Top videos
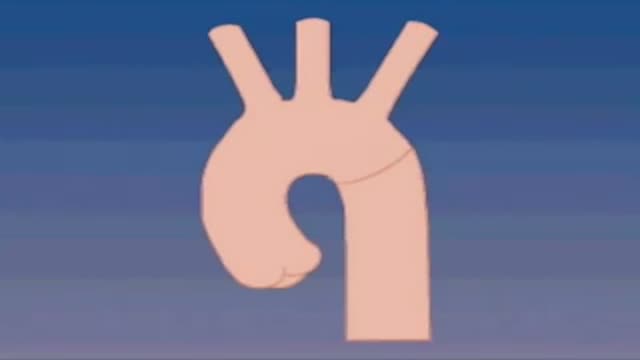
A narrowing of the major artery (the aorta) that carries blood to the body. This narrowing affects blood flow where the arteries branch out to carry blood along separate vessels to the upper and lower parts of the body. CoA can cause high blood pressure or heart damage.
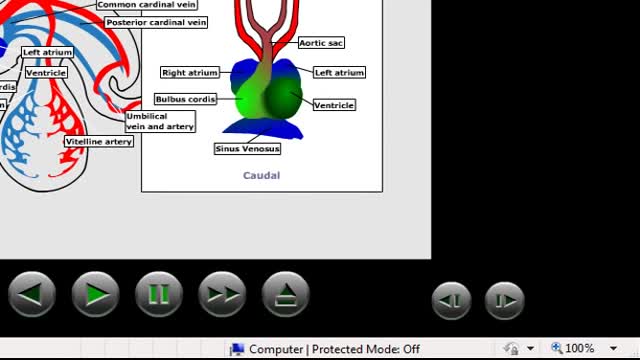
Embryonic cardiovascular system. ... The human arterial and venous systems develop from different embryonic areas. Aortic Arches. The aortic arches—or pharyngeal arch arteries—are a series of six, paired, embryological vascular structures that give rise to several major arteries .
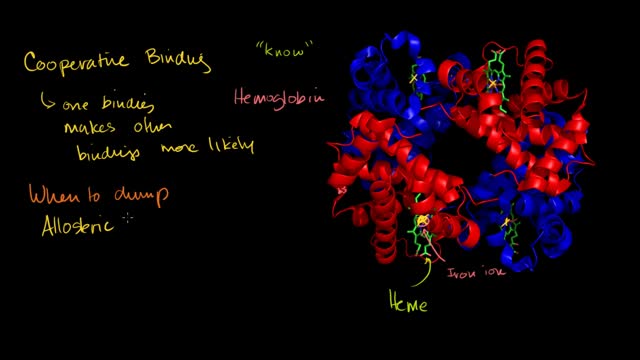
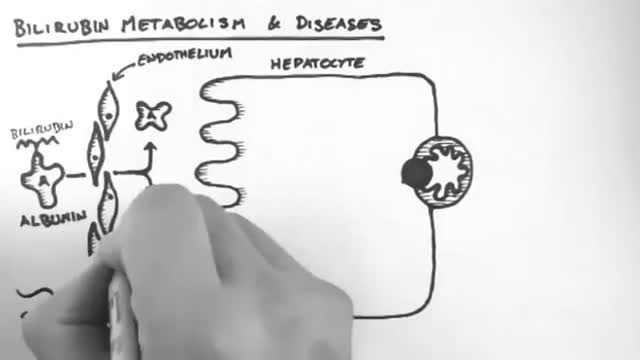
Hemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs. Hemoglobin is made up of four protein molecules (globulin chains) that are connected together.
If it gets more severe and causes symptoms, your low hemoglobin count may indicate you have anemia. A low hemoglobin count is generally defined as less than 13.5 grams of hemoglobin per deciliter (135 grams per liter) of blood for men and less than 12 grams per deciliter (120 grams per liter) for women.
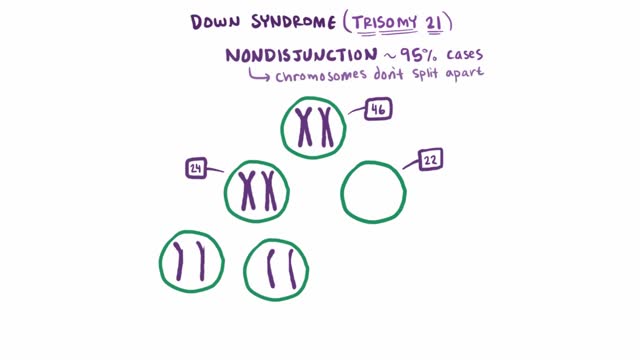
The term trisomy is used to describe the presence of three chromosomes, rather than the usual matched pair of chromosomes. For example, if a baby is born with three #21 chromosomes, rather than the usual pair, then the baby would be said to have "trisomy 21." Trisomy 21 is also known as Down syndrome. Other examples of trisomy include syndromes like trisomy 18 and trisomy 13. Again, trisomy 18 or trisomy 13 simply means the child has three copies of the #18 chromosome (or of the #13 chromosome) present in each cell of the body, rather than the usual pair.

