Top videos
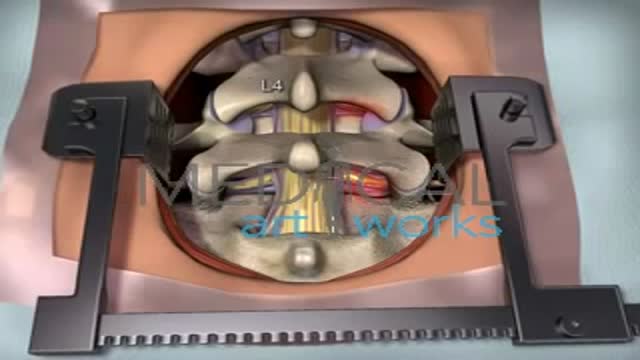
The goal of a decompression surgery is usually to relieve pain caused by nerve root pinching. There are two common causes of lumbar nerve root pressure: from a lumbar herniated disc or lumbar spinal stenosis. This type of pain is usually referred to as a radiculopathy, or sciatica. A decompression surgery involves removing a small portion of the bone over the nerve root and/or disc material from under the nerve root to relieve pinching of the nerve and provide more room for the nerve to heal. The most common types of decompression surgery are microdiscectomy and laminectomy.
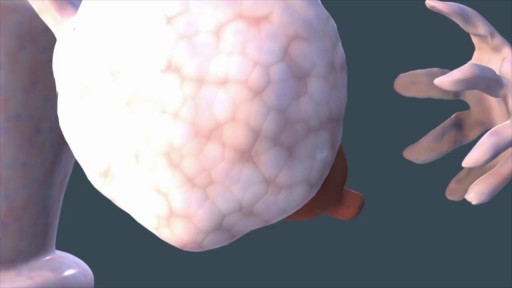
Ganglion cysts are the most common mass or lump in the hand. They are not cancerous and, in most cases, are harmless. They occur in various locations, but most frequently develop on the back of the wrist. These fluid-filled cysts can quickly appear, disappear, and change size.

very day, specialists deliver high-quality care in 68 disciplines in health centres across Canada. Yet many Canadians know very little about what many specialists actually do, and the important role these disciplines play in Canada’s health care system. This video provides a brief high-level overview of what Internal Medicine Specialists actually do, their training, and their role in Canadian health care.

The timing of the nausea or vomiting can indicate the cause. When appearing shortly after a meal, nausea or vomiting may be caused by food poisoning, gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining), an ulcer, or bulimia. Nausea or vomiting one to eight hours after a meal may also indicate food poisoning.
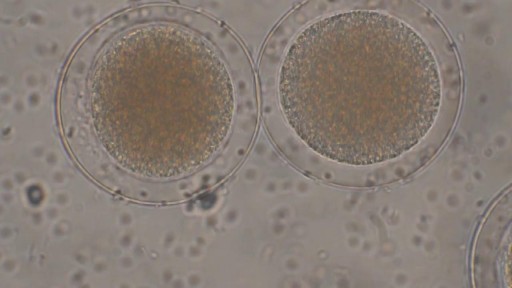
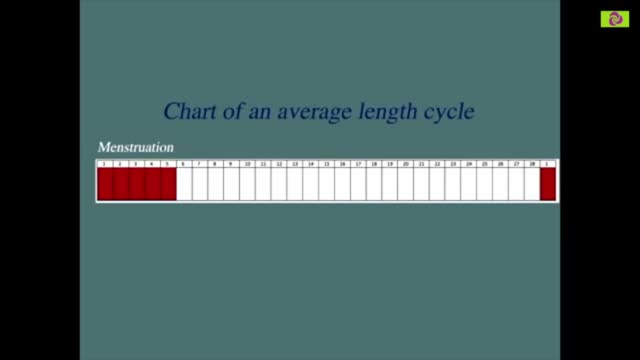
Sperm Meets Egg: Weeks 1 to 3 of Pregnancy. Something magical is about to happen! Watch as the ovulation process occurs, and then millions of sperm swim upstream on a quest to fertilize an egg. Your due date is calculated from the first day of your last menstrual period

