Top videos
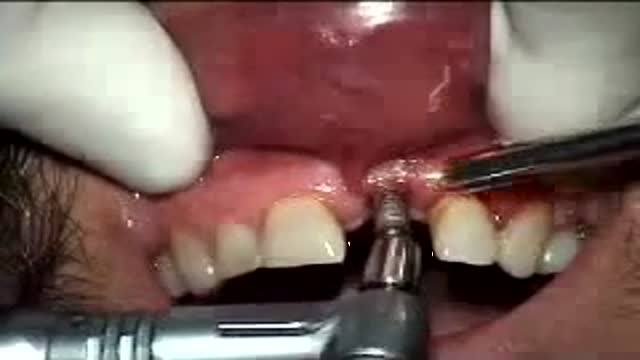
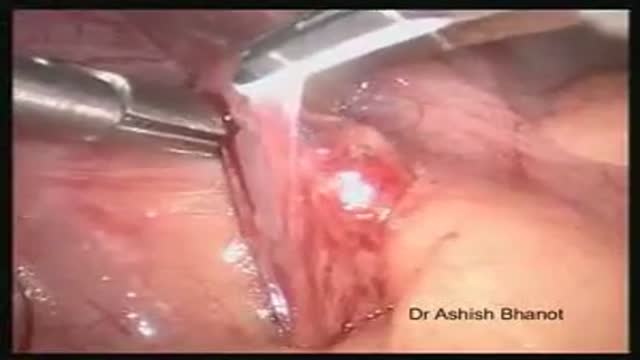
Although the success rate of dental implant is very high, there are about 10% of failure in all dental implantation. The cause is usually related to the bone quality of the implant site. Once the implant failed, it can be easily removed, wait for 6 weeks and re-implant again. It is easier to remove a failed implant than a natural tooth.
Fungal infections in bone marrow transplant patients. PURPOSE OF REVIEW: Invasive fungal infections have become the leading infectious cause of death in recipients of hematopoietic cell transplantation. Several factors have led to a renaissance in the study of invasive fungal infections.

Glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is the result of defects in the processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown within muscles, liver, and other cell types. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and acquired.
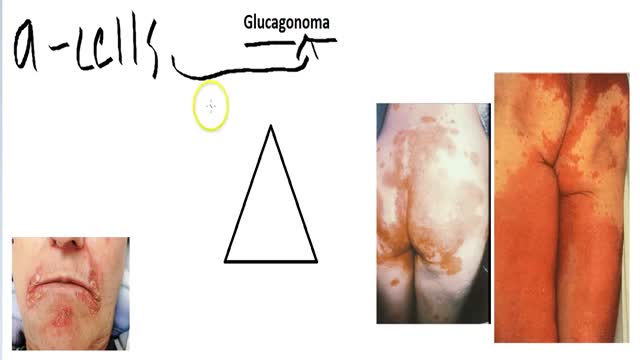
A glucagonoma is a rare tumor of the alpha cells of the pancreas that results in the overproduction of the hormone glucagon. Alpha cell tumors are commonly associated with glucagonoma syndrome, though similar symptoms are present in cases of pseudoglucagonoma syndrome in the absence of a glucagon-secreting tumor.

Alendronate Sodium is used for the following diseases and conditions: osteoporosis, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Alendronate Sodium improves the patient's condition by performing the following functions: slowing down the bone loss and helps to keep the bones strong and less likely to break. Side effects are possible with Alendronate Sodium, but do not always occur. Some of the side effects may be rare but serious. Consult your doctor if you observe any side effects, especially if they do not go away. Alendronate Sodium may cause the following side-effects: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, nausea, and jaw pain

The "Get up and go" test is most commonly used to assess postural stability. In this test, the physician instructs the patient to stand up from a chair without assistance, walk a short distance, turn around, return, and sit down again. If the patient is unsteady or has difficulties during the test, further evaluation is necessary.

Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia).
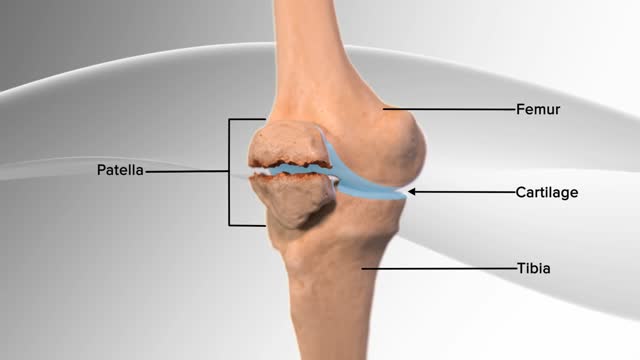
In this knee procedure, the patella is being repaired. The patella is a small, floating bone that glides over the thighbone. It connects the muscles of the thigh to the shinbone, helping the knee to move. The egg‐shell type covering on the underside of the patella and front of the femur allows for smooth motion of the knee.

-Traumatic amputation of a body part requires rapid transport of the appendage, which should be wrapped in a saline-moistened gauze, placed in a plastic bag, and transported in a container filled with ice mixed with either saline or sterile water to best preserve the body part and attempt replantation.
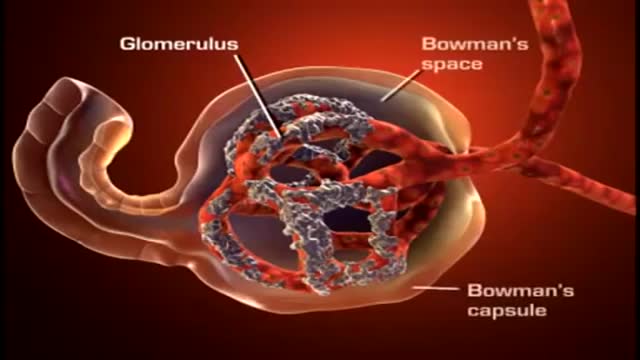
A nephron (from Greek νεφρός (nephros) meaning "kidney") is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.