Top videos
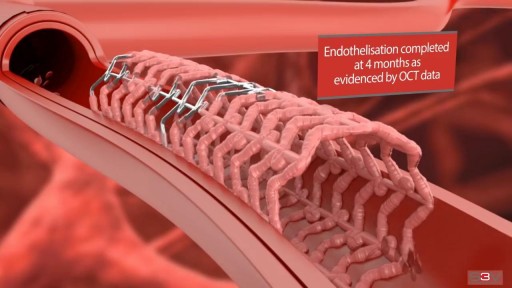
Angioplasty is a procedure to restore blood flow through the artery. You have angioplasty in a hospital. The doctor threads a thin tube through a blood vessel in the arm or groin up to the involved site in the artery. The tube has a tiny balloon on the end.
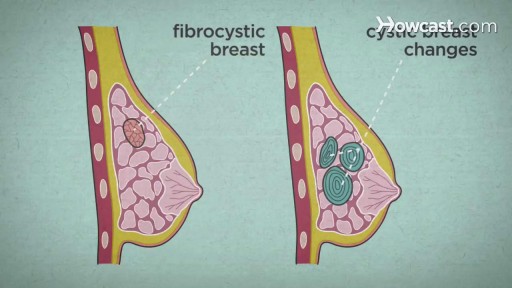
Over the course of a woman's lifetime, she may experience breast changes. While many end up being nothing to worry about, it's important to have any changes that you notice checked by a doctor -- just to be on the safe side. Here are the potential breast cancer symptoms to watch out for.
Dr. Linder is removing a patients breast implants after having five breast augmentations from three previous surgeons. She has baker 4 capsular contracture and is look forward to having them removed. The most common reasons for removing a breast implant include; heath reasons such as back pain, reoccurring complications and the desire for a different shape or size. For implant removal surgery, Dr. Linder makes an inframammary incision (along the breast crease). The implant can be removed intact, or it may need to be punctured before removal. An antibiotic solution is used to irrigate the breast pocket after implant removal. For more information about breast implant removal go to www.implantremoval.net or call Dr. Linder's office at 310-275-4513

Learn what's working for other Nursing Students! Check out our Top 10 Most Popular Lessons Here: https://bit.ly/3nda5u3
Central Line Dressing Change- Nursing Skills
FREE Nursing School Cheat Sheets at: http://www.NURSING.com
Get the full PPE Donning & Doffing lesson here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/cen....tral-line-dressing-c
Welcome to the NURSING Family, we call it the most supportive nursing cohort on the planet.
At NURSING.com, we want to help you remove the stress and overwhelm of nursing school so that you can focus on becoming an amazing nurse.
Check out our freebies and learn more at: (http://www.nursing.com)
Central Line Dressing Change - Nursing Skills:
In this video we’re going to talk about central line dressing changes. In this particular video, we’re going to look at a PICC Line, but the same strategy is also used for a Central Line. Remember the dressing should be changed every 7 days or as needed for peeling or soiling
This includes PICC lines. Sterile technique must be maintained to prevent Central-Line Associated Bloodstream Infections (CLABSI)
We love you guys! Go out and be your best selves today! And, as always, happy nursing!
Bookmarks:
0.05 Introduction
0.22 Mask application
0:36 Patient positioning
0:48 Dressing removal
1:20 Sterilization
1:26 Dressing change kit
2:14 Sterile gloves (Lesson link below)
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-01-04-sterile-gl
2:50 Cleaning the site
3:30 Bio patch application
4:20 Changing infusion caps
4:41 Labeling the dressing
5:00 Outro
Visit us at https://nursing.com/medical-disclaimer/ for disclaimer information.
NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, INC. and hold no affiliation with NURSING.com.

The anatomy of the direct and indirect inguinal hernia.
Music:
Berries and Lime by Gregory David
https://www.epidemicsound.com/track/z6iCiiyCPm/

Curious about LASIK eye surgery? NVISION's Dr. Richard Mauer talks risks, life-changing benefits, and outcomes (plus why he loves what he does!).
Want to start your journey to better vision? Schedule your complimentary consult today! https://bit.ly/3H2i0FU
NVISION: The Eye Doctors' #1 Choice in LASIK and Laser Cataract Surgery

