Top videos

Teaching Phonics To Children, How To Teach Phonics And Reading, How To Read Better, Teach Kid Read--- http://children-learning-reading.good-info.co --- Teaching phonics to children - How to Teach Phonics and Reading, Teaching children to read by teaching phonics activities is a lot like doing math, where you have to know what the numbers are, how to count, and you need to learn to add and subtract before learning to multiply and divide. Teaching phonics to children is no different where you follow a step by step approach by first teaching the child the alphabet letters and phonics sounds, and then teaching them the combination of different letters to create different words, and using words to form sentences. It is a very logical and sequential buildup of phonics knowledge and reading ability. Before a child can learn to read, he or she must first learn the alphabet letters, and know the sounds represented by the letters. It's usually easier to teach some consonants and short vowels first before moving on to more complicated things such as consonant digraphs (2 consonants formed to produce one sound, such as "ch" or "ph") and long vowels. As you can see, teaching children to read by the phonics method helps them develop phonemic awareness, and it is also a very logical and straight forward approach. Start off by teaching your child the phonics sounds. You can choose to teach your child in alphabetic order going from A to Z, or you can teach several commonly used consonant sounds and vowels, and go from there. For example, you may start teaching your child /a/, /c/, and /t/ (slashes denote sound of the letters). Once your child has learn to quickly recognize these letters and properly sound out their sounds, you can then teach them to blend /c/, /a/, /t/ to make the words "cat", or "tac", or "at". As you introduce more letters and phonics sounds in your lesson plans, you can generate more words, and slowly introduce short, simple sentences to your reading lessons. Depending on the age of your child, I would suggest keeping the phonics lessons relatively short - around 5 to 10 minutes. Sometimes, just 3 to 5 minutes for a short lesson is plenty, and you can easily teach these short phonics lessons 2 or 3 times each day for a total of 10 to 15 minutes. >> Teach your child to read today using our step-by-step, proven method for teaching young children to read http://children-learning-reading.good-info.co

Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Symptoms Of Anxiety Attack, Shortness Of Breath Anxiety --- http://panic-attacks-anxiety.good-info.co --- Newly Discovered Panic "Off Switch" Gives You Anxiety Relief Without Pills or Therapy Here's an interesting fact about anxiety and panic attacks: Did you know that just like the hiccups, doctors still can't agree exactly why they happen to you? And did you also know there's a 60-second solution to panic and anxiety that you can do anywhere? Yes, it takes you just one minute and I'm going to share it with you today. Until one day about a year ago, I thought I might be doomed to let panic attacks rule my life. And I made this free online presentation to tell you about the one discovery about panic and general anxiety that finally cut through the confusion and changed everything. Pay very close attention, because whether you've only had one or two "attacks" so far… or even if you've been having them for years and it seems like a life sentence you'll never escape from… You're about to discover one weird thing that panic, anxiety and the hiccups – yes, the hiccups – have in common that goes right back to the stone age. Discover How To Begin Eliminating Panic And Anxiety From Your Life Forever Click Here: http://panic-attacks-anxiety.good-info.co

Pictures Of Shingles, Images Of Shingles, Cause Of Shingles, Can You Catch Shingles, Cause Shingles --- http://shingles-cure.good-info.co/ ---- Home Remedy For Shingles Treatment. There are surprisingly diverse amounts of treatments that can be used for viruses, especially one in particular known as Shingles. Shingles is the type of virus that is annoyingly unpredictable. Some people get it while others do not, and while it predominant after a certain age, most people can go their whole lives without ever seeing a hint of it. Yet, we all have it living inside of us. The first step to treating the virus correctly is to understand what can set it off. The first pre-requisite is to have had chicken-pox before. Most things manage to squeeze through an immune system if it is weak enough and the shingles virus is no different. In some cases that can kill someone with a weak enough system The shingles virus can also ‘wake up’ if sufficient levels of stress agitate a person’s immune system. As mentioned before, the virus is unpredictable, and even if you meet all the requirements you could go through your entire life without one outbreak. The second step to treating the virus is catching it in time. 72 hours after you first begin to notice symptoms of shingles is pushing your luck so within that time frame some type of treatment should be instigated. For the most part, for a disease like shingles, the main source of relief comes from skin creams and pain killers. Neither of which is a cure for the pain, but which do happen to fall under the heading of ‘home remedy’ Wet rags can be used to soothe the inflamed and tender skin, and a binding with a substance known as aluminum acetate can protect the infected area without causing further irritation. Calamine lotion is a fail safe for almost any sort of skin irritation so it would be smart to go through the aisles at your local grocery store to find products similar. Then of course there are the most obvious measures that need to be taken during your do it yourself treatment sessions. Stay out of