Top videos
Brown-Séquard syndrome is an incomplete spinal cord lesion characterized by a clinical picture reflecting hemisection injury of the spinal cord, often in the cervical cord region. (See Presentation.) Patients with Brown-Séquard syndrome suffer from ipsilateral upper motor neuron paralysis and loss of proprioception, as well as contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation. A zone of partial preservation or segmental ipsilateral lower motor neuron weakness and analgesia may be noted. Loss of ipsilateral autonomic function can result in Horner syndrome. (See Etiology, Presentation, and Workup.) As an incomplete spinal cord syndrome, the clinical presentation of Brown-Séquard syndrome may range from mild to severe neurologic deficit. (See Presentation.) Brown-Séquard–plus syndrome The pure Brown-Séquard syndrome reflecting hemisection of the cord is not often observed. A clinical picture composed of fragments of the syndrome or of the hemisection syndrome plus additional symptoms and signs is more common. These less-pure forms of the disorder are often referred to as Brown-Séquard–plus syndrome.[1] Interruption of the lateral corticospinal tracts, the lateral spinal thalamic tract, and at times the posterior columns produces a picture of a spastic, weak leg with brisk reflexes and a strong leg with loss of pain and temperature sensation. Note that spasticity and hyperactive reflexes may not be present with an acute lesion.
Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects the brain and spinal cord. Early MS symptoms include weakness, tingling, numbness, and blurred vision. Other signs are muscle stiffness, thinking problems, and urinary problems. Treatment can relieve MS symptoms and delay disease progression.
Clopidogrel keeps the platelets in your blood from coagulating (clotting) to prevent unwanted blood clots that can occur with certain heart or blood vessel conditions. Clopidogrel is used to prevent blood clots after a recent heart attack or stroke, and in people with certain disorders of the heart or blood vessels. Clopidogrel may also be used for other purposes not listed in this medication guide
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a multisystem disease affecting the digestive system, sweat glands, upper and lower respiratory tracts, and the reproductive tract, but progressive lung disease continues to be the major cause of morbidity and mortality [1]. CF is characterized by abnormal transport of chloride and sodium across the respiratory epithelium, resulting in thickened, viscous airway secretions [2]. Over a highly variable time course ranging from months to decades after birth, individuals eventually develop chronic infection of the respiratory tract with a characteristic array of bacterial flora [3], leading to progressive respiratory insufficiency and eventual respiratory failure. The rate of progression varies widely, depending in part on genotype (including gene modifiers) as well as environmental factors. Registry data from CF Centers in the United States, Canada, and Europe indicate a median survival of about 41 years [4]. Females with CF appear to have higher morbidity and mortality than males [5]. This "gender gap" is modest but consistent across many populations and is hypothesized to be due to the pro-inflammatory effects of estrogens.
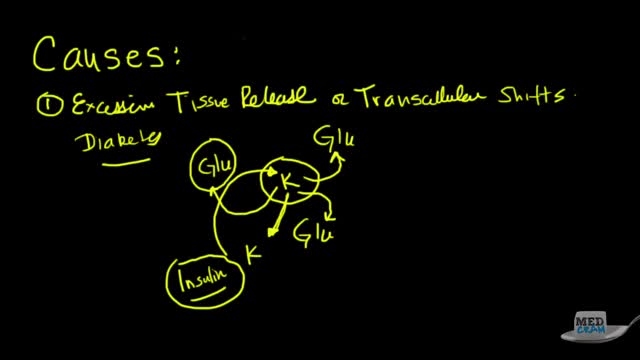
Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium concentration higher than the upper limit of the normal range; the range in infants and children is age-dependent, whereas the range for adults is approximately 3.5-5.5 mEq/L. The upper limit may be considerably higher in young or premature infants, as high as 6.5 mEq/L.[5] Degrees of hyperkalemia are defined as follows[6] : 5.5-6.0 mEq/L – Mild 6.1-7.0 mEq/L – Moderate ≥7.0 mEq/L – Severe levels higher than 7 mEq/L can lead to significant hemodynamic and neurologic consequences. levels exceeding 8.5 mEq/L can cause respiratory paralysis or cardiac arrest and can quickly be fatal. Because of a paucity of distinctive signs and symptoms, hyperkalemia can be difficult to diagnose. Indeed, it is frequently discovered as an incidental laboratory finding. The physician must be quick to consider hyperkalemia in patients who are at risk for this disease process. (See Etiology.) However, any single laboratory study demonstrating hyperkalemia must be repeated to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the patient has no changes on electrocardiography (ECG). Because hyperkalemia can lead to sudden death from cardiac arrhythmias, any suggestion of hyperkalemia requires an immediate ECG to ascertain whether ECG signs of electrolyte imbalance are present (see Workup). Continuous ECG monitoring is essential if hyperkalemia is confirmed. Other testing is directed toward uncovering the condition or conditions that led to the hyperkalemia (see Workup). The aggressiveness of therapy for hyperkalemia is directly related to the rapidity with which the condition has developed, the absolute level of serum potassium, and the evidence of toxicity. The faster the rise of the potassium level, the higher it has reached, and the greater the evidence of cardiotoxicity, the more aggressive therapy should be. In severe cases, treatment focuses on immediate stabilization of the myocardial cell membrane, rapid shifting of potassium to the intracellular space, and total body potassium elimination. In addition, all sources of exogenous potassium should be immediately discontinued. (See Treatment.)
