Top videoer
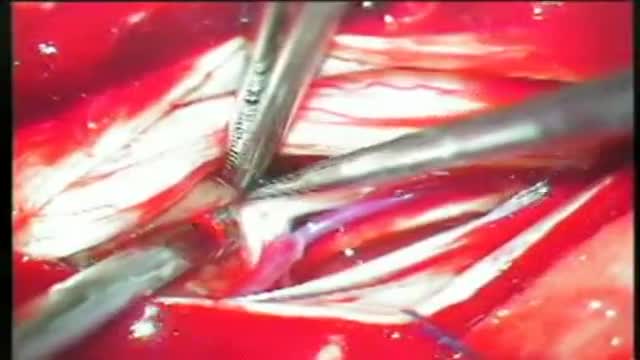
Schwannomas are usually located in the angle between the cerebellum and the pons, in the back of the skull (the posterior fossa). Description Schwannomas are usually very slow-growing. Symptoms Common symptoms of Schwannoma are one-sided hearing loss and buzzing or ringing in the ear. Dizziness may also occur, although it is less common. If the tumor affects the facial nerve (the 7th cranial nerve, which is located next to the 8th cranial nerve), facial paralysis may occur. Other symptoms include difficulty in swallowing, impaired eye movement, taste disturbances, and unsteadiness. Incidence Schwannomas account for about 8% of all primary brain tumors. They typically occur in middle-aged adults, and females are twice as likely as males to have this tumor. Cause Like many tumor types, the exact cause of Schwannoma is not known. However, it is believed to occur when there is a defect in a gene that normally prevents tumors from forming. Treatment Total removal using microsurgical techniques is often possible. Stereotactic radiosurgery may be used as an alternative to surgery in some patients.
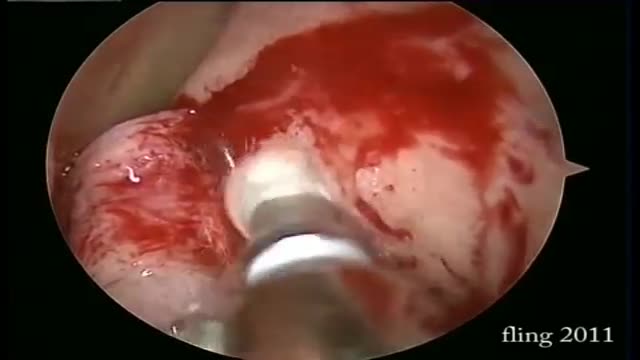
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a procedure performed for the treatment of tearing (epiphora) due to blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. Tears originate in the lacrimal gland, located at the upper outer margin of the eye. As tears cross the eye with each blink, they are directed into small openings in the eyelids called puncta. From this point, tears travel through a pathway known as the canalicular system into the lacrimal sac. The lacrimal sac is located between the eye and the nose, and funnels tears into the nasal cavity through the nasolacrimal duct (Figure 1). As this is quite a long path for tears to travel, there can be many causes of excessive tearing. Blockage of the nasolacrimal duct is one common cause, and can be treated by creating a direct opening from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity in a procedure known as DCR. The evaluation and management of tearing may involve both an ophthalmologist and an otolaryngologist.
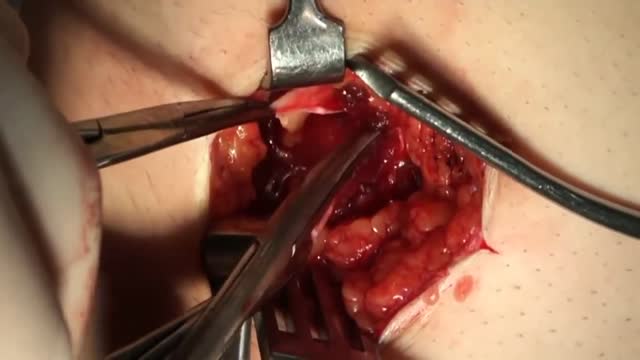
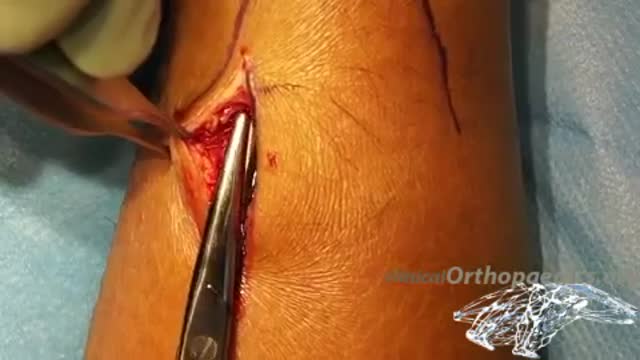
An appendectomy (sometimes called appendisectomy or appendicectomy) is the surgical removal of the vermiform appendix. This procedure is normally performed as an emergency procedure, when the patient is suffering from acute appendicitis.