the sun since the heat and UV rays can cause unbearable pain against already brutalized skin. Also, keep yourself from scratching at the area since, like the chicken-pox, you will only end up making it worse. If you do not believe me then consider the unlucky individuals who do not have the rash on a small area, but rather all over their bodies. Anti-itch cream would probably be more than appreciated at that point. Should the time come where the virus is making repeated appearances, then it may be time to throw in the towel and head for the hospital. The reason is that after the first outbreak, it isn’t unusual that the virus that was originally stored in the roots of your nerves ‘burned’ itself out. However, continual outbreaks are indications of something deeper that can only grow worse as the attacks continue. Some victims of the virus have described the sensation as having your flesh eaten from the inside out. Once the pain reaches that level, stubbornness should be put on the backburner. If you are forced to go to your local doctor, you may be provided with some of the medicines that have recently been created to help fight off shingles. They are by no means brand names, but neither are they over the counter drugs either. After a few more years to study their effectiveness, there is no reason why this new medication cannot ease the pain caused by shingles, and even, eventually cure it. In this presentation, shows you some unique and rare methods to get rid of shingles naturally in as little as 14 days! This is based on proven techniques used by shingles sufferers without the use of pills and other medication. Get Rid of Shingles will also boost your energy and health dramatically and improve the quality of your life. IMPORTANT NOTE: I can't leave this video up for long, so be sure to watch it from beginning to end while it's still here. REMEMBER: Watch the whole video, as the ending will pleasantly surprise you. click here: http://shingles-cure.good-info.co/

Ringworm On Chin, Best Way To Treat Ringworm, How Do I Get Rid Of Ringworm, How To Stop Ringworm --- http://ringworm-cure.plus101.com ---- I'm going to share with you how to cure Ringworm in less than 3 days by using these proven methods that have worked for thousands of people around the world with Ringworm. Not only that, but these same methods work for children, as well as adults, and even pets. Whether you have athlete's foot or jock it, this will work for you, as those are both types of Ringworm. This fungal infection can be cured without drugs or medications. It's important to understand that. In fact, there are many home remedies for Ringworm that have worked for thousands of years for treating many ailments and skin conditions. Below I will list a few. First, understand there are 3 primary methods to cure Ringworm. You must do all 3 if you want to know how to cure Ringworm as fast as possible. Over the 5 years I've spent studying and learning about Ringworm, I've tried almost every treatment and home remedy available. I've found this to be the most effective and fastest way to cure Ringworm. 1) Treat the rash with home remedies and treatments. There are many home remedies for Ringworm available, as well as natural treatments, that are good for the skin and can promote healing rapidly. Not only do they get rid of the itchiness, pain or discomfort, but they also heal the rash and prevent it from coming back again. 2) Use bathing procedures. Bathing procedures are a powerful way to cure Ringworm, especially when you add home remedies and ingredients to the bath. This again, promotes healing, and helps get rid of all symptoms associated with Ringworm. 3) Consume the right foods and supplements. A proper diet is important to cure Ringworm. Treating Ringworm externally is not enough - you need to provide the body with what it needs to fight off the infection and boost the immune system, so you never have to worry about it again. Nutrition, hydration, rest, and supplementation are all equally important. Follow these 3 methods and you will be cured from Ringworm within days. If you sit and wait, and do nothing, it will only get worse and you will suffer much longer than you need to. To find out more on how to cure Ringworm in 3 days or less, check out the Fast Ringworm Cure e-book program that goes into all the ways to cure Ringworm fast, along with a list of home remedies and treatments that you can apply right away. William Oliver is a nutritionist, medical researcher, and author of the Fast Ringworm Cure e-book. To find out how to cure Ringworm in 3 days or less, click below: http://ringworm-cure.plus101.com

Curious about physiotherapy or wanting to know how to properly perform an exercise? Check us out on Social Media! Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/striveptandperformance/ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/striveptandperf/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/StrivePTandPerf Blog: http://www.strivept.ca/blog

There can be a number of psychological triggers that cause nightmares in adults. For example, anxiety and depression can cause adult nightmares. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) also commonly causes people to experience chronic, recurrent nightmares. Nightmares in adults can be caused by certain sleep disorders
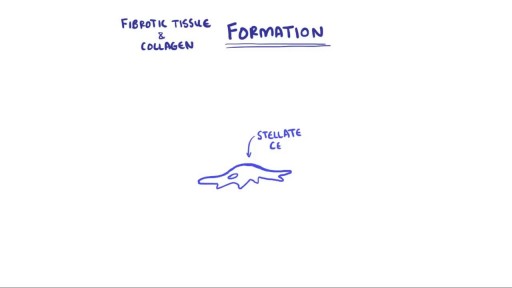
Hepatitis and chronic alcohol abuse are frequent causes. Liver damage caused by cirrhosis can't be undone, but further damage can be limited. Initially patients may experience fatigue, weakness, and weight loss. During later stages, patients may develop jaundice (yellowing of the skin), gastrointestinal bleeding, abdominal swelling, and confusion. Treatments focus on the underlying cause. In advanced cases, a liver transplant may be needed.
