Top videos

In dark or dim light, the pupil dilates to allow more light into the eye to improve vision. Normal pupil size tends to range between 2.0 and 5.0 millimeters, depending on the lighting. The younger you are, the larger your pupils tend to be.

Curious about physiotherapy or wanting to know how to properly perform an exercise? Check us out on Social Media! Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/striveptandperformance/ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/striveptandperf/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/StrivePTandPerf Blog: http://www.strivept.ca/blog

The best way to make condoms work as well as possible is to use them correctly every single time you have vaginal, oral, and anal sex. That means wearing it the whole time, from start to finish. Make sure the condom is rolled on your penis the right way before there’s any skin-to-skin genital contact. Read more about how to use condoms correctly.

Curious about physiotherapy or wanting to know how to properly perform an exercise? Check us out on Social Media! Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/striveptandperformance/ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/striveptandperf/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/StrivePTandPerf Blog: http://www.strivept.ca/blog
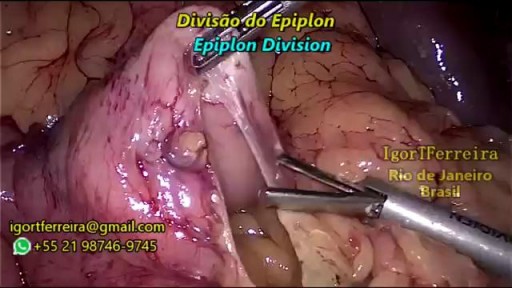
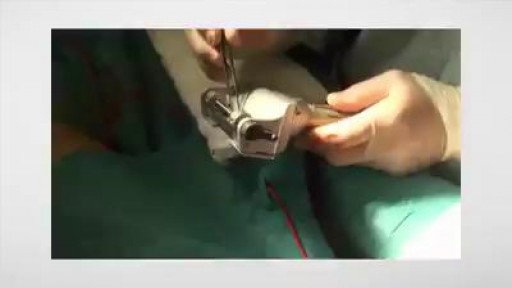
a sleeve gastrectomy with very few edditing. During the start 3 smal spleen perforations caused by Veres Needle were identified, caused by a giant spleen undentified on pre operatory ultrasound. They were controled with gauze compression and at the end of the surgery surgicel was placed and no complications were observed. Patient discharged 3 days after the surgery.
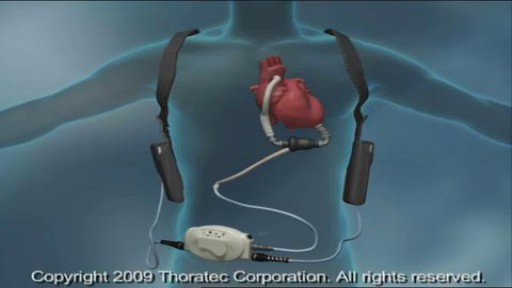
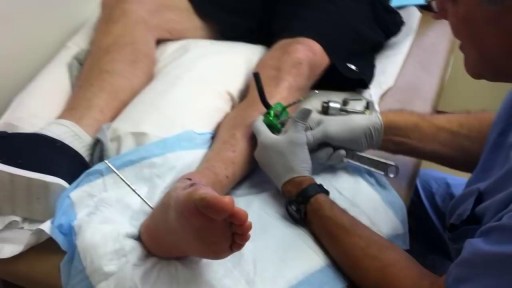
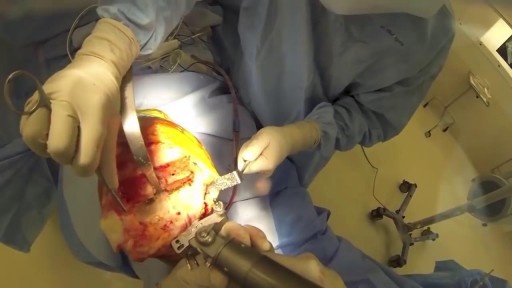
A ventricular assist device (VAD) — also known as a mechanical circulatory support device — is an implantable mechanical pump that helps pump blood from the lower chambers of your heart (the ventricles) to the rest of your body. A VAD is used in people who have weakened hearts or heart failure. Although a VAD can be placed in the left, right or both ventricles of your heart, it is most frequently used in the left ventricle. When placed in the left ventricle it is called a left ventricular assist device (LVAD). You may have a VAD implanted while you wait for a heart transplant or for your heart to become strong enough to effectively pump blood on its own. Your doctor may also recommend having a VAD implanted as a long-term treatment if you have heart failure and you're not a good candidate for a heart transplant.
The spine is made flexible by discs located between each vertebra and ligaments made of tough elastic fibers which hold the vertebrae together. The spine gives the body stability and protects the spinal cord which is located in a narrow canal that runs through the center of each vertebra.