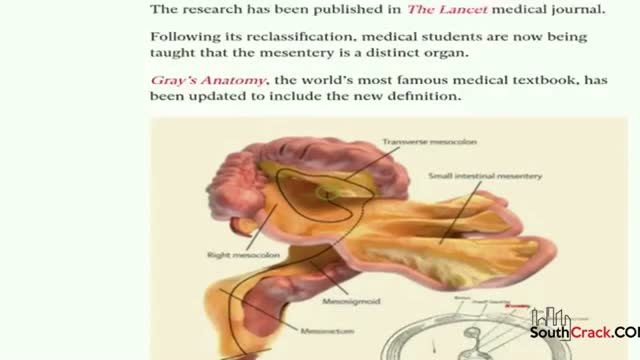
an. 4, 2017 -- Scientists say they've identified a new organ in the body -- a swath of tissue dubbed the mesentery that connects the intestine to the abdomen and holds everything in place. For years, anatomical experts have thought the organ was composed of several different segments of tissue, as opposed to being one single structure, according to Discover magazine. Since an organ must be one structure that performs a vital function, it was not deemed worthy of organ status. But recent research from doctors at the University Hospital Limerick in Ireland shows that the mesentery is actually one single band of tissue, the magazine reported Tuesday. It begins at the pancreas and wraps around the small intestine and colon. Its purpose: to hold these organs in position so they can perform their respective functions. "Without it you can't live," lead researcher Dr. J. Calvin Coffey, a colorectal surgeon at Limerick, told the magazine. "There are no reported instances of a Homo sapien living without a mesentery." "Understanding how and why our digestive system is arranged the way it is could be crucial to our understanding of diseases like Crohn's and irritable bowel syndrome," Coffey added. "There are a lot of diseases that we are stalled on, and we need to refresh our approach to these diseases," Coffey said. "Now that we've clarified its [the mesentery's] structure, we can systematically examine it. We're at a very exciting place right now." The discovery was published recently in the Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology journal.
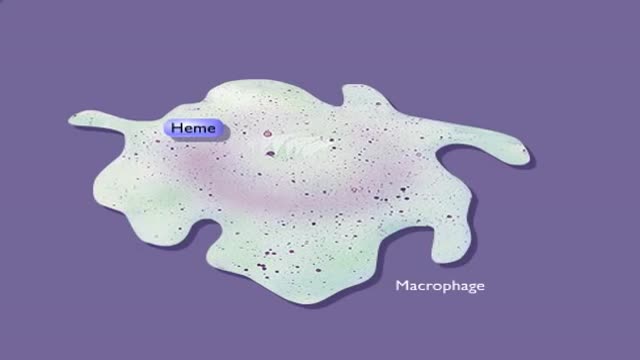
Red blood cells, which form one of the major constituents of blood, are characterized by the absence of nuclei, hence they are unable to undergo cellular division or generate new erythrocytes from old ones. This eventually leads to cell disintegration, which typically occurs 4 months after the fully developed red blood cells have been in circulation within the bloodstream. During the degeneration of the red blood cells, some components of the hemoglobin are excreted from the body while other parts are conserved.

Waardenburg syndrome is a group of genetic conditions that can cause hearing loss and changes in coloring (pigmentation) of the hair, skin, and eyes. Although most people with Waardenburg syndrome have normal hearing, moderate to profound hearing loss can occur in one or both ears. The hearing loss is present from birth (congenital). People with this condition often have very pale blue eyes or different colored eyes, such as one blue eye and one brown eye. Sometimes one eye has segments of two different colors. Distinctive hair coloring (such as a patch of white hair or hair that prematurely turns gray) is another common sign of the condition. The features of Waardenburg syndrome vary among affected individuals, even among people in the same family.

