Top videos
Generic minoxidil is known to treat hair-fall issues in men and women, it is best for hair growth, hair re-development, etc. it is available in the strength of 5mg and easily available at online pharmacy store. For more information visit to http://www.medstorerx.com/generic-minoxidil.aspx

Is Shingles Contagious, What Are Shingles, Herpes Zoster Pictures, Shingles Home Remedies --- http://shingles-cure.good-info.co/ --- If You Are A Newcomer To This Disease, I Hate To Be The Bringer Of Bad News But You Should Know That The List Of Potential Symptoms Is Depressingly Long. These Include The Following: A General Feeling Of Muscle Pain To Begin With, Almost Like Flu A Tingling, Burning Type Sensation In A Specific Area Of The Skin Fever And Headache And Sometimes A Swelling Of The Lymph Nodes A Band Of Spots And Then A Rash At A Specific Part Of Your Body – Very Often The Head Or The Side Of The Trunk Infection Over The Site Of The Rash – Leaving It Prone To Additional Tissue Damage From Bacteria Postherpetic neuralgia leading to chronic nerve pain Ulceration Of The Eye – In Those Cases Where The Shingles Rash Occurs In The Area Of The Eye – Known As Zoster Ophthalmicus. Stress And Depression – Particularly Where The Illness Lingers On For A Long Period Everyone Is Different And Not Everyone Will Experience All Of Those Symptoms. However Even The Most Mild Case Of Shingles Can Be Extremely Debilitating – Something Of Which I Am All Too Aware. Tired Of Fighting A Never Ending Battle Against Shingles? Sick Of Being Told That There´s Nothing You Can Do To Speed Up Recovery? Wherever You Are In Your Fight Against Shingles, I Can Help In this presentation, shows you some unique and rare methods to get rid of shingles naturally in as little as 14 days! This is based on proven techniques used by shingles sufferers without the use of pills and other medication. Get Rid of Shingles will also boost your energy and health dramatically and improve the quality of your life. IMPORTANT NOTE: I can't leave this video up for long, so be sure to watch it from beginning to end while it's still here. REMEMBER: Watch the whole video, as the ending will pleasantly surprise you. click here: http://shingles-cure.good-info.co/

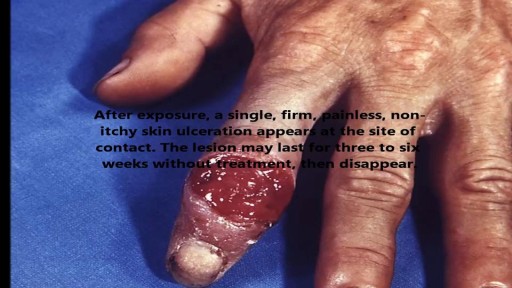
Iodine For Ringworm, Best Ointment For Ringworm, Where Do You Get Ringworm, How To Treat Ring Worms ---- http://ringworm-cure.plus101.com --- Ringworms, contrary to the common notion, do not come from worms. Tinea, which is the medical term for ringworms, is a fungal infection seen on the skin's surface. Knowing how to cure ringworm is important because ringworms can be highly contagious. It can be contracted from direct contact with the host (person or animal) as well as by other means such as having contact with the host's clothes. Swimming pools can also be a place where ringworms are transmitted from one person to another. How To Cure Ringworm - Understanding Aspects and Options Different means on how to cure ringworm are available and they sometimes vary in accordance with where the ringworm is located (it can appear in areas like the nails, fingers, toes, feet, scalp, stomach, chest, thighs, and scalp), and the particular type of ringworm. • Ringworms found in the scalp are usually treated with an antifungal shampoo to keep the area dry and clean. • Ringworms found in the feet can be treated through the application of ointments. • Oral medications can also be taken in especially when ringworms are on the nails. • Sprays, powders and creams are also forms by which anti-fungal drugs are bought. These medicines may take some time to work. The infection may persist for a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity and how the body responds to the medications. How To Cure Ringworm - OTC and Prescription Medications Ringworm appears on the skin's surface as an itchy, red, circular patch. As it progresses, it expands and smaller round patches can develop. It is important to immediately identify ringworms and know how to treat them properly. There are many over the counter topical creams (anti-fungal ones) and ointment that can be bought in the market. However, some people prefer to visit the doctor and ask for a prescription. Stronger formulations are generally available via prescriptions. William Oliver is a nutritionist, medical researcher, and author of the Fast Ringworm Cure e-book. To find out how to cure Ringworm in 3 days or less, click below: http://ringworm-cure.plus101.com