Eating a high-protein breakfast has been shown to reduce cravings and calorie intake throughout the day (16, 17). Avoid sugary drinks and fruit juice. These are the most fattening things you can put into your body, and avoiding them can help you lose weight (18, 19). Drink water a half hour before meals.
Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of medical treatment for pediatric rhinosinusitis.] Because of increasing prevalence of beta-lactam–resistant bacteria in the community, administer antibiotics only for suspected infection as based on a careful history and physical examination. Direct the therapeutic regimen against the prevalent pathogens in the community and carefully consider suspicion for highly resistant bacteria. Typically, uncomplicated cases of acute sinusitis are responsive to amoxicillin. Most patients respond to this initial regimen. For children allergic to penicillin, a second- or third-generation cephalosporin can be used (only if the allergic reaction is not a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction). In cases of serious allergic reaction, a macrolide or clindamycin can be used.
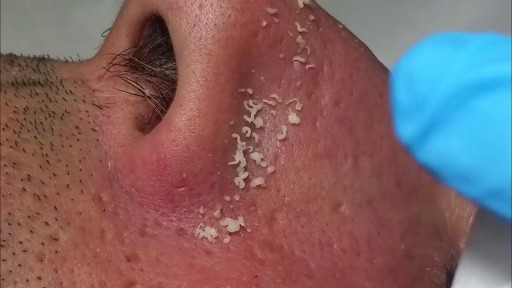
What are blackheads? Blackheads are small bumps that appear on your skin due to clogged hair follicles. These bumps are called blackheads because the surface looks dark or black. Blackheads are a mild type of acne that usually form on the face, but they can also appear on the following body parts: back chest neck arms shoulders Acne affects nearly 50 million Americans and is the most common skin disorder in the United States, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. What do blackheads look like? What causes blackheads? Blackheads form when a clog or plug develops in the opening of hair follicles in your skin. Each follicle contains one hair and a sebaceous gland that produces oil. This oil, called sebum, helps keep your skin soft. Dead skin cells and oils collect in the opening to the skin follicle, producing a bump called a comedo. If the skin over the bump stays closed, the bump is called a whitehead. When the skin over the bump opens, exposure to the air causes it to look black and a blackhead forms. Some factors can increase your chances of developing acne and blackheads, including: producing too much body oil the buildup of the Propionibacterium acnes bacteria on the skin irritation of the hair follicles when dead skins cells don’t shed on a regular basis undergoing hormonal changes that cause an increase in oil production during the teen years, during menstruation, or while taking birth control pills taking certain drugs, such as corticosteroids, lithium, or androgens Some people believe that what you eat or drink can affect acne. Dairy products and foods that increase blood sugar levels, such as carbohydrates, may play a part in triggering acne, but researchers aren’t convinced that there’s a strong connection. ADVERTISING What are symptoms of blackheads? Because of their dark color, blackheads are easy to spot on the skin. They’re slightly raised, although they aren’t painful because they aren’t inflamed like pimples. Pimples form when bacteria invade the blockage in the hair follicle, causing redness and inflammation. How are blackheads treated? Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments Many acne medications are available at drug and grocery stores and online without a prescription. These medications are available in cream, gel, and pad form and are put directly on your skin. The drugs contain ingredients such as salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and resorcinol. They work by killing bacteria, drying excess oil, and forcing the skin to shed dead skin cells. Prescription medications If OTC treatment doesn’t improve your acne, your doctor may suggest that you use stronger prescription medications. Medications that contain vitamin A keep plugs from forming in the hair follicles and promote more rapid turnover of skin cells. These medications are applied directly to your skin and can include tretinoin, tazarotene, or adapalene. Your doctor may also prescribe another type of topical medication that contains benzoyl peroxide and antibiotics. If you have pimples or acne cysts in addition to your blackheads, this type of medication may be particularly helpful. Manual removal Dermatologists or specially trained skin care professionals use a special instrument called a round loop extractor to remove the plug causing the blackhead. After a small opening is made in the plug, the doctor applies pressure with the extractor to remove the clog. Microdermabrasion During microdermabrasion, a doctor or skin care professional uses a special instrument that contains a rough surface to sand the top layers of your skin. Sanding the skin removes clogs that cause blackheads. Chemical peels Chemical peels also remove clogs and get rid of the dead skins cells that contribute to blackheads. During a peel, a strong chemical solution is applied to the skin. Over time, the top layers of the skin peel off, revealing smoother skin underneath. Mild peels are available over the counter, while stronger peels are performed by dermatologists or other skincare professionals. Laser and light therapy Laser and light therapies use tiny beams of intense light to decrease oil production or kill bacteria. Both lasers and light beams reach below the surface of the skin to treat blackheads and acne without damaging the top layers of the skin. How can blackheads be prevented? You can prevent blackheads without spending a lot of money by trying a few of the following ideas: Wash regularly Wash your face when you wake up and before you go to bed to remove oil buildup. Washing more than twice each day can irritate your skin and make your acne worse. Use a gentle cleanser that doesn’t make your skin red or irritated. Some acne cleansing products have antibacterial ingredients that kill P. acnes bacteria. Consider washing your hair every day, too, particularly if it’s oily. Hair oils can contribute to clogged pores. It’s also important to wash your face after you eat oily foods such as pizza, because oil from these foods can clog pores. Use oil-free products Any product that contains oil can contribute to new blackheads. Choose oil-free or noncomedogenic makeup, lotions, and sunscreens to avoid making your problem worse. Try an exfoliating product Exfoliating scrubs and masks remove dead skin cells from your face and can help reduce blackheads. Look for products that don’t irritate your skin.
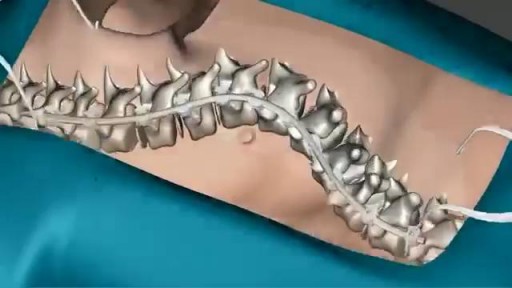
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that occurs most often during the growth spurt just before puberty. While scoliosis can be caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most scoliosis is unknown. Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some children develop spine deformities that continue to get more severe as they grow. Severe scoliosis can be disabling. An especially severe spinal curve can reduce the amount of space within the chest, making it difficult for the lungs to function properly. Children who have mild scoliosis are monitored closely, usually with X-rays, to see if the curve is getting worse. In many cases, no treatment is necessary. Some children will need to wear a brace to stop the curve from worsening. Others may need surgery to keep the scoliosis from worsening and to straighten severe cases of scoliosis.