Ever heard medical terms like MRI or EKG? Funny speaker for nurses and doctors and all-around healthcare speaker Dr. Brad Nieder discusses the funny medical jargon he's encountered during his medical career.
He jokes about medical acronyms and big healthcare terms. His funny medical humor makes the conference attendees burst with laughter and he reads the medical definition for "laugh."
As an experienced physician and keynote speaker, he's perfect for any in-person or virtual conference or event. He's also a great healthcare speaker to bring in for continuing medical education (cme) units!
Learn more about Brad's keynote and virtual speaking, and book him for your next conference or virtual event: https://www.HealthyHumorist.com
Find Dr. Brad on social media:
https://www.facebook.com/HealthyHumor...
https://www.linkedin.com/in/BradNieder
https://twitter.com/HealthyHumorist
https://www.youtube.com/c/BradNiederMD
https://vimeo.com/BradNieder
Brad Nieder, MD, CSP*
The Healthy Humorist
Doctor, Keynote Speaker, Clean Comedian
*CSP=Certified Speaking Professional
"Medical Lingo"
From the DVD "The Healthy Humorist in Orlando: Laughter is the Best Medicine"
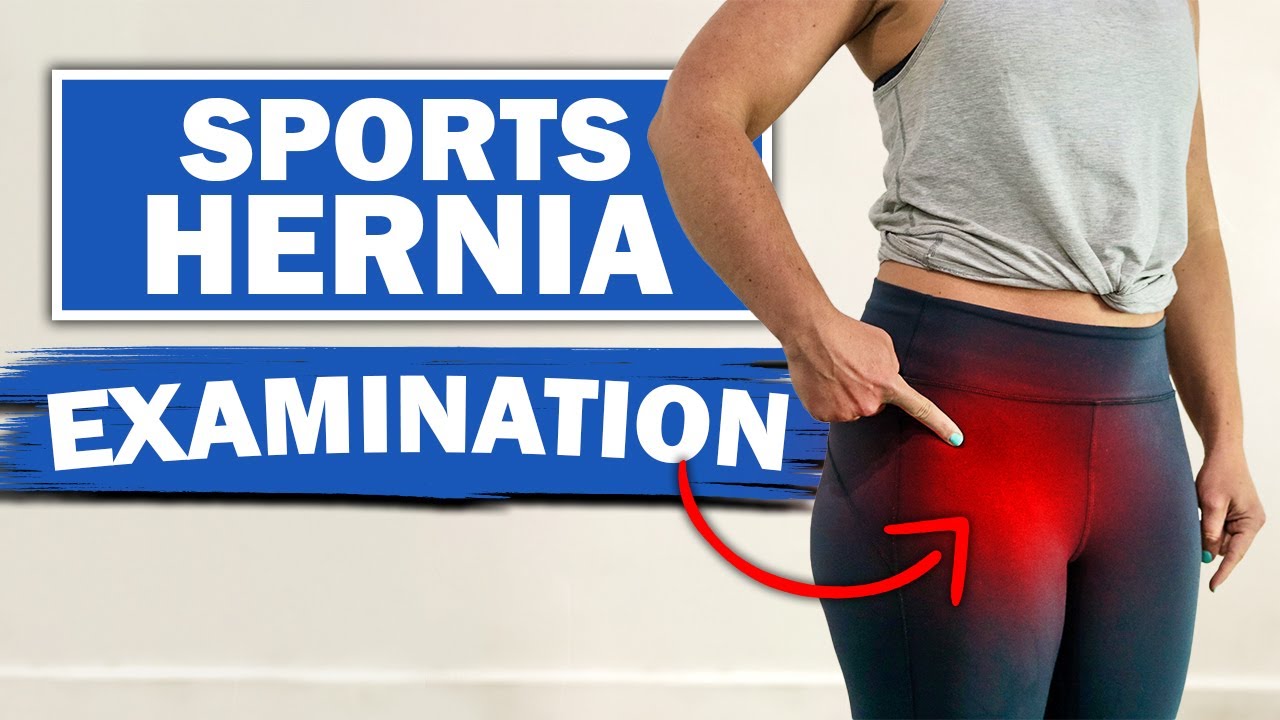
We will show you what a sports hernia examination (aka athletic pubalgia, gilmore's groin, lower abdominal pain) and rule out a diagnosis of hip impingement. Rehab exercises are suggested based on the results.
If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, don't hesitate to schedule a sports hernia examination. I can help you determine the best treatment plan to promote your recovery and avoid future injury. Subscribe to my channel to stay updated on the latest medical news and tips!
If you would like to know more about sports hernias and other diagnoses for front of hip, groin, adductor and lower abdominal strain, watch our detailed webinar here: https://bit.ly/37thtNF
For treatment, come visit us or schedule a virtual session. www.p2sportscare.com
Costa Mesa CA 715-502-4243
#sportshernia #abdominal #hippain
Sports Hernia Diagnosis
What Is A Sports Hernia?
A sports hernia is tearing of the transversalis fascia of the lower abdominal or groin region. A common misconception is that a sports hernia is the same as a traditional hernia. The mechanism of injury is rapid twisting and change of direction within sports, such as football, basketball, soccer and hockey.
The term “sports hernia” is becoming mainstream with more professional athletes being diagnosed. The following are just to name a few:
Torii Hunter
Tom Brady
Ryan Getzlaf
Julio Jones
Jeremy Shockey
If you follow any of these professional athletes, they all seem to have the same thing in common: Lingering groin pain. If you play fantasy sports, this is a major headache since it seems so minor, but it can land a player on Injury Reserve on a moments notice. In real life, it is a very frustrating condition to say the least. It is hard to pin point, goes away with rest and comes back after activity, but is hardly painful enough to make you want to stop. It lingers and is always on your mind. And if you’re looking for my step-by-step sports hernia rehab video course here it is.
One the best definitions of Sport hernias is the following by Harmon:
The phenomena of chronic activity–related groin pain that it is unresponsive to conservative therapy and significantly improves with surgical repair.”
This is truly how sports hernias behave in a clinical setting. It is not uncommon for a sports hernia to be unrecognized for months and even years. Unlike your typical sports injury, most sports medicine offices have only seen a handful of cases. It’s just not on most doctors’ radar. The purpose of this article is not only to bring awareness about sports hernias, but also to educate.
Will you find quick fixes in this article for sports hernia rehab?
Nope. There is no quick fix for this condition, and if someone is trying to sell you one, they are blowing smoke up your you-know-what.
Is there a way to decrease the pain related to sports hernias?
Yes. Proper rehab and avoidance of activity for a certain period of time will assist greatly, but this will not always stop it from coming back. Pain is the first thing to go and last thing to come. Do not be fooled when you become pain-free by resting it. Pain is only one measure of improvement in your rehab. Strength, change of direction, balance and power (just to name a few) are important, since you obviously desire to play your sport again. If you wanted to be a couch potato, you would be feeling better in no time. Watching Sports Center doesn’t require any movement.
Why is this article so long?
There is a lot of information on sports hernias available to you on the web. However, much of the information is spread out all over the internet and hard for athletes to digest due to complicated terminology. This article lays out the foundational terminology you will need to understand what options you have with your injury. We will go over anatomy, biomechanics, rehab, surgery, and even the fun facts. The information I am using is from the last ten years of medical research, up until 2016. We will be making updates overtime when something new is found as well. So link to this page and share with friends. This is the best source for information on sports hernias you will find.
Common Names (or Aliases?) for Sports Hernias
Sportsman’s Hernia
Athletic Pubalgia
Gilmore’s Groin
How Do You Know If You Have A Sports Hernia?
Typical athlete characteristics:
Male, age mid-20s
Common sports: soccer, hockey, tennis, football, field hockey
Motions involved: cutting, pivoting, kicking and sharp turns
Gradual onset
How A Sports Hernia Develops
Chronic groin pain typically happens over time, which is why with sports hernias, we do not hear many stories of feeling a “pop” or a specific moment of injury. It is the result of “overuse” mechanics stemming from a combination of inadequate strength and endurance, lack of dynamic control, movement pattern abnormalities, and discoordination of motion in the groin area.
#SPORTSHERNIAEXAM #california