Homemade Body Wraps For Weight Loss, Cheap Body Wraps That Work, Body Wraps To Lose Weight ---- http://do-body-wraps-work.plus101.com -- Cellulite and loose and flabby skin can often drain your confidence. You have maybe considered plastic surgery, but the risks and costs are just not reasonable. Fortunately, there are body wraps, which can offer alternative to plastic surgery. Getting a body wrap at a salon can be very expensive - multiple sessions can cost hundreds of dollars. The WrapYourselfSlim ebook shows readers how to get rid of their flabby stomaches and cellulite through the recipes made in the home kitchen. Which recipe is the best when wanting to seek drastic results? What Is The Best Body Wrap Recipe? One of the best body wrap recipes contains the ingredients of olive oil, green clay, water, herbs sea salt, and essential oils. You can select the oils and herbs such as lemongrass, sage, rosemary, rose petal powder, neem powder, lavender, ground basil, grapefruit, ginger root powder, alfalfa leaf powder, and rosehip powder. Measure out two tablespoons of olive oil, 1 cup of green clay, 2 cups of water, and a 1/2 cup of sea salt. Boil the water, then thoroughly stir inside of the sea salt until it has dissolved. Add your selected herbs, olive oil, and green clay, then stir til a paste has formed for you to set this mixture aside for cooling. Once the paste has cooled enough for your skin to handle, rub it on to your body, then cover it with sheets or towels cut into strips. Keep it on for one full hour before removing. A great tip that you should keep in mind when wanting to see the best results is to detoxify your body a couple days before applying the wrap on to yourself. Drink plenty of water before you apply the wrap on to yourself so you can see the highest results possible. You will definitely see significant results right after taking the wrap off, as the skin will instantly absorb the nutrients of the ingredients. This is better than the typical weight loss cream that you find today. Use this easy-to-prepare affordable formula to help contour your abs, thighs, hips buttocks, etc ... in less than two weeks! Stop procrastinating! Click Here for instant access to my recipes & start losing inches, detoxifying your body, and improving your skin right away! http://do-body-wraps-work.plus101.com

» A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus (from the Latin rēnēs, “kidneys,” and calculus, “pebble”), is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine. » Urolithiasis (UL) is one of the most common diseases, with approximately 7.6% incidence in Western India. Although most patients have only one stone episode, 25% of patients experience recurrent stone formation. UL therefore has a significant impact on quality of life and socioeconomic factors.
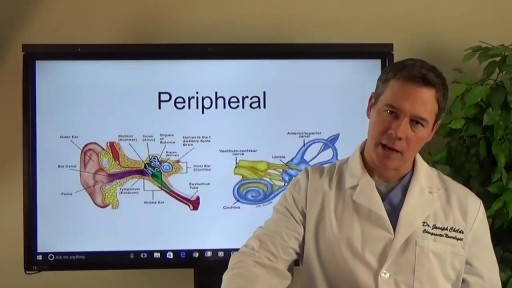
Symptoms of dizziness can result from many conditions such as; (vestibular) inner ear disorders, neck injuries or muscle tightness, neuropathy, central nervous system problems, metabolic issues, or psychological disorders. Our therapists are trained to screen for more serious conditions (such as neurological and cardiovascular disorders) as well as effectively evaluate and treat conditions which are appropriate for physical therapy intervention.