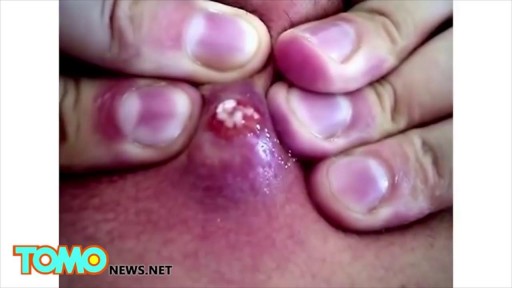
Top videos

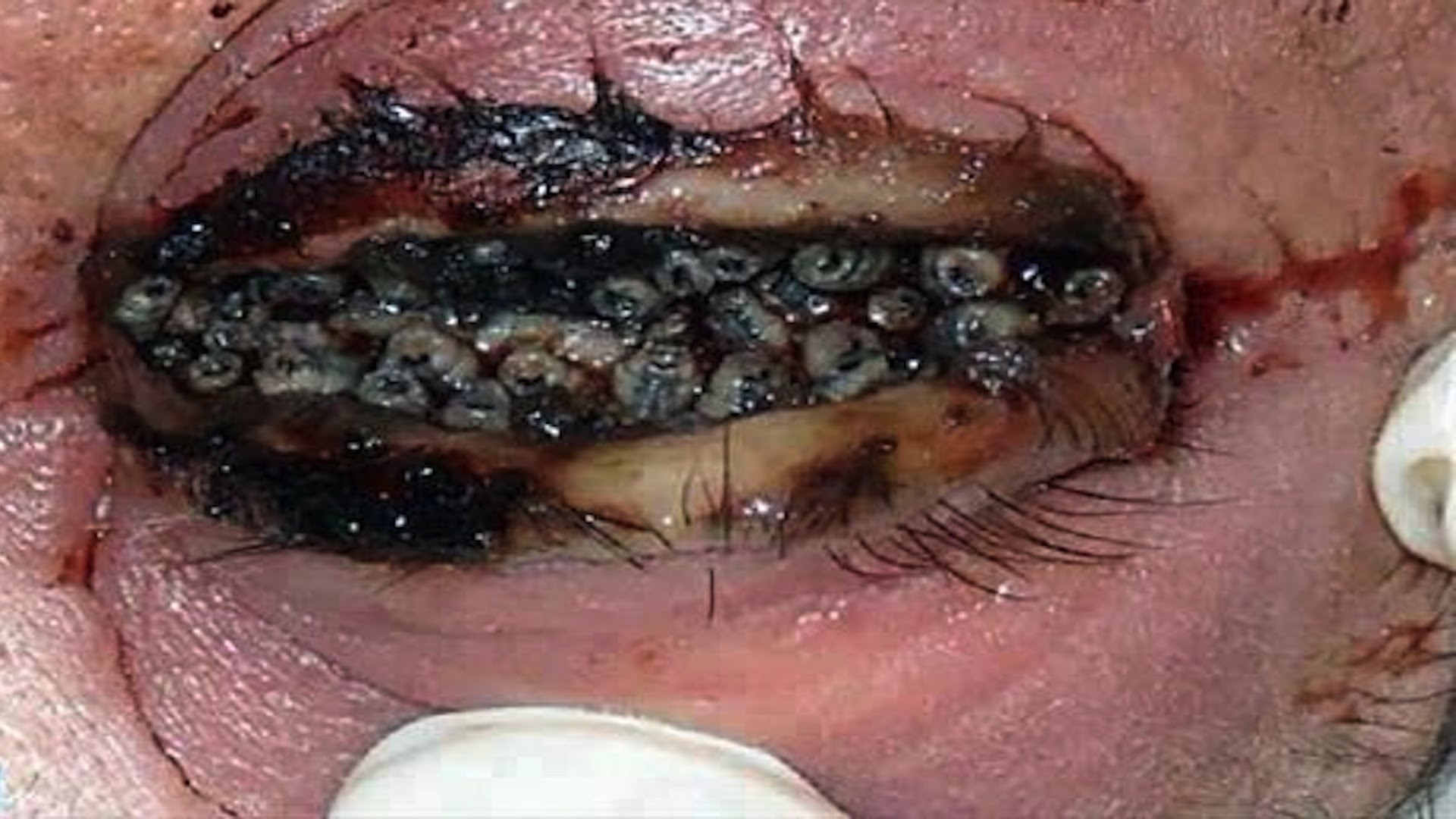
4000 Grafts Hair Transplant Surgery Result after 7months by Dr. Ariganesh Chandrasegaran (MD, PGI Chandigarh) at DermaClinix. DermaClinix is known for the best hair transplant in Chennai as well as across India. Dramatic transformation by our flagship patented procedure B.E.S.T. (Bio-Enhanced Simultaneous Transplant Technique) FUE which helps in achieving almost complete survival with early and natural looking results. Book Your Free Consultation: +91 8939636222, 04428282606. More at https://www.hairtransplantchennai.org