Hyponatremia is a condition that occurs when the level of sodium in your blood is abnormally low. Sodium is an electrolyte, and it helps regulate the amount of water that's in and around your cells. In hyponatremia, one or more factors — ranging from an underlying medical condition to drinking too much water during endurance sports — causes the sodium in your body to become diluted. When this happens, your body's water levels rise, and your cells begin to swell. This swelling can cause many health problems, from mild to life-threatening. Hyponatremia treatment is aimed at resolving the underlying condition. Depending on the cause of hyponatremia, you may simply need to cut back on how much you drink. In other cases of hyponatremia, you may need intravenous fluids and medications
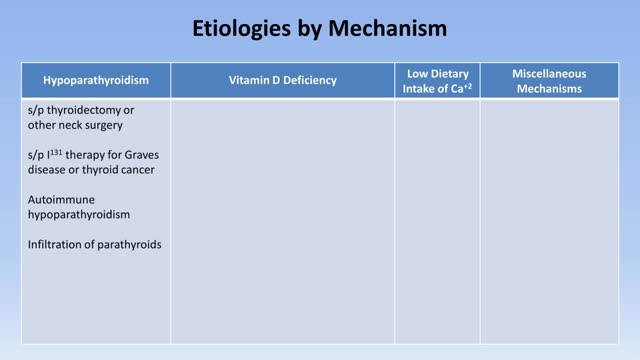
In neonates, hypocalcemia is more likely to occur in infants born of diabetic or preeclamptic mothers. Hypocalcemia also may occur in infants born to mothers with hyperparathyroidism. Clinically evident hypocalcemia generally presents in milder forms and is usually the result of a chronic disease state. In emergency department patients, chronic or subacute complaints secondary to mild or moderate hypocalcemia are more likely to be a chief complaint than severe symptomatic hypocalcemia. Once laboratory results demonstrate hypocalcemia, the first question is whether the hypocalcemia is true—that is, whether it is representative of a decrease in ionized calcium. The presence of chronic diarrhea or intestinal disease (eg, Crohn disease, sprue, chronic pancreatitis) suggests the possibility of hypocalcemia due to malabsorption of calcium and/or vitamin D. The patient's past medical history should be explored for pancreatitis, anxiety disorders, renal or liver failure, gastrointestinal disorders, and hyperthyroidism or hyperparathyroidism. Previous neck surgery suggests hypoparathyroidism; a history of seizures suggests hypocalcemia secondary to anticonvulsants. The patient may have a recent history of thyroid, parathyroid, or bowel surgeries or recent neck trauma. The length of time that a disorder is present is an important clue. Hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism are lifelong disorders. Instead, acute transient hypocalcemia may be associated with acute gastrointestinal illness, nutritional deficiency, or acute or chronic renal failure. In an elderly patient, a nutritional deficiency may be associated with a low intake of vitamin D. A history of alcoholism can help diagnose hypocalcemia due to magnesium deficiency, malabsorption, or chronic pancreatitis. Inquire about recent use of drugs associated with hypocalcemia, including the following: Radiocontrast Estrogen Loop diuretics Bisphosphonates Calcium supplements Antibiotics Antiepileptic drugs Cinacalcet Other considerations in the history include the following: Family history of hypocalcemia Low-calcium diet Lack of sun exposure
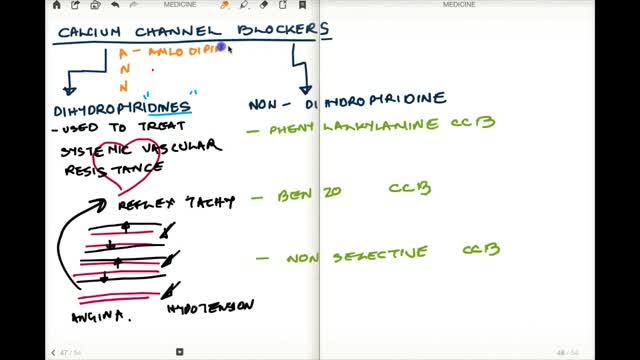
Calcium channel blockers prevent calcium from entering cells of the heart and blood vessel walls, resulting in lower blood pressure. Calcium channel blockers, also called calcium antagonists, relax and widen blood vessels by affecting the muscle cells in the arterial walls. Some calcium channel blockers have the added benefit of slowing your heart rate, which can further reduce blood pressure, relieve chest pain (angina) and control an irregular heartbeat. Examples of calcium channel blockers Some calcium channel blockers are available in short-acting and long-acting forms. Short-acting medications work quickly, but their effects last only a few hours. Long-acting medications are slowly released to provide a longer lasting effect. Several calcium channel blockers are available. Which one is best for you depends on your health and the condition being treated. Examples of calcium channel blockers include: Amlodipine (Norvasc) Diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others) Felodipine Isradipine Nicardipine Nifedipine (Adalat CC, Afeditab CR, Procardia) Nisoldipine (Sular) Verapamil (Calan, Verelan) In some cases, your doctor might prescribe a calcium channel blocker with other high blood pressure medications or with cholesterol-lowering drugs such as statins.