Like a fine whiskey barrel and wine cellar, cannabis also comes at its best when aged in a dark, cool place. Though there is no steadfast expiration date for cannabis, the method you use for preserving the cannabis makes a big difference in maintaining the buds’ freshness and potency. The question is, how do you store cannabis in a way that could extend its longevity while maintaining the vigor and freshness? Experts have described different methods. However, here are some time-proven methods that are easy and inexpensive and require very less equipment. Use air-tight glass containers to store the weed Use clean air-tight glass containers or jars to store cannabis. You can buy glass containers from any ordinary supermarket or hardware store. The tricky part is to make sure you do leave some air in the container while the air stored with cannabis isn’t in detrimental extent. Always leave 1/4 space at the top of the canister or container. Do not fill the containers to the brim with the buds. If you leave no air, then the buds will dry out. If you have too much air, the buds will get damp and moldy. Freeze your cannabis in a convenient temperature The best way to store your buds is in air-tight glass jars, in a cool and dark place under an ideal temperature between 60 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit. If you need to store a high volume of cannabis, you can freeze them after keeping them completely dry for a period of 4 weeks. On this note, you should know that you must not handle frozen buds until it becomes normal in room temperature as trichomes become brittle and can easily break off in freezing temperature. Refrigerate your cannabis (Not Recommended) Even if you use airtight jars, cannabis can grow mold in the fridge. So, you should avoid storing cannabis in the fridge. If you can’t help but doing it, make sure the weed is completely dry and put them in the back where the humidity and temperature don’t fluctuate. Plastic Baggies (Worst method!) Albeit this is very common among people who aren’t expert in handling cannabis, this is the worst of all storage methods. Cannabis gets brittle and dries out in plastic bags. It also loses its natural smell, and the potency deteriorates sharply. So, it should be avoided entirely or can be used for a short-term if there is no better alternative. Here are some things you should know while storing cannabis - Make sure cannabis has been cured for at least 4 weeks before putting them into long-term storage. Without proper curing before storage, the buds can lose their strength and smoothness. - Sunlight can stop the medicinal qualities of cannabis. Your cannabis, if stored correctly, can maintain its medicinal qualities for a few years. Exposure to Sun will turn your cannabis brown, no matter how you have stored it away. - Air-tight, nonporous glass jar are the best way for storing the buds for long term. You can use metal or plastic box/bag, but that could reduce the smell and taste after a while. - Avoid heat and middling temperature in the place where you store your buds. The ideal temperature is 60-70°F (15-21°C) or under 32°F (0°C). Extra heat, cold or middling temperature cause the cannabis potency to decrease. - Keep your cannabis away from any electronic devices or appliances that will expose the cannabis to heat. Keeping cannabis on top of a microwave, or near a laptop or mobile charge is a bad idea. Now, as you know that how to store cannabis properly and make it last for years, enjoy the best form of your weeds even it comes from the previous year. Do write to us in the comments section if you have any questions. Also, don’t forget to hit the subscribe button below. Visit OnlineMedicalCard.com now to get an MMJ recommendation online in less than 10 minutes.

Spinal stenosis can put pressure on the spinal cord and the nerves within the spine. It commonly occurs in the neck and lower back. The condition is often caused by age-related wear and tear. Symptoms, if they occur, include pain, numbness, muscle weakness, and impaired bladder or bowel control. Treatment includes medication, physical therapy, and possibly surgery