All Solution of Male Disorder Male Infertility Diagnostic and Treatment Re-Slim Care Latest Technology in Pakistan Dr. Aslam Naveed is a well known sexologist in Pakistan. He has treated more than 1 Lac patients since last 30 years of clinical Practice in sexology, he knows how to help the people facing sexual disorders. Contact: 02134965050, 03432821919, 0345-8314663 http://www.sexologistpakistan.com/ https://www.facebook.com/menssexcareclinic/ https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCagSSgdEgQJWl_xfFM12BwA https://twitter.com/bettersexcare https://www.instagram.com/dr.aslamnaveed/ ADDRESS: Men’s Care Modern Hospital, Opposite, Safari Park, University Road, Karachi, Pakistan.

Hernia symptoms test diagnosis and surgery - This lecture explains about hernia symptoms, diagnosis and surgery to cure hernia disease. Stay tuned to this video lecture to get answer of the following questions -
what is hernia disease?
hernia symptoms?
hernia test?
hernia diagnosis?
hernia treatment?
Specifically the hernia surgery is explained in this video. So stay tuned to this video to more about hernia repair and details about hernia symptoms and diagnosis.
Watch this video lecture if you have hernia and want to know about hernia surgery and hernia operation related information.
For more information, log on to-
http://[a]www.shomusbiology.com%2F[/a]
Get Shomu's Biology DVD set here-
http://[a]www.shomusbiology.com%2F[/a]dvd-store/
Download the study materials here-
http://shomusbiology.com/bio-materials.html
Remember Shomu’s Biology is created to spread the knowledge of life science and biology by sharing all this free biology lectures video and animation presented by Suman Bhattacharjee in YouTube. All these tutorials are brought to you for free. Please subscribe to our channel so that we can grow together. You can check for any of the following services from Shomu’s Biology-
Buy Shomu’s Biology lecture DVD set- [a]www.shomusbiology.com%2Fdvd-store[/a]
Shomu’s Biology assignment services – [a]www.shomusbiology.com%2Fassignment[/a] -help
Join Online coaching for CSIR NET exam – [a]www.shomusbiology.com%2Fnet-coaching[/a]
We are social. Find us on different sites here-
Our Website – www.shomusbiology.com
Facebook page- https://www.facebook.com/ShomusBiology/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/shomusbiology
SlideShare- www.slideshare.net/shomusbiology
Google plus- https://plus.google.com/113648584982732129198
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/su....man-bhattacharjee-2a
Youtube- https://www.youtube.com/user/TheFunsuman
Thank you for watching the health tutorial video on Hernia symptoms test diagnosis and surgery.