Top videos
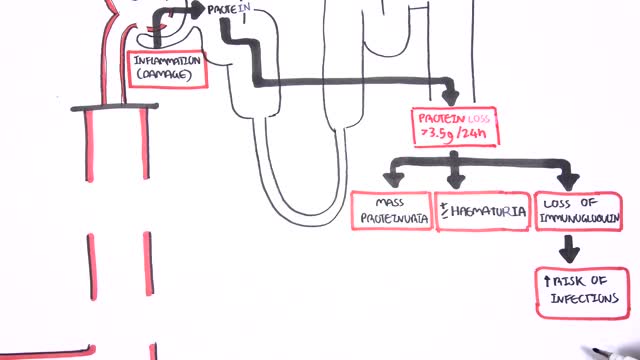
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes your body to excrete too much protein in your urine. Nephrotic syndrome is usually caused by damage to the clusters of small blood vessels in your kidneys that filter waste and excess water from your blood. Nephrotic syndrome causes swelling (edema), particularly in your feet and ankles, and increases the risk of other health problems. Treatment for nephrotic syndrome includes treating the underlying condition that's causing it and taking medications. Nephrotic syndrome can increase your risk of infections and blood clots. Your doctor may recommend medications and dietary changes to prevent these and other complications of nephrotic syndrome.

The DASH diet is a lifelong approach to healthy eating that's designed to help treat or prevent high blood pressure (hypertension). The DASH diet encourages you to reduce the sodium in your diet and eat a variety of foods rich in nutrients that help lower blood pressure, such as potassium, calcium and magnesium.
Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis (stuh-NO-sing ten-o-sin-o-VIE-tis), is a condition in which one of your fingers gets stuck in a bent position. Your finger may straighten with a snap — like a trigger being pulled and released. Trigger finger occurs when inflammation narrows the space within the sheath that surrounds the tendon in the affected finger. If trigger finger is severe, your finger may become locked in a bent position. People whose work or hobbies require repetitive gripping actions are at higher risk of developing trigger finger. The condition is also more common in women and in anyone with diabetes. Treatment of trigger finger varies depending on the severity.
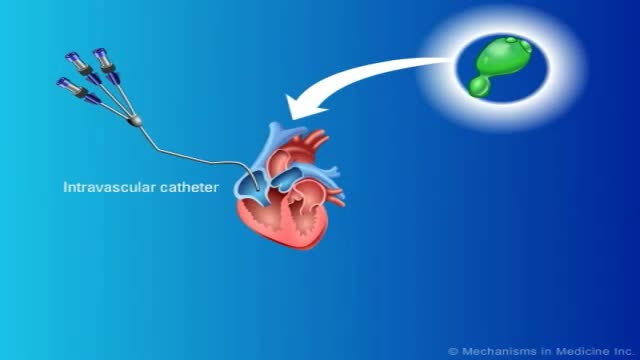
Fungal infections in bone marrow transplant patients. PURPOSE OF REVIEW: Invasive fungal infections have become the leading infectious cause of death in recipients of hematopoietic cell transplantation. Several factors have led to a renaissance in the study of invasive fungal infections.

Glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is the result of defects in the processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown within muscles, liver, and other cell types. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and acquired.
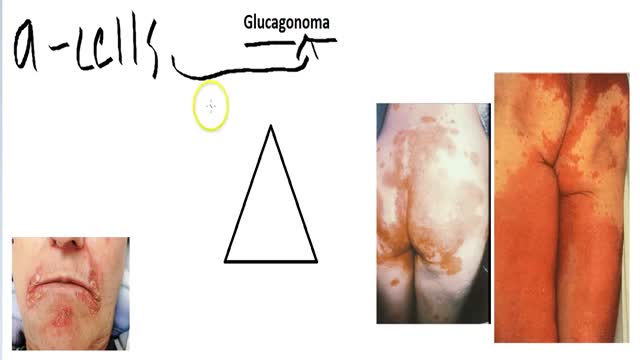
A glucagonoma is a rare tumor of the alpha cells of the pancreas that results in the overproduction of the hormone glucagon. Alpha cell tumors are commonly associated with glucagonoma syndrome, though similar symptoms are present in cases of pseudoglucagonoma syndrome in the absence of a glucagon-secreting tumor.

Alendronate Sodium is used for the following diseases and conditions: osteoporosis, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Alendronate Sodium improves the patient's condition by performing the following functions: slowing down the bone loss and helps to keep the bones strong and less likely to break. Side effects are possible with Alendronate Sodium, but do not always occur. Some of the side effects may be rare but serious. Consult your doctor if you observe any side effects, especially if they do not go away. Alendronate Sodium may cause the following side-effects: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, nausea, and jaw pain

Warfarin is an anticoagulant medication - it is used to slow down the blood-clotting process. Anticoagulants are used to prevent blood clots which may cause vein blockages, heart attack and stroke. Warfarin is known under the brand names Warfant, Jantoven, Coumadin, Lawarin, Marevan, and Waran.
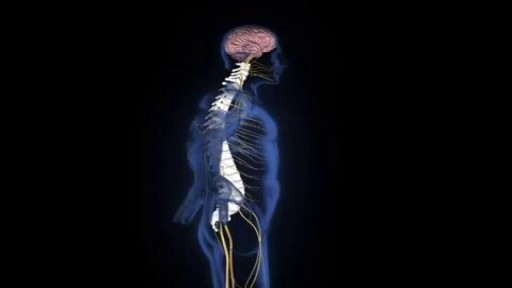
An estimated 12,500 spinal cord injuries occur in the U.S. every year, leaving the injured people, their friends, and their family, to cope with the aftermath of the catastrophe. For many, navigating the challenges of the health care system can feel a bit like going to medical school. Suddenly you're learning a veritable cornucopia of new terms, and may be spending endless hours Googling spinal cord anatomy to fill in the gaps in your knowledge. An educated patient is better equipped to advocate for his or her needs and interests. An education in spinal cord anatomy helps you understand what your doctor is saying, ask intelligent questions, and detect medical errors before they endanger your health.

Menorrhagia is the medical term for menstrual periods with abnormally heavy or prolonged bleeding. Although heavy menstrual bleeding is a common concern, most women don't experience blood loss severe enough to be defined as menorrhagia.

Water is an essential nutrient for the body, as the body loses water through perspiration, breathing, bowel movements, and in urine. Water must be consumed regularly to maintain a sufficient level. Water has many vital functions in the body, including… Serving as a lubricant. Water is a main component of saliva, which helps moisten food making it easier to swallow. Water also helps lubricate joints, reducing friction and inflammation. Water is important in body temperature regulation. When body heat rises, such as during strenuous activities, the body starts to sweat to cool itself. And sweat is made up almost entirely of water.

Tinnitus (TIN-ih-tus) is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. A common problem, tinnitus affects about 1 in 5 people. Tinnitus isn't a condition itself — it's a symptom of an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury or a circulatory system disorder