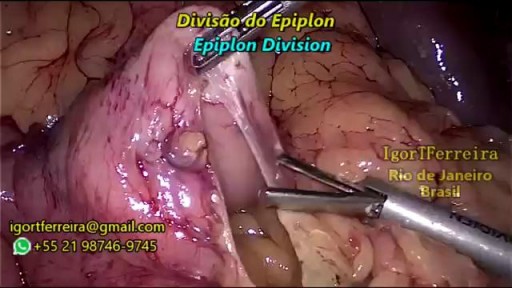
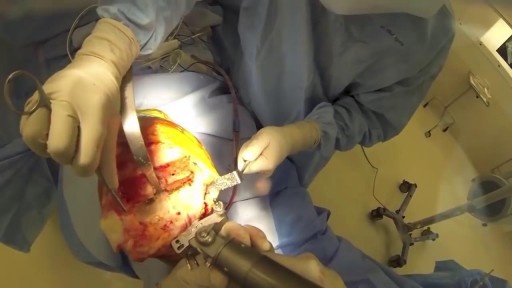
a sleeve gastrectomy with very few edditing. During the start 3 smal spleen perforations caused by Veres Needle were identified, caused by a giant spleen undentified on pre operatory ultrasound. They were controled with gauze compression and at the end of the surgery surgicel was placed and no complications were observed. Patient discharged 3 days after the surgery.
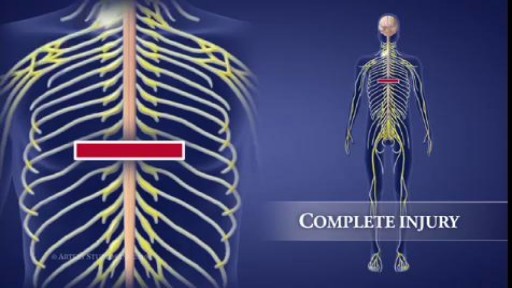
The spine is made flexible by discs located between each vertebra and ligaments made of tough elastic fibers which hold the vertebrae together. The spine gives the body stability and protects the spinal cord which is located in a narrow canal that runs through the center of each vertebra.
Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of medical treatment for pediatric rhinosinusitis.] Because of increasing prevalence of beta-lactam–resistant bacteria in the community, administer antibiotics only for suspected infection as based on a careful history and physical examination. Direct the therapeutic regimen against the prevalent pathogens in the community and carefully consider suspicion for highly resistant bacteria. Typically, uncomplicated cases of acute sinusitis are responsive to amoxicillin. Most patients respond to this initial regimen. For children allergic to penicillin, a second- or third-generation cephalosporin can be used (only if the allergic reaction is not a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction). In cases of serious allergic reaction, a macrolide or clindamycin can be used.