Sex easily falls to the wayside during pregnancy. Research shows that good sex has a significant impact upon not just the relationship, but also a woman’s ability to have an easeful and even joyful birth. Unfortunately, sex during pregnancy can be quite complicated for a variety of physical and emotional reasons. This week’s video will outline how to overcome these hurdles and make sure you continue to enjoy the wonders of sex as you embark on the first steps of parenthood.
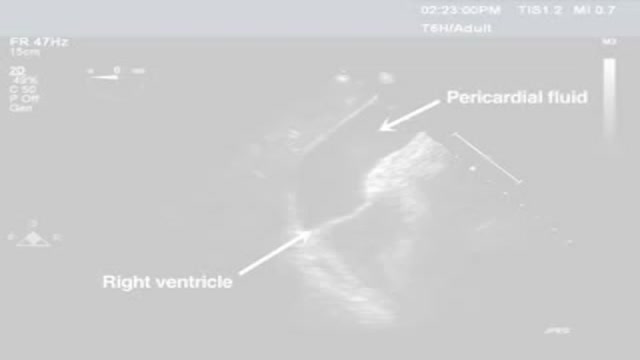
Pericardiocentesis is the aspiration of fluid from the pericardial space that surrounds the heart. This procedure can be life saving in patients with cardiac tamponade, even when it complicates acute type A aortic dissection and when cardiothoracic surgery is not available. [1] Cardiac tamponade is a time sensitive, life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis and management. Historically, the diagnosis of cardiac tamponade has been based on clinical findings. Claude Beck, a cardiovascular surgeon, described 2 triads of clinical findings that he found associated with acute and chronic cardiac tamponade. The first of these triads consisted of hypotension, an increased venous pressure, and a quiet heart. It has come to be recognized as Beck's triad, a collection of findings most commonly produced by acute intrapericardial hemorrhage. Subsequent studies have shown that these classic findings are observed in only a minority of patients with cardiac tamponade. [2] The detection of pericardial fluid has been facilitated by the development and continued improvement of echocardiography. [3] Cardiac ultrasound is now accepted as the criterion standard imaging modality for the assessment of pericardial effusions and the dynamic findings consistent with cardiac tamponade. With echocardiography, the location of the effusion can be identified, the size can be estimated (small, medium, or large), and the hemodynamic effects can be examined by assessing for abnormal septal motion, right atrial or right ventricular inversion, and decreased respiratory variation of the diameter of the inferior vena cava.
Digoxin is derived from the leaves of a digitalis plant. Digoxin helps make the heart beat stronger and with a more regular rhythm. Digoxin is also used to treat atrial fibrillation, a heart rhythm disorder of the atria (the upper chambers of the heart that allow blood to flow into the heart).
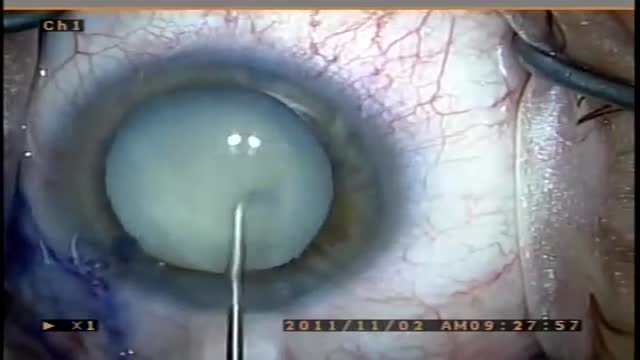
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging. Cataracts are very common in older people. By age 80, more than half of all Americans either have a cataract or have had cataract surgery. A cataract can occur in either or both eyes. It cannot spread from one eye to the other.
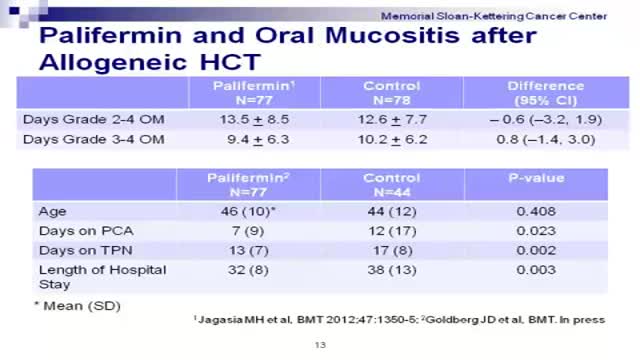
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a common complication after an allogeneic transplant, a transplant in which cells from a family member, unrelated donor or cord blood unit are used. In GVHD, the immune cells from the donated marrow or cord blood (the graft) attack the body of the transplant patient (the host).

Glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is the result of defects in the processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown within muscles, liver, and other cell types. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and acquired.

The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion (SIADH) is defined by the hyponatremia and hypo-osmolality resulting from inappropriate, continued secretion or action of the hormone despite normal or increased plasma volume, which results in impaired water excretion.

A silent heart attack is a heart attack that has few, if any, symptoms. You may have never had any symptoms to warn you that you've developed a heart problem, such as chest pain or shortness of breath. Having diabetes or prediabetes puts you at increased risk for heart disease and stroke. You can lower your risk by keeping your blood glucose (also called blood sugar), blood pressure, and blood cholesterol close to the recommended target numbersthe levels suggested by diabetes experts for good health. (
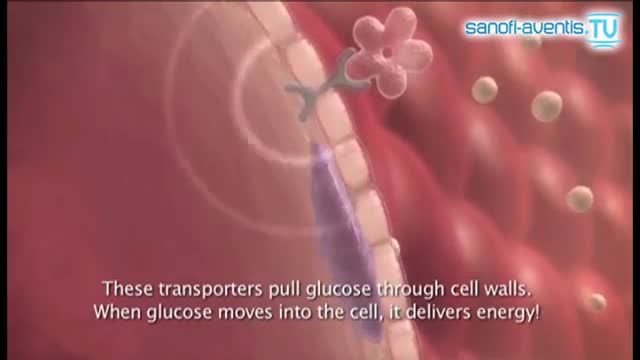
Insulin is a hormone made naturally in the pancreas that helps move sugar into the cells of your body. Your cells use the sugar as fuel to make energy. Without enough insulin, sugar stays in your bloodstream, raising your blood sugar. High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can lead to the signs and symptoms of diabetes:
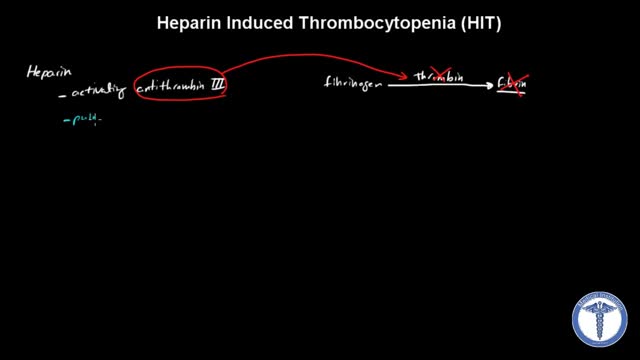
All forms of heparin (including low-molecular-weight heparin such as enoxaparin) must be stopped immediately in patients with suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) while awaiting diagnostic confirmation. Patients with HIT remain at high risk of thrombosis even after discontinuation of heparin. Therefore, an alternate, rapidly acting, non-heparin anticoagulant such as direct thrombin inhibitor (eg, argatroban, bivalirudin) must be started immediately.