Rehydration Tips: Kids & Teens (Ages 1+) Give clear liquids (avoid milk and milk products) in small amounts every 15 minutes. ... If your child vomits, start over with a smaller amount of fluid (2 teaspoons, or about 10 milliliters) and continue as above. ... After no vomiting for about 8 hours, introduce solid foods slowly.
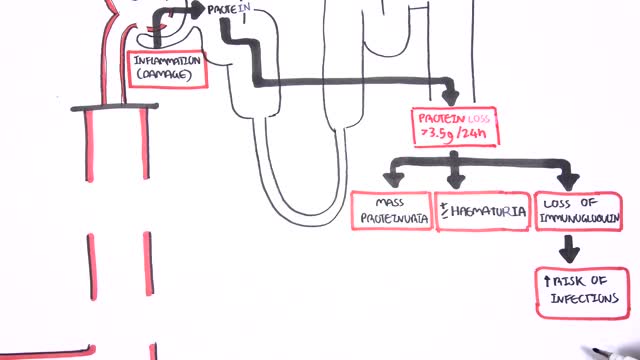
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes your body to excrete too much protein in your urine. Nephrotic syndrome is usually caused by damage to the clusters of small blood vessels in your kidneys that filter waste and excess water from your blood. Nephrotic syndrome causes swelling (edema), particularly in your feet and ankles, and increases the risk of other health problems. Treatment for nephrotic syndrome includes treating the underlying condition that's causing it and taking medications. Nephrotic syndrome can increase your risk of infections and blood clots. Your doctor may recommend medications and dietary changes to prevent these and other complications of nephrotic syndrome.

The DASH diet is a lifelong approach to healthy eating that's designed to help treat or prevent high blood pressure (hypertension). The DASH diet encourages you to reduce the sodium in your diet and eat a variety of foods rich in nutrients that help lower blood pressure, such as potassium, calcium and magnesium.
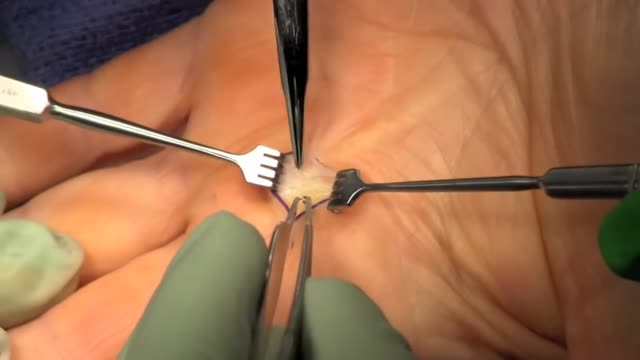
Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis (stuh-NO-sing ten-o-sin-o-VIE-tis), is a condition in which one of your fingers gets stuck in a bent position. Your finger may straighten with a snap — like a trigger being pulled and released. Trigger finger occurs when inflammation narrows the space within the sheath that surrounds the tendon in the affected finger. If trigger finger is severe, your finger may become locked in a bent position. People whose work or hobbies require repetitive gripping actions are at higher risk of developing trigger finger. The condition is also more common in women and in anyone with diabetes. Treatment of trigger finger varies depending on the severity.
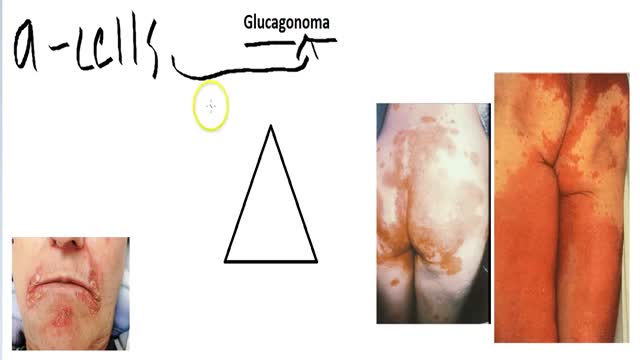
A glucagonoma is a rare tumor of the alpha cells of the pancreas that results in the overproduction of the hormone glucagon. Alpha cell tumors are commonly associated with glucagonoma syndrome, though similar symptoms are present in cases of pseudoglucagonoma syndrome in the absence of a glucagon-secreting tumor.

Alendronate Sodium is used for the following diseases and conditions: osteoporosis, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Alendronate Sodium improves the patient's condition by performing the following functions: slowing down the bone loss and helps to keep the bones strong and less likely to break. Side effects are possible with Alendronate Sodium, but do not always occur. Some of the side effects may be rare but serious. Consult your doctor if you observe any side effects, especially if they do not go away. Alendronate Sodium may cause the following side-effects: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, nausea, and jaw pain

Water is an essential nutrient for the body, as the body loses water through perspiration, breathing, bowel movements, and in urine. Water must be consumed regularly to maintain a sufficient level. Water has many vital functions in the body, including… Serving as a lubricant. Water is a main component of saliva, which helps moisten food making it easier to swallow. Water also helps lubricate joints, reducing friction and inflammation. Water is important in body temperature regulation. When body heat rises, such as during strenuous activities, the body starts to sweat to cool itself. And sweat is made up almost entirely of water.

Tinnitus (TIN-ih-tus) is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. A common problem, tinnitus affects about 1 in 5 people. Tinnitus isn't a condition itself — it's a symptom of an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury or a circulatory system disorder