An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from one of several standardized tests designed to assess human intelligence. IQ is a number meant to measure people cognitive abilities (intelligence) in relation to their age group. An I.Q between 90 and 110 is considered average; over 120, superior. Roughly 68% of the population has an IQ between 85 and 115. The average range between 70 and 130, and represents about 95% of the population.
Post-streptococcal GN is a form of glomerulonephritis. It is caused by an infection with a type of streptococcus bacteria. The infection does not occur in the kidneys, but in a different part of the body, such as the skin or throat. The strep bacterial infection causes the tiny blood vessels in the filtering units of the kidneys (glomeruli) to become inflamed. This makes the kidneys less able to filter the urine. Post-streptococcal GN is uncommon today because infections that can lead to the disorder are commonly treated with antibiotics. The disorder may develop 1 to 2 weeks after an untreated throat infection, or 3 to 4 weeks after a skin infection. It may occur in people of any age, but it most often occurs in children ages 6 through 10. Although skin and throat infections are common in children, post-streptococcal GN is a rare complication of these infections. Risk factors include: Strep throat Streptococcal skin infections (such as impetigo)
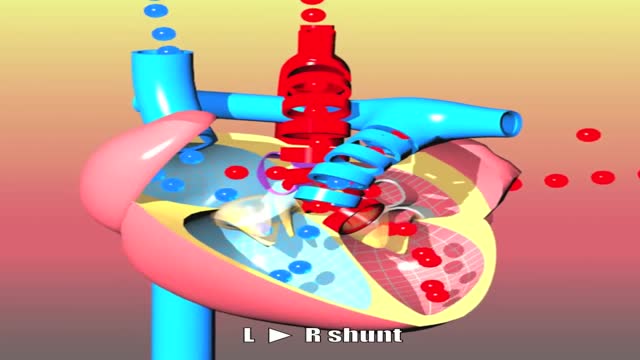
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a group of disorders that affect the connective tissues that support the skin, bones, blood vessels, and many other organs and tissues. Defects in connective tissues cause the signs and symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which vary from mildly loose joints to life-threatening complications. Previously, there were more than 10 recognized types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, differentiated by Roman numerals. In 1997, researchers proposed a simpler classification that reduced the number of major types to six and gave them descriptive names: the classical type (formerly types I and II), the hypermobility type (formerly type III), the vascular type (formerly type IV), the kyphoscoliosis type (formerly type VIA), the arthrochalasia type (formerly types VIIA and VIIB), and the dermatosparaxis type (formerly type VIIC). This six-type classification, known as the Villefranche nomenclature, is still commonly used. The types are distinguished by their signs and symptoms, their underlying genetic causes, and their patterns of inheritance. Since 1997, several additional forms of the condition have been described. These additional forms appear to be rare, affecting a small number of families, and most have not been well characterized.
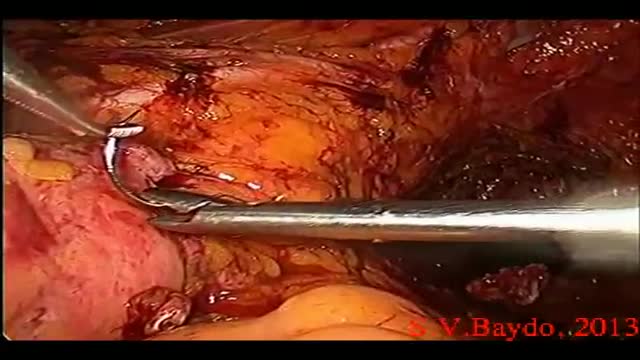
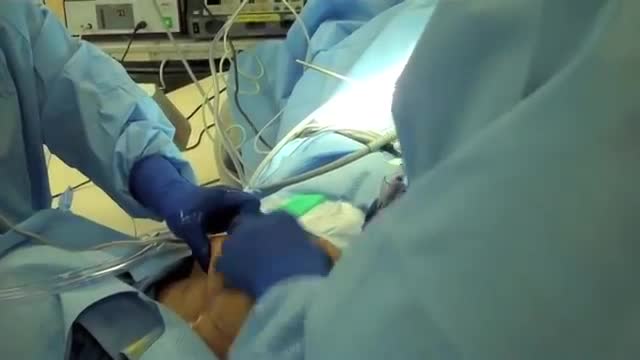
Iatrogenic injury to the ureter is a potentially devastating complication of modern surgery. The ureters are most often injured in gynecologic, colorectal, and vascular pelvic surgery. There is also potential for considerable ureteral injury during endoscopic procedures for ureteric pathology such as tumor or lithiasis. While maneuvers such as perioperative stenting have been touted as a means to avoid ureteral injury, these techniques have not been adopted universally, and the available literature does not make a case for their routine use. Distal ureteral injuries are best managed with ureteroneocystostomy with or without a vesico-psoas hitch. Mid-ureteral and proximal ureteral injuries can potentially be managed with ureteroureterostomy. If the distal segment is unsuitable for anastomosis then a number of techniques are available for repair including a Boari tubularized bladder flap, transureteroureterostomy, or renal autotransplantation. In rare cases renal autotransplantation or ureteral substitution with gastrointestinal segments may be warranted to re-establish urinary tract continuity. Laparoscopic and minimally invasive techniques have been employed to remedy iatrogenic ureteral injuries.
