Top videos
Scissor gait is a form of gait abnormality primarily associated with spastic cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy refers to brain damage that occurs before a child is five years old. Therefore, adults cannot develop cerebral palsy. However, cerebral palsy does not get better or worse with age, so when a child has the condition, he or she will continue to have the condition into adulthood.
Labyrinthitis is a mild, often self-limited condition characterized by vertigo, tinnitus, nausea, and a loss of balance. The disorder often follows a viral illness (eg, influenza). Labyrinthitis may also be caused by trauma, bacterial infection, allergies, benign tumors, and certain medications .
The "Get up and go" test is most commonly used to assess postural stability. In this test, the physician instructs the patient to stand up from a chair without assistance, walk a short distance, turn around, return, and sit down again. If the patient is unsteady or has difficulties during the test, further evaluation is necessary.
In developing countries, domestic animals (eg, dogs) are common sources of infection. In the United States, bats and wild animals (eg, raccoons) are the most common reservoirs of infection. The acquisition of rabies from bats can occur from an unrecognized bite or a scratch, and possibly by inhalation of aerosolized viral particles. Bats are found in all states except Hawaii, and spelunking (cave exploration) is a risk factor for rabies acquisition from bats.
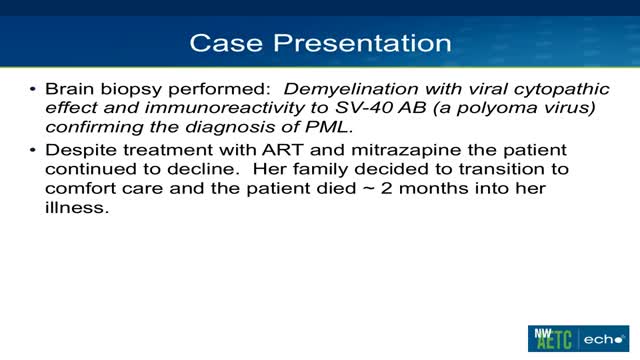
Progressive multifocalleukoencephalopathy is a demyelinating illness of the central nervous system that typically occurs in immunosuppressed patients, especially those with AIDS. It is caused by reactivation of the polyomavirus JC (JC virus) and presents with neurologic deficits including hemiparesis, gait ataxia, visual symptoms, and altered mental status. It is not seen in non-immunosuppressed patients, and fever is not typical
-Rapidly progressive weakness of the lower extremities following an upper respiratory infection, accompanied by sensory loss and urinary retention, is characteristic for transverse myelitis.
systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). This is most likely secondary to sepsis from an infection of the patient's Hickman catheter given the associated skin findings, although culture results are needed to confirm this diagnosis. The patient's low blood pressure is likely secondary to developing septic shock, and he has already appropriately been treated with intravenous fluids. Catheter removal is indicated given his hemodynamic instability. Catheter removal is also indicated in patients with severe sepsis with organ hypoperfusion, endocarditis, suppurative thrombophlebitis, or persistent bacteremia after 72 hours of appropriate antibiotic therapy. Long term catheters should also be removed if culture results are positive for S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, fungi, or mycobacteria.
Meningococcal meningitis - causes, features, symptoms and treatment
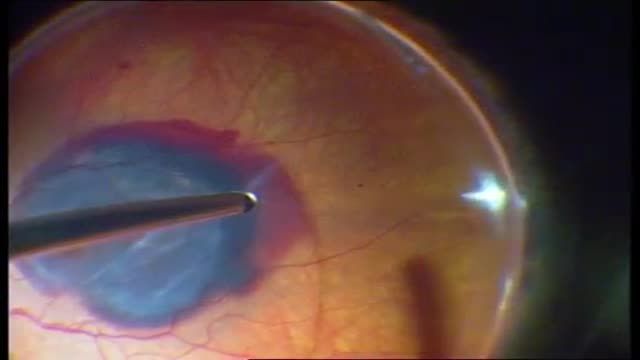
The fovea was moved 425 to 1,700 microm (965+/-262 microm) superiorly or inferiorly. Follow-up time was 2 to 12 months (median 8 months). Complications included macular pucker (3 eyes), subfoveal hemorrhage (2 eyes), macular hole (1 eye), and progression of cataract in phakic eyes (3 eyes). Thirteen of 20 eyes showed various degrees of proliferative vitreoretinopathy with epiretinal membrane formation over the inferior peripheral retina with the inferior retinal detachment stabilized by the silicone oil. One eye progressed to phthisis bulbi. Initial visual acuity ranged from 20/80 to 20/800 (median 20/150) and final visual acuity ranged from light perception to 20/200 (median 20/1000).
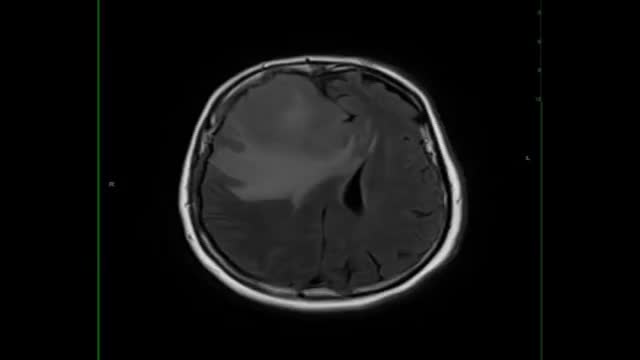
Lymphoma is a cancer that arises from the cells of the lymphatic system. In the brain, this type of cancer is called Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL). Location. Lymphoma occurs most often in the cerebral hemisphere, but may also involve the cerebrospinal fluid, the eyes, or the spinal cord.
