Top videos

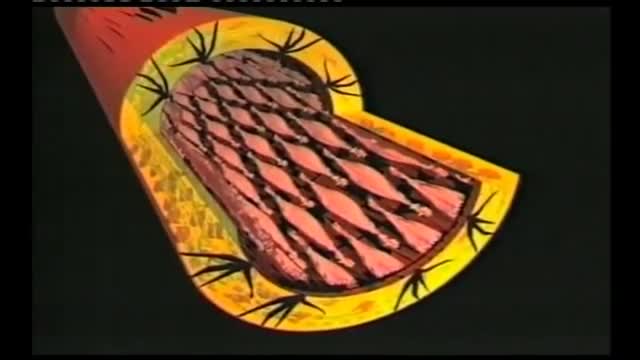
This is the biggest known operation ever.The Whipple procedure(pancreatoduodenectomy) is the most common operation performed for pancreatic cancer and may be used to treat other cancers such as small bowel cancer. Surgeons remove the head of the pancreas, most of the duodenum (a part of the small intestine), a portion of the bile duct and sometimes a portion of the stomach. After the pancreatoduodenectomy, the surgeon reconstructs the digestive tract. At Mayo Clinic, surgeons perform more than 100 Whipple procedures annually. Patients leave the hospital in an average of 14 days.

A testicular examination is mainly performed on male patients who present with testicular pathology e.g. pain, swelling, a lump. Although titled testicular examination it involves the examination of the penis, scrotum and testes. As this is an intimate examination it is pertinent to gain a good rapport with your patient, maintain good communication and ensure the patient’s dignity at all times. Remember to offer a chaperone for this skill. For the purposes of your exam, you will most likely be examining a mannequin.
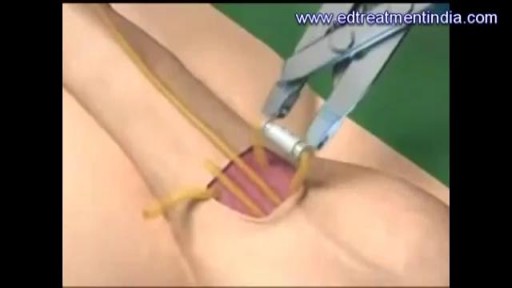
A penile prosthesis is another treatment option for men with erectile dysfunction. These devices are either malleable (bendable) or inflatable. The simplest type of prosthesis consists of a pair of malleable rods surgically implanted within the erection chambers of the penis. With this type of implant the penis is always semi-rigid and merely needs to be lifted or adjusted into the erect position to initiate sex. This type of implant is a good choice for men with spinal cord injuries and/or limited hand strength. Today, many men choose a hydraulic, inflatable prosthesis, which allows them to have an erection when they choose, and it's easier to conceal. It is also more natural. A penile implant is usually used when there is a clear medical cause for ED and when the problem is unlikely to resolve or improve naturally or with other medical treatments. Sometimes a penile prosthesis is implanted during surgery to reconstruct the penis when scarring has caused erections to curve (Peyronie's disease). Penile implant surgeries take about an hour and are typically done in an outpatient center. A man can resume sexual intercourse by 6 weeks after surgery.

Many over-the-counter medications can help relieve heartburn. The options include: Antacids, which help neutralize stomach acid. Antacids may provide quick relief. But they can't heal an esophagus damaged by stomach acid. H-2-receptor antagonists (H2RAs), which can reduce stomach acid. H2RAs don't act as quickly as antacids, but may provide longer relief. Proton pump inhibitors, such as lansoprazole (Prevacid 24HR) and omeprazole (Prilosec OTC), which also can reduce stomach acid.
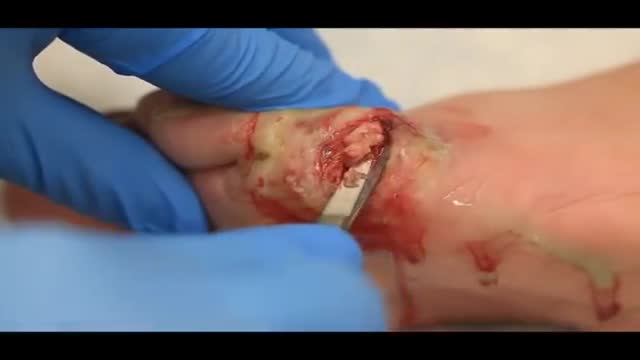
Treatment may not be needed for an eschar if it is part of the natural healing process. However, if an eschar looks like it may have a wound infection – symptoms can include oozing fluid such as pus or blood, your clinician will likely recommend topical treatment or debridement to help control and remove the infection.