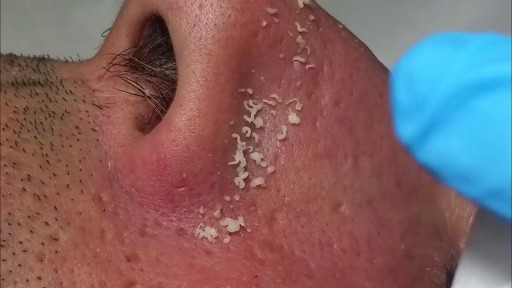
What are blackheads? Blackheads are small bumps that appear on your skin due to clogged hair follicles. These bumps are called blackheads because the surface looks dark or black. Blackheads are a mild type of acne that usually form on the face, but they can also appear on the following body parts: back chest neck arms shoulders Acne affects nearly 50 million Americans and is the most common skin disorder in the United States, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. What do blackheads look like? What causes blackheads? Blackheads form when a clog or plug develops in the opening of hair follicles in your skin. Each follicle contains one hair and a sebaceous gland that produces oil. This oil, called sebum, helps keep your skin soft. Dead skin cells and oils collect in the opening to the skin follicle, producing a bump called a comedo. If the skin over the bump stays closed, the bump is called a whitehead. When the skin over the bump opens, exposure to the air causes it to look black and a blackhead forms. Some factors can increase your chances of developing acne and blackheads, including: producing too much body oil the buildup of the Propionibacterium acnes bacteria on the skin irritation of the hair follicles when dead skins cells don’t shed on a regular basis undergoing hormonal changes that cause an increase in oil production during the teen years, during menstruation, or while taking birth control pills taking certain drugs, such as corticosteroids, lithium, or androgens Some people believe that what you eat or drink can affect acne. Dairy products and foods that increase blood sugar levels, such as carbohydrates, may play a part in triggering acne, but researchers aren’t convinced that there’s a strong connection. ADVERTISING What are symptoms of blackheads? Because of their dark color, blackheads are easy to spot on the skin. They’re slightly raised, although they aren’t painful because they aren’t inflamed like pimples. Pimples form when bacteria invade the blockage in the hair follicle, causing redness and inflammation. How are blackheads treated? Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments Many acne medications are available at drug and grocery stores and online without a prescription. These medications are available in cream, gel, and pad form and are put directly on your skin. The drugs contain ingredients such as salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and resorcinol. They work by killing bacteria, drying excess oil, and forcing the skin to shed dead skin cells. Prescription medications If OTC treatment doesn’t improve your acne, your doctor may suggest that you use stronger prescription medications. Medications that contain vitamin A keep plugs from forming in the hair follicles and promote more rapid turnover of skin cells. These medications are applied directly to your skin and can include tretinoin, tazarotene, or adapalene. Your doctor may also prescribe another type of topical medication that contains benzoyl peroxide and antibiotics. If you have pimples or acne cysts in addition to your blackheads, this type of medication may be particularly helpful. Manual removal Dermatologists or specially trained skin care professionals use a special instrument called a round loop extractor to remove the plug causing the blackhead. After a small opening is made in the plug, the doctor applies pressure with the extractor to remove the clog. Microdermabrasion During microdermabrasion, a doctor or skin care professional uses a special instrument that contains a rough surface to sand the top layers of your skin. Sanding the skin removes clogs that cause blackheads. Chemical peels Chemical peels also remove clogs and get rid of the dead skins cells that contribute to blackheads. During a peel, a strong chemical solution is applied to the skin. Over time, the top layers of the skin peel off, revealing smoother skin underneath. Mild peels are available over the counter, while stronger peels are performed by dermatologists or other skincare professionals. Laser and light therapy Laser and light therapies use tiny beams of intense light to decrease oil production or kill bacteria. Both lasers and light beams reach below the surface of the skin to treat blackheads and acne without damaging the top layers of the skin. How can blackheads be prevented? You can prevent blackheads without spending a lot of money by trying a few of the following ideas: Wash regularly Wash your face when you wake up and before you go to bed to remove oil buildup. Washing more than twice each day can irritate your skin and make your acne worse. Use a gentle cleanser that doesn’t make your skin red or irritated. Some acne cleansing products have antibacterial ingredients that kill P. acnes bacteria. Consider washing your hair every day, too, particularly if it’s oily. Hair oils can contribute to clogged pores. It’s also important to wash your face after you eat oily foods such as pizza, because oil from these foods can clog pores. Use oil-free products Any product that contains oil can contribute to new blackheads. Choose oil-free or noncomedogenic makeup, lotions, and sunscreens to avoid making your problem worse. Try an exfoliating product Exfoliating scrubs and masks remove dead skin cells from your face and can help reduce blackheads. Look for products that don’t irritate your skin.