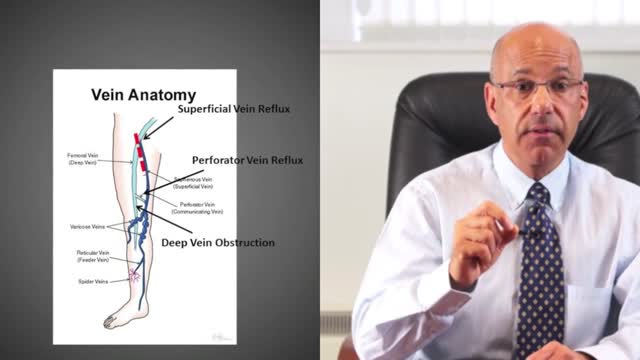
A leg ulcer is simply a break in the skin of the leg, which allows air and bacteria to get into the underlying tissue. This is usually caused by an injury, often a minor one that breaks the skin. In most people such an injury will heal up without difficulty within a week or two. However, when there is an underlying problem the skin does not heal and the area of breakdown can increase in size. This is a chronic leg ulcer.
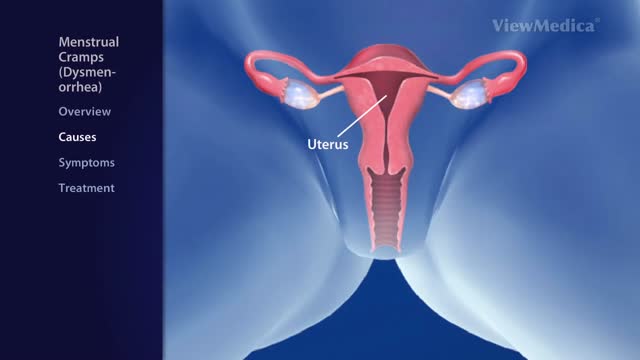
Dysmenorrhea is the medical term for pain with menstruation. There are two types of dysmenorrhea: "primary" and "secondary". Primary dysmenorrhea is common menstrual cramps that are recurrent (come back) and are not due to other diseases. Pain usually begins 1 or 2 days before, or when menstrual bleeding starts, and is felt in the lower abdomen, back, or thighs. Pain can range from mild to severe, can typically last 12 to 72 hours, and can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and even diarrhea. Common menstrual cramps usually become less painful as a woman ages and may stop entirely if the woman has a baby. Secondary dysmenorrhea is pain that is caused by a disorder in the woman's reproductive organs, such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, or infection. Pain from secondary dysmenorrhea usually begins earlier in the menstrual cycle and lasts longer than common menstrual cramps. The pain is not typically accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or diarrhea.
Is My Chest Pain a Sign Of a Heart Attack?
What Causes Chest Pain ?
How to Treat Cuts & Scrapes | First Aid Training
Approximately 10%-15% of human bite wounds become infected owing to multiple factors. The bacterial inoculum of human bite wounds contains as many as 100 million organisms per milliliter and is made up of as many as 190 different species. Many of these are anaerobes that flourish in the low redox environment of tartar that lies between human teeth or in areas of gingivitis. Most injuries due to human bites involve the hands. Hand wounds, regardless of the etiology, have a higher rate of infection than do those in other a locations. (See Pathophysiology and Etiology.) Infections associated with human bites are often far advanced by the time they receive appropriate care. Patients often wait until infection is well established before seeking medical treatment. These wounds are frequently more extensive than estimated on initial examination by the inexperienced observer and are frequently managed inadequately. (See Prognosis, Presentation, Treatment, and Medication.) Human bites have been shown to transmit hepatitis B, hepatitis C, herpes simplex virus (HSV), syphilis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis, and tetanus. Evidence suggests that it is biologically possible, but quite unlikely, to transmit human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) through human bites. (See Pathophysiology, Presentation, and Workup.)
