes alone may control their blood pressure.
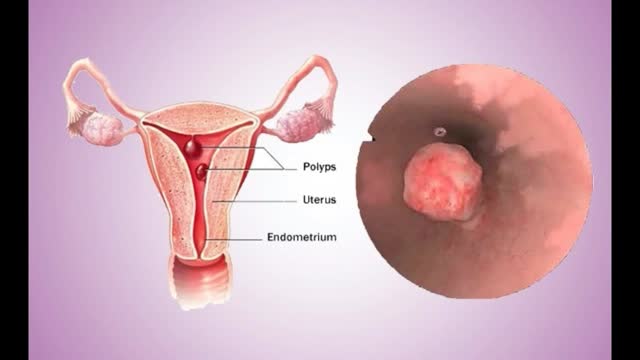
Uterine polyps are growths attached to the inner wall of the uterus that extend into the uterine cavity. Overgrowth of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) leads to the formation of uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps. These polyps are usually noncancerous (benign), although some can be cancerous or can eventually turn into cancer (precancerous polyps). Uterine polyps range in size from a few millimeters — no larger than a sesame seed — to several centimeters — golf-ball-size or larger. They attach to the uterine wall by a large base or a thin stalk.
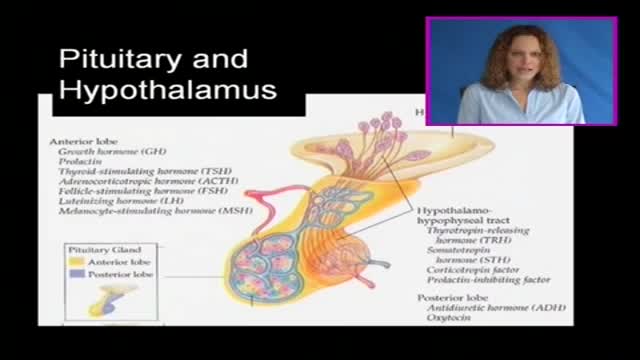
The pituitary gland is often portrayed as the "master gland" of the body. Such praise is justified in the sense that the anterior and posterior pituitary secrete a battery of hormones that collectively influence all cells and affect virtually all physiologic processes. The pituitary gland may be king, but the power behind the throne is clearly the hypothalamus. As alluded to in the last section, some of the neurons within the hypothalamus - neurosecretory neurons - secrete hormones that strictly control secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary. The hypothalamic hormones are referred to as releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones, reflecting their influence on anterior pituitary hormones.

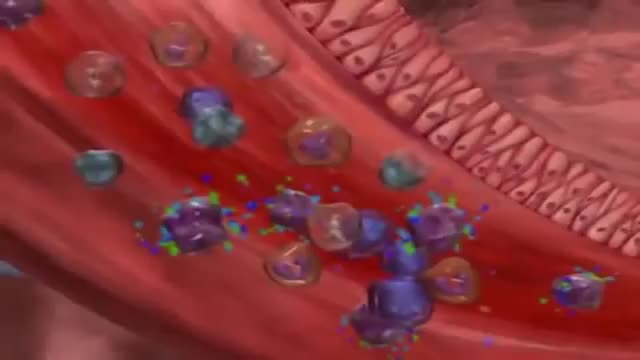
Adrenoleukodystrophy, or ALD, is a deadly genetic disease that affects 1 in 18 000 people. It most severely affects boys and men. This brain disorder destroys myelin, the protective sheath that surrounds the brain's neurons -- the nerve cells that allow us to think and to control our muscles.
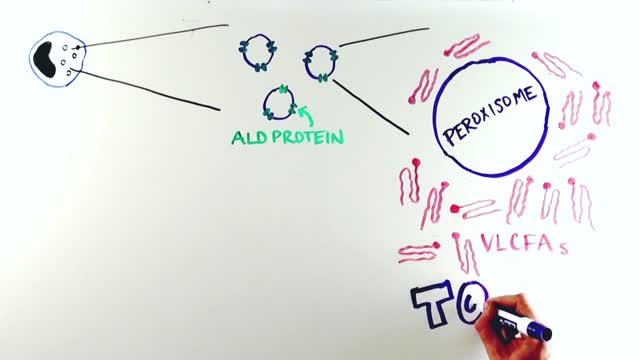
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy is a genetic disorder that occurs primarily in males. It mainly affects the nervous system and the adrenal glands, which are small glands located on top of each kidney. In this disorder, the fatty covering (myelin) that insulates nerves in the brain and spinal cord is prone to deterioration (demyelination), which reduces the ability of the nerves to relay information to the brain. In addition, damage to the outer layer of the adrenal glands (adrenal cortex) causes a shortage of certain hormones (adrenocortical insufficiency). Adrenocortical insufficiency may cause weakness, weight loss, skin changes, vomiting, and coma.

