Top videos

How To Stop Bloating, Belching And Flatulence, How To Reduce Bloating And Gas, Flatulence Cause ---- http://flatulence-cure.plus101.com --- Relieve Flatulence by Changing Your Diet 1. Flatulence is a problem for many people - although the seriousness naturally varies considerably from person to person. In some cases, what one person would consider problem flatulence will not be an issue for another. However most people who have problem flatulence will want to make a change - and if you want to relieve flatulence then you may find that the best way of doing so is to make a change in your diet. Changing your diet is considered to be a quite extreme reaction to a problem when over the counter remedies to relieve flatulence already exist. However, there should be no doubt that a natural solution is more desirable. 2. Know The Problem And Relieve Flatulence People who have problem flatulence are often quick to put the problem down to something which may be unconnected. We can usually feel quite confident that the reason for flatulence is dietary, and that a dietary solution is the best way to relieve flatulence. However, before we do this it is essential that we take a long view of the situation. This can best be done by looking at the potential causes of our problem flatulence, and a food diary can be the first step in a plan to relieve flatulence - as heavy as it sounds, writing things down helps us notice patterns. 3. Consider what you eat over the course of a day. Remember that what you eat will affect how much you break wind, and everything else to do with your digestion. How much you eat will also play a part. When you write down what you eat, you should also include a record of any particular cases of flatulence you have had in the aftermath of that meal - whether you do this as you go along, or when you next come to record what you ate is up to you. In order to decide your "relieve flatulence" plan, knowing what foods and what quantities are involved where flatulence is common will help you out massively. Flatulence relief should be natural, and this is the best natural way of evaluating it. 4. What If Problem Foods Are Your Favorites? Flatulence "problem foods" differ between people. It depends considerably upon your definition of a problem and also upon how your digestive system works. One person may have a problem with beans but find broccoli completely innocuous, while others will feel that the reverse is true for them. You won't relieve flatulence by looking at a list and recognising that the foods on there will have to be cut from your diet. You may by doing that deny yourself a good, healthy food which has no ill-effect on you. Instead, you should consider what your food diary - your "relieve flatulence" planner - is telling you. 5. No-one likes having to give up foods they love. But by keeping a food diary it may be possible to diagnose conditions like lactose intolerance or celiac disease. These are essential pieces of knowledge to relieve flatulence, and should be paid close attention. The quickest way to relieve flatulence that is natural and will work is to audit your diet. Finally, it's been revealed how you can cure flatulence quickly and easily... All FULLY Naturally Just see for yourself... http://flatulence-cure.plus101.com

Iodine For Ringworm, Best Ointment For Ringworm, Where Do You Get Ringworm, How To Treat Ring Worms ---- http://ringworm-cure.plus101.com --- Ringworms, contrary to the common notion, do not come from worms. Tinea, which is the medical term for ringworms, is a fungal infection seen on the skin's surface. Knowing how to cure ringworm is important because ringworms can be highly contagious. It can be contracted from direct contact with the host (person or animal) as well as by other means such as having contact with the host's clothes. Swimming pools can also be a place where ringworms are transmitted from one person to another. How To Cure Ringworm - Understanding Aspects and Options Different means on how to cure ringworm are available and they sometimes vary in accordance with where the ringworm is located (it can appear in areas like the nails, fingers, toes, feet, scalp, stomach, chest, thighs, and scalp), and the particular type of ringworm. • Ringworms found in the scalp are usually treated with an antifungal shampoo to keep the area dry and clean. • Ringworms found in the feet can be treated through the application of ointments. • Oral medications can also be taken in especially when ringworms are on the nails. • Sprays, powders and creams are also forms by which anti-fungal drugs are bought. These medicines may take some time to work. The infection may persist for a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity and how the body responds to the medications. How To Cure Ringworm - OTC and Prescription Medications Ringworm appears on the skin's surface as an itchy, red, circular patch. As it progresses, it expands and smaller round patches can develop. It is important to immediately identify ringworms and know how to treat them properly. There are many over the counter topical creams (anti-fungal ones) and ointment that can be bought in the market. However, some people prefer to visit the doctor and ask for a prescription. Stronger formulations are generally available via prescriptions. William Oliver is a nutritionist, medical researcher, and author of the Fast Ringworm Cure e-book. To find out how to cure Ringworm in 3 days or less, click below: http://ringworm-cure.plus101.com

Homemade Body Wraps For Weight Loss, Cheap Body Wraps That Work, Body Wraps To Lose Weight ---- http://do-body-wraps-work.plus101.com -- Cellulite and loose and flabby skin can often drain your confidence. You have maybe considered plastic surgery, but the risks and costs are just not reasonable. Fortunately, there are body wraps, which can offer alternative to plastic surgery. Getting a body wrap at a salon can be very expensive - multiple sessions can cost hundreds of dollars. The WrapYourselfSlim ebook shows readers how to get rid of their flabby stomaches and cellulite through the recipes made in the home kitchen. Which recipe is the best when wanting to seek drastic results? What Is The Best Body Wrap Recipe? One of the best body wrap recipes contains the ingredients of olive oil, green clay, water, herbs sea salt, and essential oils. You can select the oils and herbs such as lemongrass, sage, rosemary, rose petal powder, neem powder, lavender, ground basil, grapefruit, ginger root powder, alfalfa leaf powder, and rosehip powder. Measure out two tablespoons of olive oil, 1 cup of green clay, 2 cups of water, and a 1/2 cup of sea salt. Boil the water, then thoroughly stir inside of the sea salt until it has dissolved. Add your selected herbs, olive oil, and green clay, then stir til a paste has formed for you to set this mixture aside for cooling. Once the paste has cooled enough for your skin to handle, rub it on to your body, then cover it with sheets or towels cut into strips. Keep it on for one full hour before removing. A great tip that you should keep in mind when wanting to see the best results is to detoxify your body a couple days before applying the wrap on to yourself. Drink plenty of water before you apply the wrap on to yourself so you can see the highest results possible. You will definitely see significant results right after taking the wrap off, as the skin will instantly absorb the nutrients of the ingredients. This is better than the typical weight loss cream that you find today. Use this easy-to-prepare affordable formula to help contour your abs, thighs, hips buttocks, etc ... in less than two weeks! Stop procrastinating! Click Here for instant access to my recipes & start losing inches, detoxifying your body, and improving your skin right away! http://do-body-wraps-work.plus101.com