You might not notice signs or symptoms of Hashimoto's disease at first, or you may notice a swelling at the front of your throat (goiter). Hashimoto's disease typically progresses slowly over years and causes chronic thyroid damage, leading to a drop in thyroid hormone levels in your blood. The signs and symptoms are mainly those of an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism). Signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism include: Fatigue and sluggishness Increased sensitivity to cold Constipation Pale, dry skin A puffy face Hoarse voice Unexplained weight gain — occurring infrequently and rarely exceeding 10 to 20 pounds, most of which is fluid Muscle aches, tenderness and stiffness, especially in your shoulders and hips Pain and stiffness in your joints and swelling in your knees or the small joints in your hands and feet Muscle weakness, especially in your lower extremities Excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia) Depression
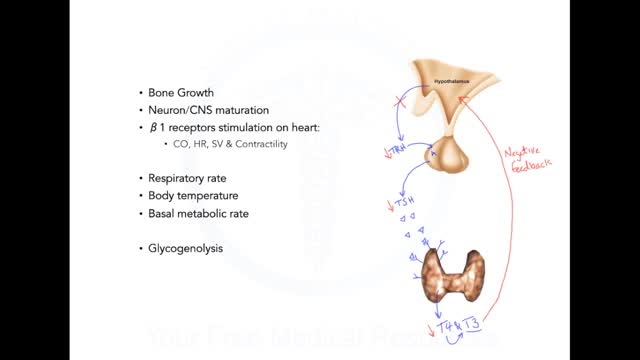
Graves disease is an autoimmune disorder that leads to an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism). An autoimmune disorder is a condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. Causes The thyroid gland is an important organ of the endocrine system. The gland is located at the front of the neck above where the collarbones meet. This gland releases the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which control body metabolism. Controlling metabolism is important for regulating mood, weight, and mental and physical energy levels. When the body makes too much thyroid hormone, the condition is called hyperthyroidism. (An underactive thyroid leads to hypothyroidism.) Graves disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is due to an abnormal immune system response that causes the thyroid gland to produce too much thyroid hormone. Graves disease is most common in women over age 20. But the disorder can occur at any age and can affect men as well. Symptoms Younger people may have these symptoms: Anxiety or nervousness, as well as problems sleeping Breast enlargement in men (possible) Problems concentrating Fatigue Frequent bowel movements Hair loss Heat intolerance and increased sweating Increased appetite, despite having weight loss Irregular menstrual periods in women Muscle weakness of the hips and shoulders Moodiness, including irritability and anger Rapid or irregular heartbeat Shortness of breath with activity Tremor Many people with Graves disease have problems with their eyes: The eyeballs may seem to be bulging out and may be painful. Eyes can feel irritated and be tearing. Double vision may be present. Older people may have these symptoms: Rapid or irregular heartbeat Chest pain Memory loss Weakness and fatigue
EART (Health Education and Rescue Training) Wilderness First Aid is an intensive course that covers patient examination and evaluation, body systems and anatomy, wound care, splinting, environmental emergencies, and backcountry medicine. Hands-on simulations provide first-hand training in treating patients. This is an excellent course taught by experienced Wilderness First Responders and Emergency Medical Technicians and is highly recommended to all wilderness travelers. People who pass the courses will receive a Wilderness First Aid certification from the Emergency Care and Safety Institute (ECSI) which is good for 2 years. Participants who successfully pass CPR and HEART Wilderness First Aid will have met the First Aid requirements for OA Leader Training.
Seeing blood in your urine can cause anxiety. While in many instances there are benign causes, blood in urine (hematuria) can also indicate a serious disorder. Blood that you can see is called gross hematuria. Urinary blood that's visible only under a microscope is known as microscopic hematuria and is found when your doctor tests your urine. Either way, it's important to determine the reason for the bleeding. Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Postmenopausal bleeding (PMB) is defined for practical purposes as vaginal bleeding occurring after twelve months of amenorrhoea, in a woman of the age where the menopause can be expected.[1] Hence it does not apply to a young woman, who has had amenorrhoea from anorexia nervosa, or a pregnancy followed by lactation. However, it can apply to younger women following premature ovarian failure or premature menopause. Unscheduled bleeding in women of menopausal age taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) should be managed in the same way from a practical perspective.[2] 'Unscheduled bleeding' is defined as non-cyclical bleeding still continuing six months after commencing HRT or after six months of amenorrhoea.
Shingles is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. Although shingles can occur anywhere on your body, it most often appears as a single stripe of blisters that wraps around either the left or the right side of your torso. Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus — the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you've had chickenpox, the virus lies inactive in nerve tissue near your spinal cord and brain. Years later, the virus may reactivate as shingles. While it isn't a life-threatening condition, shingles can be very painful. Vaccines can help reduce the risk of shingles, while early treatment can help shorten a shingles infection and lessen the chance of complications.