ADC was first identified early in the AIDS epidemic as a common and novel CNS syndrome.(4,5) The three components of the term, AIDS dementia complex embody central features of the condition. AIDS emphasizes its morbidity and poor prognosis, particularly when its severity is at stage 2 or greater (see Table 1), a severity comparable to other clinical AIDS-defining complications of HIV-1 infection. Dementia designates the acquired and persistent cognitive decline with preserved alertness that usually dominates the clinical presentation and determines its principal disability. Complex emphasizes that this disease not only impairs the intellect, but also concomitantly alters motor performance and, at times, behavior. This involvement of the nervous system beyond cognition is evidence of a wider involvement of the CNS than occurs in some other types of dementia such as Alzheimer's disease. Additionally, myelopathy may be an important, indeed predominating, aspect of ADC, and organic psychosis may also be a feature in a subset of patients (see Rheumatologic and Musculoskeletal Manifestations of HIV). These manifestations are therefore also encompassed within this term. By contrast, neither neuropathy nor functional psychiatric disturbance are included in ADC.
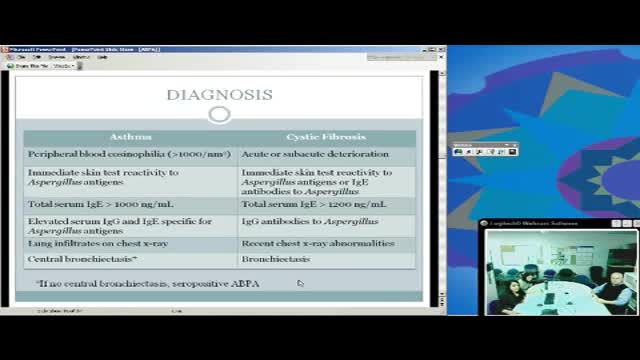
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a condition characterised by an exaggerated response of the immune system (a hypersensitivity response) to the fungus Aspergillus (most commonly Aspergillus fumigatus). It occurs most often in patients with asthma or cystic fibrosis.
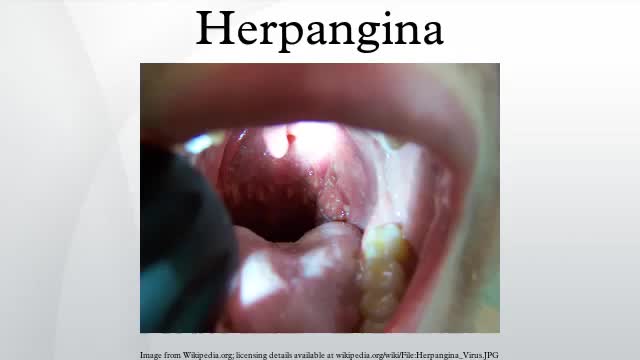
Herpangina is a common childhood illness caused by a virus. It is characterized by small, blister-like ulcers on the roof of the mouth and in the back of the throat. The infection may also cause a sudden fever, sore throat, headache, and neck pain.
The word enuresis is derived from a Greek word (enourein) that means “to void urine.” It can occur either during the day or at night (though some restrict the term to bedwetting that occurs at night). Enuresis can be divided into primary and secondary forms.
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia).
Galactosemia
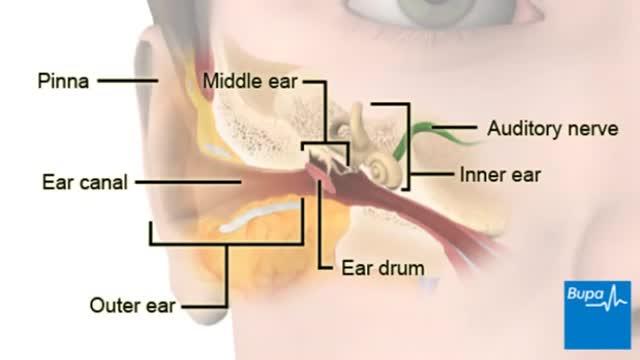
Uncomplicated acute otitis media (AOM) should be treated empirically with amoxicillin. Recurrent AOM should raise concern for beta-lactamase resistance and warrants treatment with amoxicillin-clavulanic acid. Ototopical medications are unnecessary, even if there is tympanic membrane perforation.
This is a Video in Clinical Medicine from the New England Journal of Medicine. Tympanocentesis in Children with Acute Otitis Media Overview Tympanocentesis is defined as needle aspiration of fluid from the middle ear. In children with acute otitis media, drainage of pus from the middle ear results in a rapid and marked improvement in symptoms and enables the clinician to prescribe tailored antimicrobial therapy. This video will demonstrate the technique of tympanocentesis. Indications Tympanocentesis is recommended in children with refractory acute otitis media, in immunocompromised children with otitis media, and in children with suppurative complications of acute otitis media, . . . .
Bulimia (boo-LEE-me-uh) nervosa, commonly called bulimia, is a serious, potentially life-threatening eating disorder. People with bulimia may secretly binge — eating large amounts of food — and then purge, trying to get rid of the extra calories in an unhealthy way. For example, someone with bulimia may force vomiting or engage in excessive exercise. Sometimes people purge after eating only a small snack or a normal-size meal.