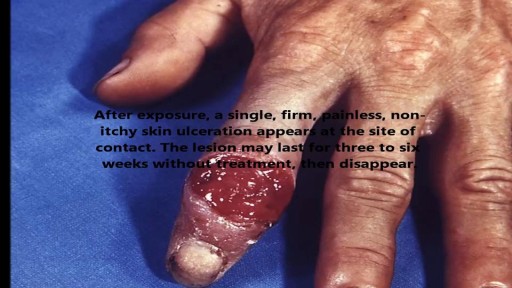
» A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus (from the Latin rēnēs, “kidneys,” and calculus, “pebble”), is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine. » Urolithiasis (UL) is one of the most common diseases, with approximately 7.6% incidence in Western India. Although most patients have only one stone episode, 25% of patients experience recurrent stone formation. UL therefore has a significant impact on quality of life and socioeconomic factors.
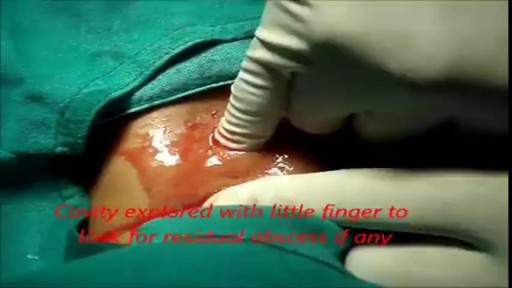
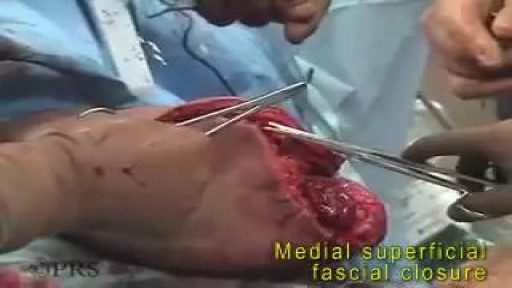
She is a twenty years young female presented with large cystic swelling in anterior aspect of neck. The swelling was of size 6cmx 6cm x5 cm ,tense tender, cystic just above sternal nutch.This was diagnosed as large neck abscess ./nRepeated aspiration done but the swelling reappeared. So Incision & Drainage planned under local anaesthesia./nPatient in supine position. Surgery part painted and draped. Local anaesthesia 2% xylocaine with adrenaline used for field block.After giving local anaesthesia, I used a no 11 blade for stab incision at the most prominent part of the swelling, where skin was thin and fluctuation present./nPus drained form that opening. Little dilatation of opening to be done with artery forceps or sinus forceps. Complete pus drainage to be ensured.Little finger can be introduced inside the pus cavity to ensure proper drainage of pus. The cavity I use to clean with a gauge piece. If necessary curette biopsy can be taken from the wall of the cavity.These wounds usually need daily proper dressing for faster healing.
Symptoms of dizziness can result from many conditions such as; (vestibular) inner ear disorders, neck injuries or muscle tightness, neuropathy, central nervous system problems, metabolic issues, or psychological disorders. Our therapists are trained to screen for more serious conditions (such as neurological and cardiovascular disorders) as well as effectively evaluate and treat conditions which are appropriate for physical therapy intervention.

In dark or dim light, the pupil dilates to allow more light into the eye to improve vision. Normal pupil size tends to range between 2.0 and 5.0 millimeters, depending on the lighting. The younger you are, the larger your pupils tend to be.

Curious about physiotherapy or wanting to know how to properly perform an exercise? Check us out on Social Media! Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/striveptandperformance/ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/striveptandperf/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/StrivePTandPerf Blog: http://www.strivept.ca/blog

The best way to make condoms work as well as possible is to use them correctly every single time you have vaginal, oral, and anal sex. That means wearing it the whole time, from start to finish. Make sure the condom is rolled on your penis the right way before there’s any skin-to-skin genital contact. Read more about how to use condoms correctly.
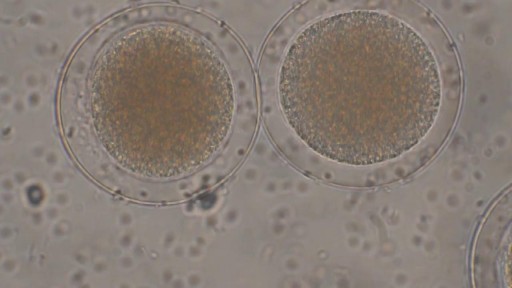
Sperm Meets Egg: Weeks 1 to 3 of Pregnancy. Something magical is about to happen! Watch as the ovulation process occurs, and then millions of sperm swim upstream on a quest to fertilize an egg. Your due date is calculated from the first day of your last menstrual period