Fungal infections in bone marrow transplant patients. PURPOSE OF REVIEW: Invasive fungal infections have become the leading infectious cause of death in recipients of hematopoietic cell transplantation. Several factors have led to a renaissance in the study of invasive fungal infections.

Glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is the result of defects in the processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown within muscles, liver, and other cell types. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and acquired.

Nelson syndrome refers to a spectrum of symptoms and signs arising from an adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)–secreting pituitary macroadenoma after a therapeutic bilateral adrenalectomy. The spectrum of clinical features observed relates to the local effects of the tumor on surrounding structures, the secondary loss of other pituitary hormones, and the effects of the high serum concentrations of ACTH on the skin. [1] The first case was reported by Nelson et al in 1958. [2]

You may have heard that some positions, such as your partner on top (missionary position), are better than others for getting pregnant. In fact, there's no evidence to back these theories up. Experts just haven't done the research yet. What experts have done, though, is use scanning to show what's going on inside when you're doing the deed. The research looked at two positions: the missionary position and doggy style. (Doggy style being when you're on all fours, and your partner enters you from behind). Common sense tells us that these positions allow for deep penetration. This means that they're more likely to place sperm right next to your cervix (the opening of your uterus). The scans confirm that the tip of the penis reaches the areas between the cervix and vaginal walls in both of these positions. The missionary position allows the penis to reach the area at the front of the cervix. The rear entry position reaches the area at back of the cervix. It's amazing what some experts spend their time doing, isn't it! Other positions, such as standing up, or woman on top, may be just as good for getting sperm right next to the cervix. We just don't know yet. http://www.babycentre.co.uk/sex-for-getting-pregnant#ixzz4XKnPLbxL
Possible complications include: Cardiovascular disease. ... Nerve damage (neuropathy). ... Kidney damage (nephropathy). ... Eye damage (retinopathy). ... Foot damage. ... Skin conditions. ... Hearing impairment. ... Alzheimer's disease.
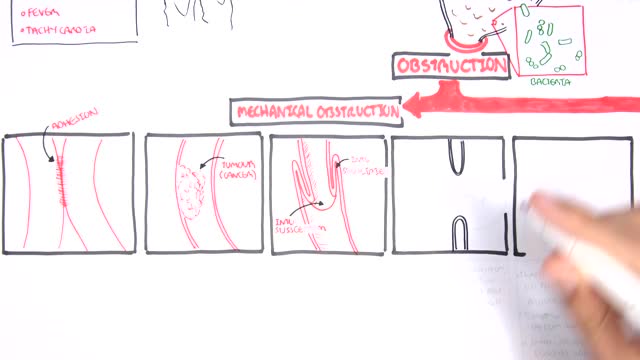
A small-bowel obstruction (SBO) is caused by a variety of pathologic processes. The leading cause of SBO in industrialized countries is postoperative adhesions (60%), followed by malignancy, Crohn disease, and hernias, although some studies have reported Crohn disease as a greater etiologic factor than neoplasia.