Purchase a license to download a non-watermarked copy of this video here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.....com/-/galleries/all-
Voice by: Sue Stern.
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
Perfect for patient education purposes.
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
LASIK, or "laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis," is the most commonly performed laser eye surgery to treat myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. The goal of the treatment is to reshape the cornea to correct the refractive error of the eye.
The cornea is the transparent dome-shaped structure in front of the eye. The cornea refracts light and accounts for about two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. Altering the curvature of the cornea changes the way light rays enter the eye. As a result, the light rays can be focused properly onto the retina for clearer vision.
For nearsighted people, the laser is used to flatten the cornea. For farsighted people, the cornea is made steeper. For patients with astigmatism, the laser is used to smooth the irregularly-shaped cornea into a more regular shape.
The outer layer of the cornea - the epithelium – is capable of replacing itself within a few days after being damaged or removed. The deeper layer of the cornea – the stroma, on the contrary, is a permanent corneal tissue with very limited regenerative capacity. The stroma, if reshaped by a laser, will remain that way permanently.
In this procedure, a thin, circular "FLAP" is created in the surface of the cornea to gain access to the permanent corneal tissue. This can be done with a mechanical cutting tool called a microkeratome, OR, for a blade-free experience, by a femtosecond laser. An excimer laser is then used to remove some corneal tissue to reshape the cornea. Excimer laser uses cool ultraviolet light beams to vaporize microscopic amounts of tissue in a precise manner to accurately reshape the cornea. The excimer laser is computer-controlled and is programmed based on the patient’s refractive error. The flap is then laid back in place and is allowed to heal.
LASIK eye surgery is mostly painless and can be completed within minutes. Improved vision can usually be seen overnight.
PRK, or photorefractive keratectomy, was the first type of laser eye surgery for vision correction and is the predecessor to the popular LASIK procedure. In PRK, NO flap is created. Rather, the epithelial cells on the eye surface are simply removed. An excimer laser is then used to reshape the cornea just like it does in LASIK.
The vision correction outcomes of PRK surgery are comparable to those of LASIK, but the recovery period is longer. This is because the epithelium is completely removed in PRK and it takes a few days to regenerate. PRK patients also have more discomfort and haziness of vision in the first few days after the surgery. Improved vision also takes longer to achieve.
PRK does, however, offer certain advantages. Because PRK does not involve creation of a flap, which contains both epithelial and deeper stromal tissue, the entire thickness of the stroma is available for treatment. The treatment range is therefore higher. This is particularly useful for patients with high levels of myopia or for those whose cornea is too thin for LASIK. PRK is also free of flap-related complication risks.

Home Remedies For Acid Reflux, Ginger For Acid Reflux, Heartburn After Gallbladder Removal --- http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co --- Stop using Pepto Bismol until you read the following… There is BREAKING scientific news reporting that many of America’s most popular antacids – both the ones you buy at the drug store and the ones you need prescriptions for… Are linked to more than a dozen forms of potentially DEADLY cancers. Click this link now to get the full story and see if you’re at risk. You’ll find out about a “just discovered” alternative to antacids…. Something that can permanently cure even the worst cases of acid reflux in as little few days, and that doesn’t require any pills or medications. Click Here: http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co

http://eliminar-celulite.plus101.com --- Exercicios Para Celulite, Redução De Celulite, O Que Da Celulite, Como Melhorar Celulite. Primeiro eu criei uma lista dos músculos da parte de trás, e aqui estão eles, começando da parte de cima (região dos quadris) e descendo até os tornozelos: Glúteo máximo Glúteo médio Glúteo mínimo Tensor da fascia lata Piriforme Semimembranoso Semitendinoso Bíceps femoral Sartorio Popliteo Soleo Gastrocnêmio Músculo Plantar Tibial Posterior São 14 aí - e eu nem listei os que estão em um nível mais profundo. Tampouco listei os músculos menores que têm um papel importante em sua biomecânica e são as camadas musculares que são estimuladas para tonificação, levantamento e suavização das camadas de pele que cobrem esses músculos. Agora que você sabe onde a causa da reversão da celulite acontece, você pode entender por que agora é possível que você se livre de problemas com a celulite em suas áreas problemáticas e pontos críticos. Então assistir ao vídeo de apresentação fará muito mais sentido agora. http://eliminar-celulite.plus101.com
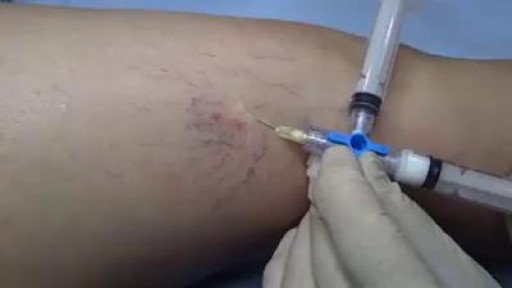
Several options are available to remove spider veins — thin red lines or weblike networks of blood vessels that appear on your legs and feet. Spider veins are usually harmless, though they can sometimes cause aching, burning or pain, especially when you've been standing for long periods. If you have symptoms or are concerned about the appearance of spider veins, treatment options include: Sclerotherapy. In this procedure, your doctor injects the veins with a solution that scars and closes those veins, causing the blood to reroute through healthier veins. In a few weeks, treated spider veins fade. Although the same vein may need to be injected more than once, sclerotherapy is usually effective if done correctly. Sclerotherapy doesn't require anesthesia and can be done in your doctor's office. Side effects include swelling, itching and skin color changes in the treated area. Laser surgery. Laser surgery works by sending strong bursts of light into the vein that make the vein slowly fade and disappear. No incisions or needles are used. The treatment is often less effective than sclerotherapy, particularly for larger veins. Side effects may include redness, bruising, itching, swelling and permanent skin tone changes. After treatment, blood vessels fade over several months, but they may not disappear completely. Also, new spider veins can develop in the same area.
Generic minoxidil is known to treat hair-fall issues in men and women, it is best for hair growth, hair re-development, etc. it is available in the strength of 5mg and easily available at online pharmacy store. For more information visit to http://www.medstorerx.com/generic-minoxidil.aspx