Parathyroid cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of a parathyroid gland. The parathyroid glands are four pea-sized organs found in the neck near the thyroid gland. The parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone (PTH or parathormone). PTH helps the body use and store calcium to keep the calcium in the blood at normal levels.

NTIS refers to a syndrome found in seriously ill or starving patients with low fT3, usually elevated RT3, normal or low TSH, and if prolonged, low fT4. It is found in a high proportion of patients in the ICU setting, and correlates with a poor prognosis if TT4 is <4ug/dl. The patho-physiology includes suppression of TRH release, reducedT3 and T4 turnover, reduction in liver generation of T3, increased formation of RT3, and tissue specific down-regulation of deiodinases, transporters, and TH receptors. Although long debated, tissue TH levels are definitely reduced, and tissue hypothyroidism is presumably present. This is often not clinically evident because of the brief duration, and reduced but not absent tissue levels of TH. Although recognized for nearly 4 decades, interpretation of the syndrome is contested, because of lack of data. Some observes, totally without data, argue that it is a protective response and should not be treated. Other observers (as in this review) present available data suggesting, but not proving, that thyroid hormone replacement is appropriate, not harmful, and may be beneficial. The best form of treatment (TRH,TSH,or T3+T4) and possible accompanying treatments (GHRH, Cortisol, nutrition, insulin) lack consensus. In this review current data are laid out for reader’s review and judgment.

There are 3 genetic types of FHH based on chromosome location. FHH type 1 accounts for 65% of cases and is due to inactivating mutations in the CASR gene, localized to 3q21.1. This gene encodes the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Loss of CaSR function results in a reduction in the sensitivity of parathyroid and renal cells to calcium levels so hypercalcemia is perceived as normal. The other 35% have either a mutation GNA11 (19p13.3) seen in FHH type 2 or AP2S1 (19q13.2-q13.3) seen in FHH type 3 (see these terms) or in genes not yet discovered. FHH is rarely caused by auto-antibodies against CaSR in those without a mutation.

When taking oral corticosteroids longer term, you may experience: Clouding of the lens in one or both eyes (cataracts) High blood sugar, which can trigger or worsen diabetes. Increased risk of infections. Thinning bones (osteoporosis) and fractures. Suppressed adrenal gland hormone production
The usual reason given for people getting fat is that they eat too much and/or exercise too little. That reflects one of the basic laws of thermodynamics—I forget which one. The amount of energy you put into a system minus the energy you take out has to be stored somewhere i.e. FAT! This formulation—true though it is—does not entirely explain obesity since some people seem to eat more than fat people and exercise no more than these same fat people, and yet they are not fat! Chalking this fact up to the general perversity of the universe is not sufficient explanation. Other factors must come into play. I mention below some of the ideas thoughtful people have proposed to explain why fat people become fat:

CPAP is a treatment that uses mild air pressure to keep your breathing airways open. It involves using a CPAP machine that includes a mask or other device that fits over your nose or your nose and mouth, straps to position the mask, a tube that connects the mask to the machine’s motor, and a motor that blows air into the tube. CPAP is used to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including sleep apnea. It also may be used to treat preterm infants who have underdeveloped lungs.
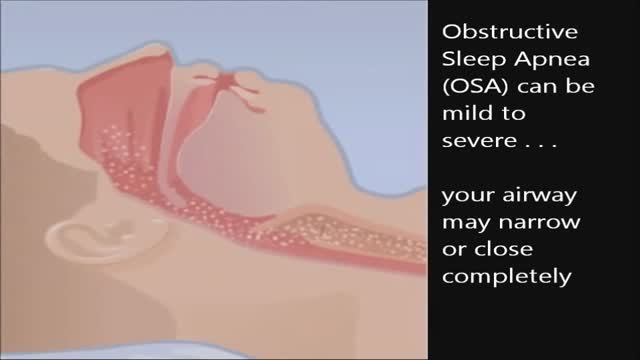
CPAP, or continuous positive airway pressure, is a treatment that uses mild air pressure to keep the airways open. CPAP typically is used by people who have breathing problems, such as sleep apnea. CPAP also may be used to treat preterm infants whose lungs have not fully developed.

There are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration. The airway, which includes the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, carries air between the lungs and the body's exterior.

Gastroparesis -- literally “paralyzed stomach” -- is a serious condition manifested by delayed emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine after a meal. There is no cure for gastroparesis, but treatment can speed gastric emptying and relieve gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.